5 Best Laptops for Revit 2025 (Latest Update)
The best laptop for Revit will depend on whether or not you are a student or a professional:
As for prices:
- A portable laptop with ANY dedicated GPU will be more expensive.
- If you work mostly at an office, you can make do with heavier machines which are much less expensive.
A faster and easier way to make sure you buy the right laptop is to look at the size of your projects:
A) If you work on 10 story houses or small buildings ( files in the ~50MB range), you only need to spend 500-700 dollars. (2-4GB vRAM dGPU).
B) If files are in the range of 1GB or more : 4-6GB vRAM GPU. No more than a 6GB vRAM GPU. However, 16-32GB RAM and a recent Core i7/Ryzen 7 CPU (900-1300 dollars) is a must.
Most people I’ve worked with fall into the A category.
What about workstation GPUs?
If we are talking about Revit, they’re useless.
Why?
Revit is mostly CPU-dependent. The GPU helps with Viewport (rotating model in 3D).
But Viewport & Drafting are still mostly CPU tasks.
Best Laptop Specs for Revit
Let us be a bit more specific about the hardware you need (you can find more details at the end).
Keep the following in mind when reading these recommendations and reviews:
small=3-10 story building / house
Big=facility/large building
CPU
Although recent versions of Revit have implemented VERY multi-threaded functions (they use lots of CPU cores)…
The large majority of design tasks are not multithreaded, the only use the speed of one core or one thread. Thus more cores on a CPU isn’t going to speed up drawing/modeling.
What about rendering?
Rendering in draft quality will be instantaneous with any modern CPU.
Rendering at higher quality will benefit from more CORES. However, since most modern CPUs have at least 4-6 cores. It should still be plenty fast regardless of # of cores.
Recommended CPUs
Students & small models: Any 8th-14th gen Intel Core i5 or 3th-8th gen Ryzen 5 CPU. Ex: Core i5 13420H / Ryzen 5 7535HS. Older generations (Ex: 8th gen Intel / 3rd gen Ryzen) will be somewhat slower when rendering but will have more or less the same performance when drafting.
Pros / bigger models: An “H” Core i5 or Ryzen 5 CPU (Ex: Core i5 13420H / Ryzen 5 7535HS) is good too but a Core i7 or Ryzen 7 is recommended: . Ex: Core i7 14700HX / Ryzen 7 8845HX
GPU
A dedicated graphics card ( ‘vRAM‘ – video RAM memory) makes viewport actions smoother: zooming, navigating and rotating a 3D model.
Student or small models: Even 2GB vRAM GPUs like the MX450, MX550 will do. Though 4GB vRAM dGPUs like 1650GTX & 2050RTX are overkill they’re not that much more expensive.
Integrated GPUs will work with small models too as long as they’re recent. Use this chart to see where you can find the fastest integrated graphics.
Pros or large models: 4GB vRAM recommended: 1650GTX, 2050RTX, 3050RTX. 6GB vRAM GPUs are future & bullet proof: RTX 2060, RTX 3060, RTX 4050, etc.
Warning: Do not spend money on 8GB vRAM GPUs UNLESS you’re also using third-party GPU renderers. Rendering in Revit is a CPU-task and viewport or navigating through a large complex 3D model will be faster with more RAM rather than more vRAM.
RAM
8GB: Good for small to medium models or ~50MB files .
16GB: A must for +700MB files or for multitasking too. Ex: running Revit+ Sketch Up, PhotoShop, NavisWorks.
32GB: Reduces rendering times. Performance gains beyond 32GB is small (for rendering).
64GB: Helps with viewport of extremely large and complex models. Ex: dense and intricate HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning) systems, particularly those with highly detailed ductwork, piping, and mechanical equipment.
Storage
SSDs is a MUST. Solid State Drives massively increase any read/write file data related task.
Now as I showed in my post: Laptop storage speed comparison. The differences are minimal when it comes to real world applications. There’s no need to be picky about which PCie generation to choose UNLESS you know you’re going to transfer lots and lots of files several times a day (PCIe 5.0 is then a good investment).
Display
You’re going to be staring at this thing for how many hours a day? Right. So besides using the 20 / 20 rule, you want a large and if possible a high resolution QHD display. The extra screen space and resolution gain from QHD over FHD is SIGNIFICANT.
A matte finish is a nice bonus (makes the display easy on the eyes). If you can’t get a matte finish, you can always buy a antiglare filter.
Top 5 Best Laptops For Revit
When you pick a laptop out of this list, keep in mind:
A) All laptops have fast CPUs with the recommended specs so drawing/modeling performance will be almost the same.
B) VIEWPORT & Rendering performance will depend on the # cores , RAM and GPU. If you work with 500MB-1GB files you need a 4GB vRAM as the minimum AND you need to max out RAM.
C) For ~50MB files a laptop with a Core i5 or Ryzen 5 CPU + a 2GB vRAM is the minimum.
1. MSI Thin 15
Best Budget Laptop For Revit

Core i5 12450H
16GB DDR5
RTX 2050 4GB vRAM
512GB PCIe NVMe SSD
15” 144Hz FHD
5.1 lbs
2 hours
If you are an architect, civil engineer or interior designer working for a small firm that has a small team of CAD engineers, it isn’t likely you’ll be working with projects that require a high amount of ‘vRAM’.
Most of your work will be limited to buildings, apartments, small houses and schools, etc, and for that you need NOTHING more than a 4GB vRAM GPU. In fact, the 4GB vRAM GPU on this laptop is OVERKILL because Revit doesn’t use the GPU for all functions except for viewport (rotating a model in 3D).
Hardware
A 4GB vRAM should be enough to viewport into buildings with 20-40 floors.
Truth is…these kind of projects can run on integrated graphics but you’ll start to lag (somewhat) if you have to work on the details inside every floor. Viewport and walkthroughs (after applying a high quality render) will flicker and run somewhat slow with integrated graphics card. However, nothing dramatic.
Having a 4GB vRAM GPU prevents all of that and makes navigating through these projects smooth.
You can even opt for a 2GB vRAM GPU and have the same smoothness in viewport however those laptops with 2GB vRAM GPUs are only slightly cheaper.
3050RTX/1650GTX vs 2050RTX:
The most powerful 4GB vRAM GPU is the 3050Ti followed by the 3050RTX Non-Ti. However both are on average 100-150 dollars more expensive. Are they worth the extra cash? No.
vRAM is the same and though they have more CUDA cores they do not help with rendering on Revit because rendering is primarily CPU-dependent. As for the 1650GTX, it has pretty much the same performance as the RTX 2050. However, they will usually come with a slower (slightly older) CPU.
vRAY & GPU Rendering
If you’re using GPU renderers like vRAY then the 3050Ti may be worth the extra cash ONLY if the render previews have very highly detailed textures and take long to render. This will improve your workflow because you try and render textures/shaders FASTER .
CPU: Core i5 12450H
The problem with cheaper 1650GTX laptops (GPU has approx. the same performance as the RTX 2050) is that they usually come with older CPUs. Some even have a 9th generation Intel Core i5 CPU!
This laptop is by no means the fastest or the latest. However, it’s still somewhat recent (we are in the 14th generation now) so single-thread performance is substantially higher than older generation and closer to more recent generations.
Of course, you can make do with those old CPUs too.
Rendering may take 10 min longer and so on but nothing that will compromise your workflow significantly. However, 2050RTX laptops cost just as much as 1650GTX laptops.
Again even if you find a cheaper laptop with a 1650GTX the price difference won’t be worth the loss in clock speed performance between the CPUs (Of course if you find a 1650GTX laptop with the same CPU as this one by all means go for it).
What about Ryzen CPUs?
Ryzen Core i5 CPUs can be a better option than Intel counterparts. Simply because Ryzen 5 CPUs, as shown in my post comparing the performance of Ryzen vs Intel Laptop CPUs, have better multi core performance (this means each core runs at almost the same clock speed ACROSS all cores which isn’t always the case with Intel). Better multi-core performance means FASTER rendering and also SLIGHTLY faster viewport.
As of late Nov 2024, I could not find a ryzen 5 with a 2050RTX around the same price as this model though.
RAM & Storage: 8GB RAM DDR4 vs 16GB RAM DDR5
Unlike the MSI model I posted early in the year, this laptop supports DDR5 which is the fastest RAM technology on laptops as of 2024. If we are talking about budget laptops with dedicated graphics, you’ll only find DDR5 RAM on laptops with the latest CPUs or laptops with recent Ryzen 5 CPUs Ex: Ryzen 5 7535HS.
Performane gains with a DDR5 vs a DDR4 however isn’t significant for Revit. I’d estimate things would run 5% faster in viewport. However, rendering will be significantly faster (~15%).
Unlike the earlier MSI model, this model has 16GB RAM out of the box as opposed to 8GB and this will give you SIGNIFICANT performance gains with viewport and even more so with rendering.
Storage: 1TB is deal to store pretty much every project you work on during 5 years. However, this model only comes with 512GB. This should not be an issue if you use an external storage to save older projects (or the cloud) or just simply upgrade storage as shown in my how to upgrade Storage .
| MSI Thin 15 | |
| PROS | CONS |
|
|
2. Lenovo LOQ 15AHP9
The Best Laptop For Revit 2024

AMD Ryzen 7 8845HS
16GB DDR5
NVIDIA RTX 4050 6GB vRAM 100W
512GB PCIe NVMe
15” FHD
5.7 lb
2 hours
A 6GB vRAM dedicated GPU laptop will give you the best performance/money ratio as far as Revit goes.
You’ll have smooth walkthroughs with shaders/textures with vRAY & smooth viewport with very complex & large models on Revit without having to pay for an 8GB vRAM dGPU (can cost an extra 500-800 dollars).
Going beyond 6GB vRAM isn’t a bad move but the performance gains will be very very small. However, if you use vRAY and GPU renderers, the performance gains will be significant.
GPU: 4050RTX (6GB vRAM) 100W
4050RTX 100W vs All other 6GB vRAM GPUs:
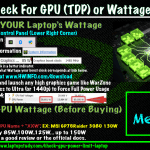
When you shop for mid-tier dedicated graphics on laptops. In other words, 6GB vRAM dedicated graphics. The most important single spec of said laptop (after the CPU) is “GPU wattage“. This concept is useful for gaming but can be extended to viewport & rendering tasks since higher wattage means that each “CORE” of the GPU will do any graphics processing at much higher clock speeds.
CUDA Cores vs vRAM
You already know vRAM is the memory where your model is stored for FAST 3D manipulation, it pretty much acts the same RAM does for software/windows.
CUDA cores acts the same way CPU cores do. They have clock speeds and a GPU can have far more cores than a CPU. These little cores do all the graphics & image processing such as viewport/rendering shaders/etc.
If you have these CUDA cores running at FASTER speeds, then obviously the graphics processing will be faster and the performance with 3D objects & images will be faster. This is why you should always try to get a GPU running at higher wattages (power measured in Watts). Since higher power input means more energy for each of these cores to reach their maximum potential.
When you pick a higher wattage GPU as opposed to a lower wattage GPU (they can be the exact same GPU just running at different power), the most obvioust performance gains will be seen when you use GPU-renderers (vRAY). However, if you’re NOT using third party renderers besides the default rendering engine on Revit, you DO NOT NEED to worry about GPU wattage.
Unfortunately, wattage isn’t listed by manufacturers.
So you will need to do some research on your own to find out what the wattage is before purchase.
Large models: 4GB vRAM vs 6GB vRAM?
I’ve had to work with large models on several occassions last year and as far as viewport (3D manipulation & navigating through a model) is concerned me and my colleague so no performance difference between 4GB vRAM and 6GB vRAM.
However…when we worked on a file in the range of ~2GB basically the design of a residential building in a block. The model included all houses around the block AND the residential building had VERY detailed interiors with plugins to add high quality objects and such (LOD 400-500).
Viewport was faster with the 6GB vRAM GPU (~60fps) compared to the 4GB vRAM GPU (35-40fps). This difference is significant but it doesn’t really translate to a smoother workflow. However, these results can be extrapolated to much more complex models and there should be a significant performance difference on viewport then.
CPU: Ryzen 7 8845HS vs Core i7 14700HX
This laptop has the LATEST RYZEN 7 CPU (8th gen). Now whether you pick a Ryzen 7 or the latest 14th gen Core i7 doesn’t make a HUGE difference but it’s still significant.
As I showed in my “Intel vs Ryzen Laptop CPU Performance Comparison“….both in single-threaded and multi-threaded tasks, the Core i7 14700H should be the best choice. Unfortunately a Core i7 14700H adds a lot more to the total price thus you’ll get the best bang for your buck with Ryzen 7 shown here which should not be that much slower.
For drawing/modeling and viewport, performance differences should be minimal. However performance differences when rendering will be noticeable. A three story house on a 500m sq area with details outside may take around 20 min as opposed to 24 min with the Core i7 14700H.
| Lenovo LOQ 15AHP9 | |
| PROS | CONS |
|
|
3. HP 15.6
Best Cheap Laptop For Revit 2025

AMD Ryzen 5 7520U
16GB LPDDR5
Radeon Vega 7
256GB PCIe NVMe SSD
15” FHD IPS
3.3 lbs
7 hours
Windows 11 S Mode
For most people using Revit (I’d say about 50%) especially interior designers, there’s no need for dedicated graphics.
That’s because small models (one house, small apartments) use very VIDEO memory and rely far more on RAM. Thus the graphics cards that come by default on laptops ‘integrated GPUs’ should be more than enough.
GPU: Integrated
Of course that doesn’t mean you should pick any integrated graphics.
You always want to get the best bang for your buck.
On laptops you cannot browse laptops by integrated graphics but rather by their CPU. A particular Integrated Graphics (lets call it iGPU) will specifically come with some CPUs, basically, they come in pairs.
Intel Xe or Vega 7
The integrated GPUs on Ryzen CPUs (Radeon RX Vega 7) and Intel CPUs (Intel Xe) are not the fastest integrated graphics (the fastest are the Intel Arc series or the Radeon 680M but they can only be found on the most expensive CPUs which defeats the whole purpose since we are resorting to integrated graphics due to lack of money).
You can find faster versions of these two GPUs (Intel Xe & Radeon RX Vega 7 on the Core i7 and Ryzen 7) models but it makes no sense to buy those since they’re just as expensive as laptops with dedicated graphics.
| GPU | CPU |
| Intel Iris Xe 80 (1600Mhz) | Core i5 1135G7 |
| Intel Iris Xe Graphics G7 80EUs | Core i5 1230U |
| Intel Iris Xe Graphics G7 80EUs | Core i5 1345U |
| RX Vega 7 | Ryzen 5 5500U |
| RX Vega 7 | Ryzen 5 7530U |
| Radeon 610M | Ryzen 5 7520U |
This laptop has the Radeon 610M running at 1900Mhz which is on the weaker side but in return you’re getting the latest Ryzen 5 CPU.
CPU: Core i5/Ryzen 5 vs Core i3/Ryzen 3
The Ryzen 5 on this laptop is significantly faster than the Ryzen 3 and the iGPU is also slightly more powerful. If you buy the cheaper ryzen 3 versions you will have a MASSIVE performance losses due to the CPU being much slower as shown in this post.
You should ALWAYS opt for the most recent CPU you can afford even if you have to pay 50 dollars more. If not, you’ll be missing out on the performance gains that comes from higher clock speeds and more efficient cores. It won’t necessarily make your workflow slow but having these performance boosts will def have an impact on how fast you can finish the design process especially if you render continuously.
RAM: 8GB DDR4 (Upgraded To 16GB)
Viewport and navigating through larger models MAY lag with an integrated graphics if you just have 8GB RAM as opposed to 16GB RAM. The additional 8GB RAM will help ANY integrated GPU run faster as explained in my post here. Basically, the extra RAM can act as reserved ‘memory’ for the iGPU to do the processing.
Now this time I posted a model that comes with 16GB RAM out of the box…..it’s not something you should aim for when buying a laptop because it usually makes a laptop more expensive than it should be. If you this model runs out of stock and you find a cheap laptop with the same CPU but only 8GB RAM, it’d be best for you to just buy that and upgrade it to 16GB RAM later. This laptop has an additional slot for RAM upgrade and the process is relatively easy.
How to improve viewport performance despite slow-hardware?
If you buy either a laptop like this model or a weaker Ryzen 3/Core i3 and you find yourself working with a bigger model that suddenly slows down on viewport, you can improve performance by upping RAM to 16GB of course….but if that’s not enough….you can either add more RAM (32GB) or get used to good practice design.
What does that mean? Say if you’re working on small-to-medium models that are around 200MB, it’s possible that you’re using too many functions, unnecessary parts, shading, and other details. To improve performance, you can either split the file and work on each part separately (for a faster viewport) or purge the entire file to remove unused elements
| HP 15.6 | |
| PROS | CONS |
|
|
4. Surface Laptop Studio 2
Best 2 in 1 Laptop For Revit

Intel® Core™ i7 13th gen
16GB LPDRR5 RAM
NVIDIA RTX 4050
512 GB NVMe PCIe 4.0 SSD
14.4” 2400 x 1600 2 in 1 Tablet-Laptop w/ Stylus
4.37lbs
5 hours
Electrical , Computer , Chemical , Software
Civil, Mechanical , Aerospace & Aeronautical Engineers
Hardware Overview: Surface Laptop Studio 2
GPU: 4050RTX/ Ada RTX 2000 / 4060RTX
The Surface Laptop Studio 2 offers three GPU configurations. The first model has a 6GB VRAM GPU, the second has 8GB VRAM, and the third also has 8GB VRAM but features a ‘workstation’ GPU. We’ll discuss what that means later.
However, all of these options are generally overkill for Revit alone, as most users won’t find much advantage in a 6GB or 8GB VRAM GPU for typical Revit tasks.
The best choice for value is the RTX 4050 model. While still somewhat overpowered for Revit, it’s also significantly cheaper than the other two configurations.
All models come equipped with a 13th Gen Core i7, which provides excellent single-core and multi-core performance. This setup ensures you’ll have high-speed capabilities for drafting, viewport work, and rendering, performing as fast as today’s hardware allows.
[Tip] If the Surface Laptop Studio 2 is too expensive, consider the original Surface Laptop Studio, which features a 4GB VRAM GPU and a 12th Gen Core i7. Both models are capable of delivering comparable performance. [/tip]
RAM & Storage: Not upgradeable
None of the Surface Laptop Studio and none of the other Surface Devices (we’ll discuss soon) are upgradeable. Well in theory they are but it’s very risky and difficult. Thus you must buy the studio or the next devices with as much hardware as you’re going to need. For Revit purposes and BIM Software: 16GB RAM w/ 512GB Storage is the maximum and 8GB RAM w/ 256GB the minimum.
RAM used on these devices is DDR5 if you choose the latest models.
Other Surface Devices
The Surface Laptop Studio 2 is just one of the many Surface Devices that allow you to write with the stylus and draw/design with the stylus on BIM/CAD software like Revit. There’s also:
- Surface Laptop
- Surface Book
- Surface Pro
Surface Pro
The Surface Pro however is an even more interesting model than the Surface Laptop Studio 2 because it’s much cheaper and the CPU and iGPU of the most recent generations pack a lot of punch of BIM software like Revit. Most of the models ran by civil engineers or interior designers will show no lag on the Surface Pro as long as you meet the two conditions:
- You pick a recent model (which means a recent CPU). Anything from the 7th gen is fine (Currently the Surface Pro is on the 9th).
- You make sure to have 8GB RAM. (Some models especially the super old ones have only 4GB).
- An Upgrade to 16GB will massively improve performance (as discussed earlier).
Note that as of late 2024, the Surface Pro 10 has been released but it’s not only overkill CPU wise for the average Revit user but also too expensive.
Drawing/Sketching
Whether you buy the Surface Book, Laptop Studio or the Surface Pro. The drawing features and functions are pretty much the same. The sensitivity & accuracy when drawing is the same too. In fact, even if you go for much older models , the functions and accuracy are still the same. If you buy the cheaper models, you just need to update the software.
RAM: 16GB RAM is best
Where as 8GB RAM is OKAY for laptops with dedicated GPUs. If you end up with an integrated GPU as in the case of the Surface Pro, you want 16GB RAM to make up for the lack of dedicated GPU. We discussed earlier how this works.
If the Surface Pro 9 is too expensive and you’re open to buying a Surface Pro 7 or even a Surface Pro 6, then having 16GB of RAM becomes even more crucial—not just for smoother viewport performance, but also for faster performance during drafting and drawing tasks. The extra RAM helps compensate for the lower CPU power in these older models.
| Surface Devices (Pro, Book & Studio) | |
| PROS | CONS |
|
|
5. Dell Precision 7780
Best RTX A5000 Laptop For Architecture
Intel Core i9 13950HX
64GB DDR5 RAM
NVIDIA Quadro RTX A3500
1TB NVMe SSD
17.3″ FHD (1920*1080)
6.7 lbs
1 hours
This is a workstation laptop.
It’s listed here mostly for informational purposes. I don’t think I’ve ever seen ANYBODY need a workstation GPU just for Revit.
They’re certainly useful for other software, but Revit is mostly limited to interior design work, house plans, and buildings that don’t need much VRAM. Plus, its rendering engine isn’t as hardware-demanding as something like 3DS Max or Maya.
However…
Leaving Revit aside, you might find it useful for other software that requires a lot of GPU rendering power and a very fast CPU to handle extremely large BIM models with LOD 500.
The advantages of workstation laptops compared to regular laptops aren’t really just about the GPU but rather:
- Bigger / better cooling system : Since they’re bigger and thicker, it’s just more ideal for high-end hardware that needs a lot of cooling. The extra space will allow for the CPU & GPU to work at optimum temperature levels.
- Support up to 64GB or even 128GB: On Revit and most BIM software, you may be surprised to find out that those extremely complex models with LOD=500 are going to require more “RAM” rather than vRAM.
- For example: Plumb work and mechanical designs of buildings, when very detailed and used in conjuction with other software, can make files as high as 10Gigabytes and this EASILY takes 40-50GB of RAM !!!! In this scenario a WORKSTATION is a good option IF YOU NEED more than 50GB as there are only a few laptops that support 64GB RAM.
- Display: Workstation laptops are HUGE, a bigger display means a higher canvas, combine it with a higher resolution like QHD and your workflow will improve massively since you’ll a better view of plans.
Workstation GPU vs Gaming GPU
There will be a slight performance gain when working with files that reach around 10GB in size.
But the biggest difference would likely be the reduction or complete elimination of ‘artifacts’ floating around, ‘hardware error boxes,’ and ‘visual inaccuracies.’
However…
This is all speculative. Personally, I’ve never encountered these issues (at least not in a way that noticeably impacted my workflow). Artifacts and visual inaccuracies completely disappeared once I increased my RAM to match the complexity of my model.
Workstation laptops: So why are they Recommended?
They’re just being diplomatic about it.
To avoid any error boxes whatsoever, no matter what you’re doing with the software, you’ll need to make sure your hardware is up to the task.
What might come in handy (outside of Revit) is the extra VRAM that workstation GPUs offer. But this advantage is more noticeable on desktops. On laptops, even the most powerful workstation GPUs usually have the same amount of VRAM as high-end gaming GPUs, and the gaming GPUs are often half the price.
Either way, if you’re working with such large models, you’d be better off using a desktop!
| Dell Precision 7780 | |
| PROS | CONS |
|
|
Workstation GPU Performance & Prices: Buyer Beware!
If you MUST buy a workstation GPU because you’ve been forced to buy one (or perhaps you see yourself using software / plugins outside of Revit that explicitly require one) then it’s important for you to distinguish what workstation GPUs are USELESS and OBSELETE and which ones are WORTH your money.
I’m sure you don’t want to pay 2k for a 5 year old GPU that cannot perform better than our 700 dollar laptop.
Please use the following table to get an idea of where each workstation GPU stands compared to regular laptops:
| Workstation GPU | Consumer Equivalent | Cores/Shaders | Clock Speed | vRAM |
| P500 | MX150- | 256 | 1519 | 2GB |
| M620M | 950M- | 512 | 1018 | 4GB |
| P1000 | 1050GTX | 512 | 1519 | 4GB |
| P2000 | 1050Ti | 768 | 1468 | 4GB |
| T2000 | 1650/1660Ti | 1024 | 1785 | 4GB |
| RTX 5000 | 2080RTX+++ | 3072 | 1350 | 16GB |
| RTX A5000 | ~3080RTX | 6144 | 1695 | 16GB |
| Ada GPU | GPU Equivalent |
Cores/Shaders | Clock Speed | vRAM |
| RTX 5000 | RTX 4090 – | 9728 | 1680Hz | 16GB |
| RTX 4000 | = RTX 4080 | 7424 | ?? | 12GB |
| RTX 3500 | RTX 4070 – | 5120 | ?? | 12GB |
| RTX 3000 | RTX 4070 — | 4608 | ?? | 8GB |
++ much faster. – weaker . = similar performance. There’s a much bigger and complete list in the next section!
What about MacBooks? Which is the best apple laptop for Revit ?
Unfortuantely, Revit, as of 2024, still doesn’t have a Mac version. However, there are a few ways you can get Revit installed on a MacBook as shown in the official site here.
As for what MacBook or what hardware on MacBooks is best for revit, it depends on how you’re going to launch Revit:
- If you’re going to use a MacBook to NATIVELY install Revit, there is a way (although the official site doesn’t mention it). You have to a buy MacBook with an Intel Chip which are the ones released prior to 2020. For example, the 2019 16” MacBook Pro has a Intel Core i9 and a 4GB vRAM GPU (Radeon RX 5500M). You can install Windows on that OSX (natively) through BootCamp and then install Revit. This works fantastic for medium-large models especially if you find a MacBook Pro that has RAM upgraded to 16 or even 32GB !
- If you want to buy the latest M1 & M2 & M3 MacBooks, you are limited to using a virtual machine to launch Windows then Launch Revit within it. This massively reduces the amount of resources available to run Revit (because they’re being used to run the VM, OSX and background processes) and also the communication between hardware and software (within the VM) isn’t as fast as it would be if Revit was natively installed. So this is a good option IF your models are very small and limited to houses with no details within.
- If you can access a workstation remotely (be it a desktop or cloud service to launch Revit) you can use any laptop to work on Revit remotely, this includes any MacBook.
How To Buy The Best Laptop For Revit
If you are on a budget and need to buy several machines for your team then you want to give this section a good read so you don’t spend money on unncessary power.
Project Size
The best way to get the right hardware is to look at your files. If files are large you need a higher CPU and better graphics. If files stay below 100MB, then you don’t need to worry on either as much.
If you don’t have access to files then imagine this:
- 10-15 story building for a private school, a small medical center or maybe a bunch of offices then you need NO MORE than 4GB vRAM dGPU ~700$. LOD =500.
- Two-three story houses or apartments only need 2GB vRAM GPU laptops. Even an integrated GPU will do.
- Working collaboratively on bigger projects, like an entire high school campus with highly detailed interior design (LOD=500) will be bog down to 1 fps when using viewport. In this scenario, you’ll need as much vRAM as you can afford.
Revit System Requirements For Laptops
*These recommendations are based on a lecture by AutoDesk University, my past experience and input from several users through our facebook page. They apply to ALL BIM Software including the Revit packages: Revit Structure, Revit Architecture & Revit MEP.
CPU
Revit primarily relies on the CPU.
Picking a good graphics card automatically sets you up with a fast CPU on laptops.
Nonetheless, you should still know a few things about how the software uses the CPU so you can get the best bang for your buck.
a) Revit Functions
Is Revit Multi-Core?
Yes and No.
Revit started as a single-threaded application (having more cores did not improve performance).
Over time more functions and design tasks were made more and more multi-threaded however that only applies for a few functions so the focus should still be single-thread performance.
The tasks that have become more multithreaded are usually those where things need to be ‘rendered on the go’ or visuals. Ex: calculating walls and pipes intersections, loading all elements in views, etc.
Here’s a list of all multi-threaded functions.
Intel CPUs
| CPU | Base(GHz) | Turbo(GHz) | Cores(GHz) |
| i3 10050G1 | 1.2 | 3.4 | 2 |
| i3 10100U | 2.1 | 4.1 | 2 |
| i3-1115G4 | 3 | 4.1 | 2 |
| i3 1215U |
3.3 | 4.4 | 6 |
| i5 1115G4 | 2.4 | 4.2 | 4 |
| i7 1165G7 | 2.8 | 4.7 | 4 |
| i5 1240P |
3.3 | 4.4 | 8 |
| i7 1260P |
3.4 | 4.7 | 8 |
| i5-11300H | 2.6 | 4.4 | 4 |
| i5 11260H | 2.6 | 4.4 | 6 |
| i5 13420H | 1.9 | 4.6 | 8 |
| i5 14450HX | 2.0 | 4.8 | 10 |
| i7 10750H | 2.6 | 5 | 8 |
| i7-11375H | 3.3 | 5 | 4 |
| i7-11370H | 3.3 | 4.8 | 4 |
| i7 12800H | 3.7 | 4.8 | 6+8 |
| i7 13620H | 3.6 | 4.9 | 6+8 |
| i7 13650HX | 3.6 | 4.9 | 6+8 |
| i7 14000HX | 1.9 | 5.4 | 20 |
| i9-11900H | 2.5 | 4.9 | 8 |
| i9-11980HK | 3.3 | 5 | 8 |
|
i9 12900H
|
1.8
|
5
|
6+8
|
|
i9 13900H
|
1.9
|
5.4
|
6+8
|
|
i9
14900HX |
2.3
|
5.4
|
24
|
AMD CPUs
| CPU | Base (GHz) | Turbo (GHz) | Cores(#) |
| AMD Ryzen 9 8945HS | 3.8 | 5.3 | 8 |
| AMD Ryzen 9 7940HS | 4 | 5.2 | 8 |
| AMD Ryzen 9 6900HS | 3.3 | 4.9 | 8 |
| AMD Ryzen 9 5900HX | 3.3 | 4.6 | 8 |
| AMD Ryzen 7 8845HS | 3.5 | 5.1 | 8 |
| AMD Ryzen 7 7745HX | 3.6 | 5.1 | 8 |
| AMD Ryzen 7 6800HS | 3.6 | 4.7 | 8 |
| AMD Ryzen 7 5800H | 3.3 | 4.4 | 8 |
| AMD Ryzen 7 5800U | 1.9 | 4.4 | 8 |
| AMD Ryzen 7 5700U | 1.8 | 4.3 | 8 |
| AMD Ryzen 5 7535HS | 3.3 | 4.55 | 6 |
| AMD Ryzen 5 6600H | 3.3 | 4.5 | 6 |
| AMD Ryzen 5 5600H | 3.3 | 4.2 | 6 |
| AMD Ryzen 5 7530U | 2.0 | 4.5 | 8 |
| AMD Ryzen 5 5500U | 2.1 | 4.4 | 6 |
| AMD Ryzen 3 7320U |
2.4 | 4.1 | 4 |
| AMD Ryzen 3 5300U | 2.6 | 3.8 | 4 |
Multi-threaded functions are still a small fraction of all the functions on Revit. This isn’t likely to change because most functions are step by step processes: they cannot be “multi-threaded” by nature.
Now if you look at the table, you’ll notice most DECENT modern CPUs today have 6 or more cores and some even have 8 cores. Thus # of cores isn’t likely to be a limiting factor.
TL;DR: Focus on clock speed rather than number of cores.
How much clock speed is fast?
The following is an estimate but it really depends on the CPU generation and stats:
~RECENT Ryzen 3 or Core i3 if all you do is render how a building/house looks from outside.
~6th gen Ryzen 5 or 12th gen Core i5 CPUs for small models that are more detailed as you navigate within.
~6th gen Ryzen 7 or 12th gen Core i7 for detailed large buildings.
~12th gen Core i9 or 6th gen Ryzen 9 for very detailed and complex designs inside very large buildings: plumbing system, detailed building structure, electrical structure, etc…
For more “accurate benchmarks” on which CPU has better “single clock speed” performance check out my post here:
b) Rendering
Rendering is a multi-core task. This is true not just for Revit but for every other software: the cores more you have the faster the rendering.
Now if you’re doing a simple render (two story house), most modern CPUs will do it in a minute or two. The more details and the more realistic the product looks, the longer it’ll take .
- If you are a student: You’ll be limited to small buildings. Render with high quality will only take 20 min with one of the recent Intel Core i5 or Ryzen 5 CPUs which have about ~6 cores running at 4GHz. Draft quality might take 1 min.
- If you are a professional, you’ll likely come across bigger AND way more detailed high quality renders. If you don’t want to wait 1-2h, get at least a 6 core CPU though (~600-750 dollar laptops).
- However, I would consider investing on a Core i7 Ryzen 7 (8 cores running at ~5GHz) or use Cloud rendering if you want much faster high quality renders. Draft quality as usual it’s instantaneous.
GPU
A) Viewport
This means panning, zooming, orbiting, navigating, doing a walkthrough of a 3D model, etc.
Dedicated GPUs vRAM
This will only be smooth and fast once you have a graphics card that has ‘dedicated video RAM’.
The reason why some computers lag (with very large complex models) despite having a fast CPU and enough RAM is likely lack of vRAM.
Now when you buy a laptop with dedicated graphics keep this in mind:
2-4GB vRAM GPUs:
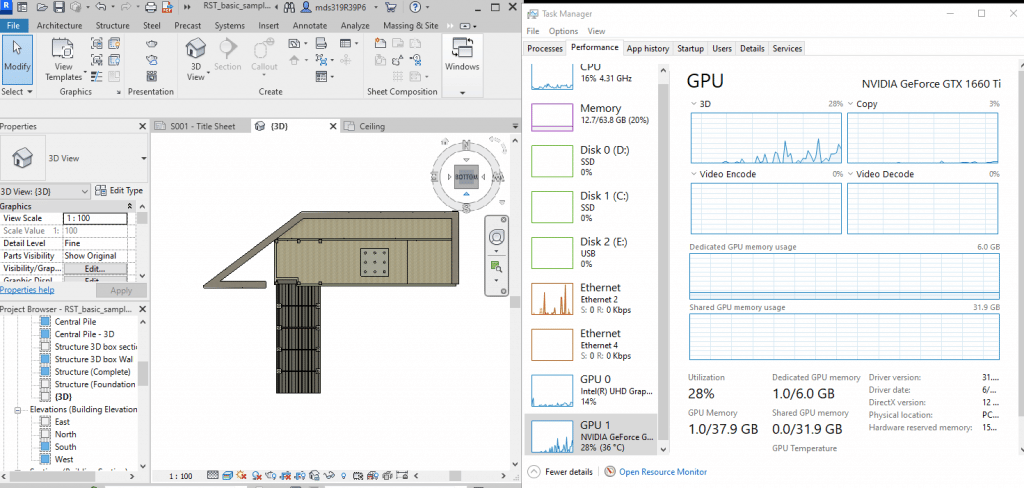
As you can see in the figure, this is a two story house and it’s only taking 1GB vRAM so you will definitely be fine 2GB vRAM dGPU (they are found on 600 dollar laptops) but it doesn’t hurt get a bit more headroom and buy a 4GB vRAM dGPU. It will also be future proof for much larger structures (~10-20 story buildings).
6GB vRAM dGPUs:
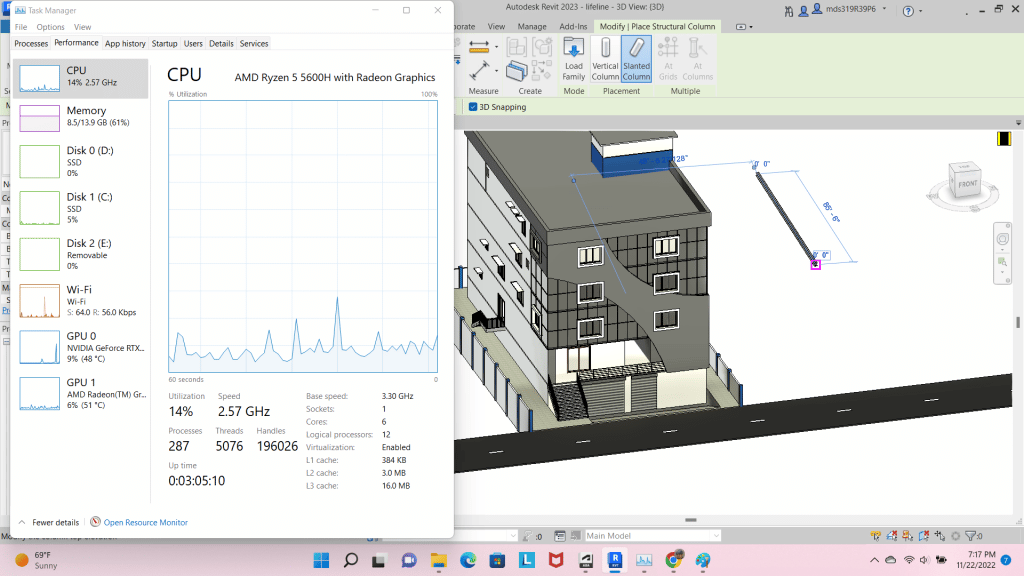
As you can see in the figure I have a 6GB vRAM dGPU.
It’s never made anything “faster” than my 4GB vRAM dGPU.
Viewport will be slightly slow when the structure’s complex, big and has a lot of objects in it (LOD=500) but nothing that will slowdown your workflow.
I personally have not found my 6GB vRAM dGPU useful yet but if you know you’ll be working with much bigger and complex structures AND doing high quality walkthroughs (Ex: 3DS Max), you MIGHT find it useful.
Before upgrading a graphics card though I would try upping RAM to 32-64GB (we’ll talk about that soon).
Viewport: Quadro vs NVIDIA GeForce
I have used one of those Quadro cards ~5 years ago ( K 2000) and I saw no improvement over the 860GTX (~1050Ti). There was a bit more lag with the GeForce 1050Ti (~20 story building) but a quick hardware usage (task manager) revealed that CPU & RAM were choking before even my dGPU (1050Ti) ran out of ‘GPU Power’ (~50% of usage) so if both machines were to have the same CPU & RAM differenes would be minimal.
That was almost 7 years ago now the architecture difference between the consumer gaming cards and workstation gaming cards is minimal so there’s almost no advantage in performance.
However, yes, you will see less artifacting with workstation cards, be able to use some special features and plug-ins but that’s about it.
Workstation GPUs if they have more vRAM will come in handy but Revit doesn’t seem to use more than 6GB vRAM (or even 4GB vRAM) .
Again I have not worked with extremely large models as one would perhaps (a mall) or a large hospital facility (with every building detailed in a single file).
B) Rendering
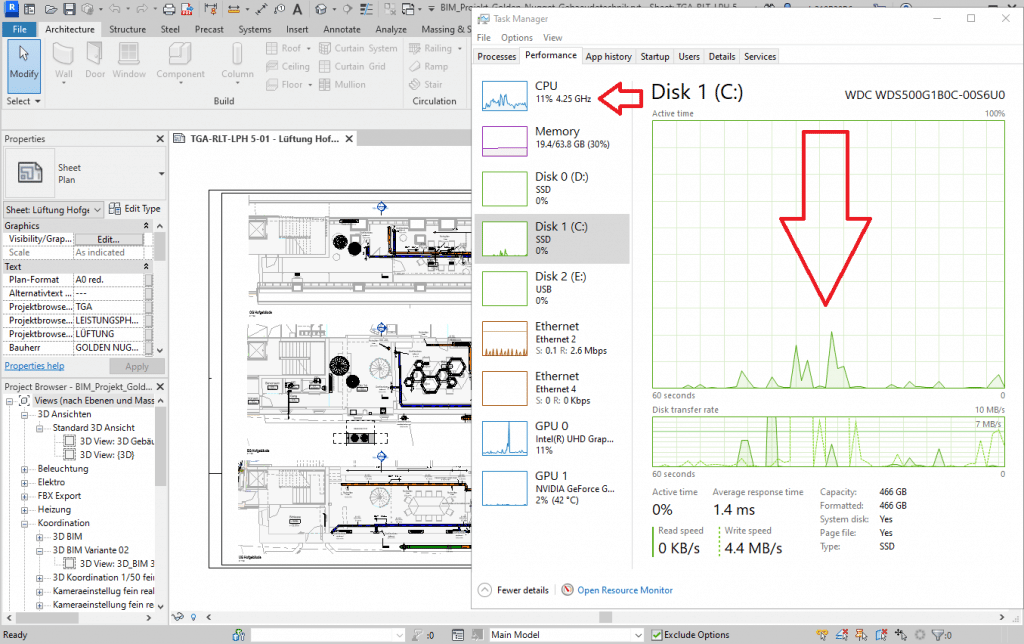
The Renderer in Revit does not use the dedicated GPU.
All the rendering work is done by the CPU. Look at how all the cores are FULLY being used in the CPU section’s task manager screenshot.
Integrated GPUs vs Dedicated GPU: Rendering
It will still takes ~20 min for a best quality render (settings shown in figure) whether you’ve got a dedicated GPU or not.
So in theory if you want to do the rendering on another laptop or the cloud, you could even settle for a computer that has an integrated GPU (if you don’t mind slightly slow viewport) and as long as your work stays pretty close in size to the above image, there should be no lag with integrated GPUs using viewport.
Ada Workstation GPUs The newest workstation laptops will have an Ada RTX GPU which has much faster CUDA Cores (or shaders) due to both the architecture being different as well as the implementation of AI optimized image processing. However, since Revit’s rendering is CPU-based , they are no more useful than other ‘gaming’ GPUs with the same amount of vRAM. However, if you’re running 3DS Max (which is pretty common among Revit users) or GPU-based renderers, they can DEFINITELY speed up the rendering processing massively. C) Hardware Acceleration: Workstation vs Consumer ‘Gaming’ Graphics Cards As some of you know software like Revit has the option to activate “hardware accelerated graphics” which means “using the GPU to improve performance with the software” as shown below: Any dedicate GPU that has ‘vRAM’ will help improve performance when using viewport as we discussed before. Now if you mean drafting & doing operations on a model being faster consumer ‘gaming’ cards CANNOT do anything here because these are floating point operations and consumer gaming cards are designed for 3D Vector operations. As for workstation GPUs, turning hardware acceleration will also improve viewport and in theory, it should ALSO improve performance when drawing and drafting because these GPUs are specifically designed for floating point operations However, they don’t help. You will notice zero performance gains with workstation cards just like you would with gaming cards. The reason why? Well it doesn’t matter. If I have to guess it may be because Revit doesn’t yet know how to make good use of ANY dedicated GPU for floating point operations like drawing, designing, etc. My experience: Workstation GPUs vs Gaming GPUs For me it has made practically make zero difference. For most people I know , both type of graphics card have performed equally well too. Yes I know, workstation are recommended by AutoDesk but that doesn’t really mean anything. If you ever hear people complaining about their GPU not being recognized by AutoDesk Revit, well I had issues with workstation GPUs too despite being listed in AutoDesk’s list of compatible GPUs too! Once you fix the issue, by updating drives, playing around with options, etc, you will see zero difference between the two. I have compared my 860M desktop with a workstation GPU and saw no difference in visual artifacts, no difference in lag when viewporting, nothing, same performance. Although mileage may vary depending on what you’re doing as some people report ‘artifacting’ and ‘glitches’. However these people still use consumer gaming cards deal with it by clicking OK when an error pops up and keep working. 1650GTX/2050RTX: This is probably the GPU that will be suficient for most of you (I’d say 90%). They sell for as low as 600 dollars compared to a workstation laptop that sells for 2-3k dollars! You’d be saving about 1400-2400 dollars and still getting the same performance when using viewport! Now if you do render on your machine, you’ll probably be able to do it faster on a workstation laptop not because of the workstation GPU but because it’s usually paired with the latest CPU . D) When are Workstation GPUs useful then? As far as I know, workstation GPUs MAY be useful in two instances: 3. RAM RAM is just as important as CPU & GPU. I did not go over it sooner because it is very rare for people to buy insufficient RAM. Even if you don’t buy a laptop with enough RAM you can always upgrade RAM later. Minimum: 8GB As a bare minimum you need 8GB RAM , this will work for students. Revit + Windows + large revit files will take most of it but you will still have about 1GB left for any background process. Rendering: 16GB and Up Ideally, if you’re going to render on a laptop, you want 16GB as a minimum. RAM is where all your files are stored for processing (rendering) so the more you have the more data your CPU has to work with at a given time. For most people, the performance gains after 16GB are insignificant. Viewport: 16GB RAM For Viewport to be smooth when working with very very large models and complex models you want to have at least 16GB RAM. In fact, if you are expiriencing lag with your current rig and you’ve been told it’s due to lack of CPU & GPU power, you might as well try upgrading RAM BEFORE you purchase a new laptop. I’ve seen machines perform x3 faster with 16 GB RAM (most of these only had 4 or 8 to begin with). 32-64GB RAM: Special Cases Some people will not work with interior design projects or build/house designs as seen in Civil Engineering but rather with detailed HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning) systems. These instances may require 32-64GB RAM for viewport to be smooth. For those models, especially when there’s a lot of ductwork, piping, and mechanical equipment involved. You better buy a laptop that has the option to upgrade RAM all the way to 64GB RAM because there’s a high chance you MIGHT need the extra RAM.
GPU
Shaders
vRAM
Speed
MX150
384
2GB-4GB
1532
MX250
384
2GB-4GB
1582
MX 230
256
2-4GB
1519
MX 350
640
2-4GB
1354
MX 450
896
2-4GB
1580
1050
640
2GB-4GB
1493
MX550
1024
4GB
1320
Name
Cores
vRAM
Speed
1050 Ti
768
4GB
1620
1650
1024
4GB
1560
1060
1280
6GB
1670
1660 Ti
1536
6GB
1590
3050Ti
2560
4GB
1485
4050
2370
6B
2560
2060
1920
6GB
1680
2080
2944
8GB
1710
2070
2304
8GB
1620
3060
3584
8GB
1780
4060
3072
8GB
2370
3070
5888
8GB
1730
3080
8704
10GB
1710
4070
4608
8GB
2175
4080
7424
12GB
2175
Workstation GPU
Consumer Equivalent
Cores/Shaders
Clock Speed
vRAM
P500
MX150-
256
1519
2GB
P520
MX150
384
1493
2GB
K2100M
GT 750M
576
667
2GB
K3100
765M-
768
706
4GB
P620
MX250/1050
512
1442
4GB
M620M
950M-
512
1018
4GB
M1000M
950M
512
1072
4GB
Pro WX 3200
RX 550
1082
640
4GB
M2000M
950M/960M
640
1197
4GB
M1200
960GTX
640
1150
4GB
P1000
1050GTX
512
1519
4GB
P2000
1050Ti
768
1468
4GB
T2000
1650/1660Ti
1024
1785
4GB
T1000
1650-
768
1455
4GB
RTX 3000
2070RTX+
1280
1380
6GB
RTX 4000
2070/2080
2560
1560
8GB
RTX 5000
2080RTX+++
3072
1350
16GB
RTX A2000
~3050Ti
2560
1200
4GB
RTX A3000
~3060RTX
4096
1560
6GB
RTX A4000
~3070RTX
5120
1560
8GB
RTX A5000
~3080RTX
6144
1695
16GB
Ada GPU
GPU
EquivalentCores/Shaders
Clock Speed
vRAM
RTX 5000
RTX 4090 –
9728
1680Hz
16GB
RTX 4000
= RTX 4080
7424
12GB
RTX 3500
RTX 4070 –
5120
12GB
RTX 3000
RTX 4070 —
4608
8GB
– Launching the software FAST
256GB vs 512GB vs 1TB (SSD Space)
256GB: found on most laptops and desktops. You can install Windows, Revit and still have about 100GB left (Windows ~50GB + Revit 40GB) , the problem is you never have just revit open you’ll also be running PhotoShop, Navisworks and probably AutoCAD + other software. If you are a student, you are likely to be okay with this much and there will be no need for upgrades.
512GB: This is the minimum for someone who’s already working as an engineer. Revit Files can take up to 700MB each . You don’t have to buy a laptop with 512GB (most will charge you way more money for 512GB) , what you can do is buy a separate SSD (~40 bucks) and do the upgrade yourself. I have a tutorial on how to do the SSD Upgrade here.
Display
It isn’t a concern for laptops because there isn’t much variety of displays on laptops.
In other words, most display will have the same specs.
Matte Display
However some laptops have a matte display which are easier on the eyes as the amount of glares is massively reduced. You aren’t likely to find this type of display though but you can always add an external filter.
IPS vs TN
Most laptops have IPS displays. They don’t have the best color accuracy but they’re far better than TN displays.
Most Revit users will see zero difference between these two types of displays though. It’s only going to be a concern for photographers and Photoshop users or anyone who has to print their work.
Resolution
More resolution means more screen space. More screen space means larger canvas and quicker access to interface bars with tools/functions.
Most laptops have 1080p, FHD (Full HD) resolutions and that’s totally fine for Revit.
However, you would be better off with 2k. The problem is that theyre USUALLY found on laptops above 1500 dollars . Some laptops however will have a QHD display for ~700 dollars (see Lenovo Ideapad 5i Pro).
Comments
If you know you are going to work on very large projects on Revit with a low budget. Not all hope is lost, you can also eliminate any lag by optimizing file management. Use worksets, linked files, and a clean family library and you may not even need to find a new laptop or computer. Revit isn’t as hardware demanding as people would like you to believe (at least for more users).
If you have any questions or comments please leave a comment below.
Author Profile
- I am physicist and electrical engineer. My knowledge in computer software and hardware stems for my years spent doing research in optics and photonics devices and running simulations through various programming languages. My goal was to work for the quantum computing research team at IBM but Im now working with Astrophysical Simulations through Python. Most of the science related posts are written by me, the rest have different authors but I edited the final versions to fit the site's format.




very helpful, thanks 🙂
Nice suggestions
Wow, the most useful post.