10 Best Laptops For Engineering (For 2025 Tools & Updates )
When engineering students start their electrical, mechanical, computer, civil, software, chemical, aeronautical, or aerospace engineering programs, their first assumption is often:
“I’m going to need a very powerful laptop with the latest processor and graphics.”
That’s not true.
Most engineering students only need a laptop with a decent CPU and 8GB of RAM.
Now…
I know what you’re thinking: “Wait, what about 3D modeling, CAD software, or other demanding programs?”
Listen…
As long as you buy ANY laptop with ANY dedicated graphics card, you’ll be able to handle ANY 3D CAD project you encounter in engineering school. In fact, you might not even need dedicated graphics!
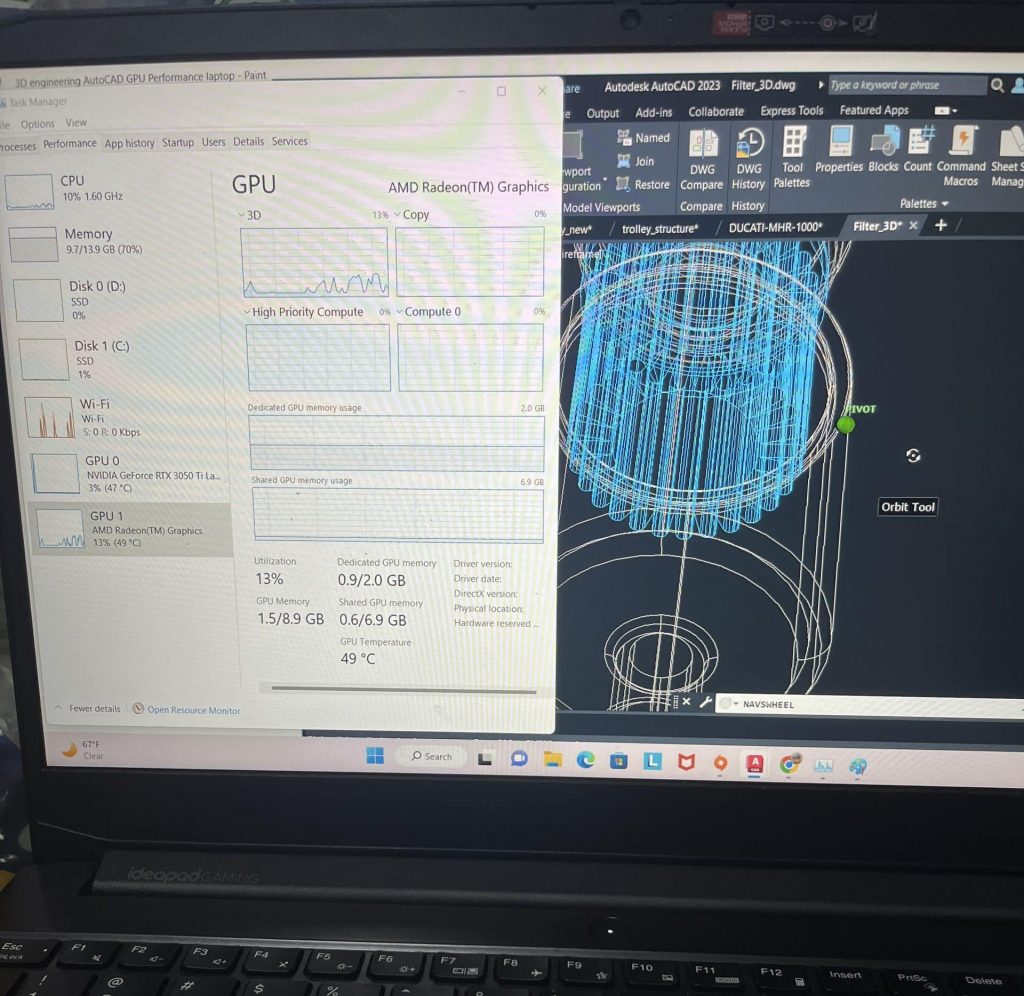
Here’s the breakdown:
In this post…
I will PROVE everything I just said with benchmarks (footage) and by going through the typical engineering curriculum.
In engineering school, there will only be a few occasions when you’ll need to run CAD software (for which you can always use the computer lab). Most of the time, you’ll be using other software, like:
Electrical & Computer Engineers: programming languages like C++ and circuit simulators like SPICE.
Mechanical & Civil Engineers: Lots of programming too.
Best Hardware for Engineering Students & Engineers
Since the CAD software you’ll use will be during your 3rd or 4th year and be limited to a few classes/projects. My advice is to not to focus on power but rather PORTABILITY.

Q: OK, good point, Any portable laptop will be fine?
Of course not. You don’t want to grab a cheap $200 laptop from Walmart. You’ll want to avoid lag, especially when you’ve got a dozen programs running alongside 20 Chrome tabs.
Basically, make sure to pick a laptop with the recommended hardware outlined in the infographic. It’ll save you a ton of headaches!
Before diving into the best laptops for engineering in 2025 (I’ll include options with both ‘recommended’ and ‘best’ hardware in the table), let me elaborate a bit more on the hardware for those who are a little more tech-savvy. If you’re not interested in the nitty-gritty, feel free to skip ahead to the best laptops section!
3D engineers: mechanical, civil and aeronautical
GPU (Graphics Card)
2D engineer: No need for dedicated graphics. Integrated graphics (which come ‘integrated to the CPU’ so to speak) is good enough even for 3D work.
3D engineer: You either go for the latest ‘integrated graphics’ which should work (though with some lag) with SMALL 3D projects in AutoCAD, SolidWorks and ANSYS*.
Or choose a laptop with ‘dedicated’ graphics to get smooth performance (if you refuse to use computer labs or another computer besides your laptop):
For smooth performance with 3D work you only need a 2-4GB vRAM such as the following:
MX250, MX350, MX450, MX550, 1050GTX, 1650GTX, 2050RTX, 3050Ti, 4050 RTX, 3060RTX
Those in red have the same performance as the latest integrated graphics. Green ones are IDEAL and the blue is overkill but may become useful after you graduate.
What about ‘workstation’ GPUs? Like Quadro? FirePro?
They’re useful for actual working engineers. Even so there’s only a small chance an actual engineer will find it useful unless he/she works in the 3D modeling department. If so check out my 3D modeling posts on AutoCAD & Solidworks.
CPU (Processor)
2D engineer: Any recent CPU released within the past 5 years. Feel free to go higher if you can afford (without compromising portability & weight)
3D engineer: At least a Core i5 or Ryzen 5 CPU released within the past 3 years.
The more recent the CPU, the better. Why? Because newer CPUs come with higher clock speeds and significantly improved integrated graphics (iGPUs), which can compensate for the lack of a dedicated GPU if you go for a laptop without one.
That said, not all CPUs with integrated graphics are equal. Some of the older CPUs, particularly 6th and 7th gen Ryzen 3 & Ryzen 5 CPUs, are worth avoiding because their integrated graphics (e.g., Radeon 610M) are too weak for anything beyond basic tasks.
More information on which integrated GPUs are found on these CPUs and their performance is shown in this link.
RAM & Storage
8GB: If you follow my advice on CPU & GPU, you’ll automatically get 8GB or 16GB. Either is plenty to multitask with 3D modes, IDE for programming, Office, and all the internet tabs you’ll need.
256GB: Bare bone minimum and found on most laptops. If you’re specializing in 3D modeling & Cad design, you may want to do the upgrade to 512GB.
The SSD generation (PCIe 5.0 vs PCIe 4.0) doesn’t matter much for most users. The speed difference is only noticeable when transferring large files in bulk, like photos or videos. For engineering work or general use, PCIe 4.0 SSDs are already more than fast enough.
Top 10 Best Laptops For Engineering Students & Engineers
I KNOW this is a long list but I tried to cover all types of laptops for engineering.
I recommend you read at LEAST the first 3 reviews. Those are the THREE most important laptops of the list.
Also keep in mind the following icons before reading a review:
Ideal.
Overkill but useful.
MAY lack power for large 3D CAD projects. Read description for more details.
1. MSI GF63 THIN 12UCX-898US
Cheap Laptop For Engineering Students
Intel Core i5 12450H
16GB RAM DDR4
2050RTX 4GB vRAM 30W
1TB PCIe NVMe SSD
15” 1080p IPS 144Hz
4.1 lbs
3 hours
Electrical , Computer , Chemical , Software
Civil, Mechanical , Aerospace & Aeronautical Engineers
This laptop is an absolute tank for pretty much any engineering student and any project you’ll run into during school. It’s packing a recent CPU and a 4GB vRAM dedicated GPU, which means it can handle both 2D and 3D work with ease.
If you’re an EE student or working mostly in 2D, this thing is overkill. You’re paying extra for GPU power you probably won’t even use—unless you’re into gaming (which, let’s be real, you probably should cut back on during those brutal first three years).
Now… 3D Engineers, Listen Up 👀
You don’t have to buy this exact laptop, but it’s one of the cheapest lightweight options with a dedicated GPU. If you can snag something like a 1650GTX or 3050RTX for less, go for it.
For actual engineers working on massive 3D CAD projects (think designing cars or machinery in SolidWorks), this laptop can get you started, but don’t expect it to crush huge assemblies (500+ parts). For that, you’ll want a 6GB vRAM GPU or higher.
Performance: 3050Ti 4GB vRAM + Ryzen 5 5600H
Here’s what you can expect:
- AutoCAD: Smooth as butter, even for 3D models.
- ANSYS & SolidWorks: Works great for assemblies under 500 parts. Viewports stay smooth, and rendering is fast thanks to the GPU’s CUDA cores and the CPU’s beefy multicore setup.
If you’re looking to specialize in 3D CAD design, though, consider leveling up to something with 6GB vRAM. You’ll thank yourself later.
What about cheaper laptops with dedicated GPUs ?
Can’t drop ~$600 on this laptop? No worries. You can still grab something with a weaker GPU that’s good enough for school-level 3D work. Here’s a quick rundown:
GPUs in red (like MX150 or MX250). Sure, they’re “dedicated,” but the performance is pretty much the same as modern integrated graphics (like Intel Xe or RX Vega). If you’re going this route, just save the cash and grab a laptop with solid integrated graphics.
How Do These GPUs Handle 3D CAD?
Most of the GPUs I listed (except the red ones) can handle assemblies up to 200 parts in software like ANSYS or SolidWorks without breaking a sweat. For engineering school projects—which rarely go over 100 parts—that’s more than enough.
Thinking About a Career in 3D Modeling? 🛠️
If you’re planning to specialize in 3D modeling (e.g., designing cars, tools, or complex machinery), try to get at least a 4GB vRAM GPU. For 500-1000 parts assemblies, you’ll need something beefier with 6GB vRAM or more. But honestly, you probably won’t run into projects like that in school unless you take an elective or decide to go all out on your senior project.
TL;DR: This laptop is a beast, but there are cheaper options that’ll get the job done if you’re just starting out.
| MSI 15 Thin | |
| PROS | CONS |
|
|
2. Surface Laptop Studio 2
Best 2 in 1 Laptop For Engineering

Intel® Core™ i7 13th gen
16GB LPDRR5 RAM
NVIDIA RTX 4050
512 GB NVMe PCIe 4.0 SSD
14.4” 2400 x 1600 2 in 1 Tablet-Laptop w/ Stylus
4.37lbs
5 hours
Electrical , Computer , Chemical , Software
Civil, Mechanical , Aerospace & Aeronautical Engineers
The MSI GF63 Laptop
This is a basic laptop with dedicated graphics but not much focus on portability. Now let’s move on to portable yet powerful laptops for all types of engineering. We’ll start with the most powerful option with dedicated graphics.
Surface Series:
If you’ve been browsing around, you’ve probably seen the Surface lineup: Surface Pro, Surface Book, and Surface Laptop Studio. These devices can also convert into a tablet, which is a game-changer for engineering students.
Surprised they’re so popular? You shouldn’t be.
- Super portable
- Amazing displays
- Long battery life (except for the Surface Laptop Studio—more on that later)
- And most importantly, they let you write equations, take notes, and even do your physics homework right on the screen.
The best part? There are many configurations for Surface devices. That means you can choose hardware tailored to your field:
- 3D engineers can go for models with higher GPU and CPU power.
- 2D engineers can stick to cheaper configurations since they don’t need much GPU power.
Surface Laptop Studio 2: Performance
The Surface Laptop Studio 2 is the most powerful Surface device.
If you’re a 2D engineer, skip this one and check out the next laptop: Surface Pro 9.
3D engineers, here’s the breakdown:
You’ve got three GPU options:
- 4050RTX
- 4060RTX
- RTX 2000 Ada
Which one should you choose?
- If this is for school projects, the 4050RTX is overkill. It’s got 6GB of vRAM, way more than you’ll need for typical engineering assignments.
- Even a 3050RTX with 4GB vRAM will handle all your school 3D work smoothly (except maybe for an extremely complex senior project).
So, if you can’t afford the latest Surface Laptop Studio 2, grab the previous version or a Surface Book. They’re cheaper and still have solid GPUs for engineering work.
But…
If you’re a working engineer or specializing in 3D CAD software (e.g., SolidWorks or ANSYS), you’ll want either:
- 4060RTX
- RTX 2000 Ada (this is a workstation GPU, theoretically more stable for software like SolidWorks/ANSYS).
Display & Design
The Surface Laptop Studio 2 is one of the heaviest Surface devices (along with the Surface Book) due to its nearly 15” display. But that larger screen is worth it.
One of the standout features of Surface devices is the high-resolution display. Most Surface models offer QHD-like resolution, which is a game-changer for productivity. Why?
- More screen space means less scrolling and more windows side by side.
- Perfect for multitasking: Imagine having a tutorial open in one window while taking notes in another, or a website’s data alongside an Excel sheet.
Whether it’s the Surface Laptop Studio 2 or another Surface device, the high-res display will definitely boost your workflow.
| Surface Laptop Studio 2 | |
| PROS | CONS |
|
|
3. Lenovo Ideapad 5i
Budget Laptop For Engineering

Intel Core i5-11300H
8GB DDR4
GeForce MX 450 2GB vRAM
512GB PCIe 4.0 SSD
16″ QHD 2.5K
4.2 lbs
4 hours
Electrical , Computer , Chemical , Software
Civil, Mechanical , Aerospace & Aeronautical Engineers
This is one of my top favorite budget laptops for two reasons:
- The power is just right: This laptop features a 2GB vRAM dedicated GPU, which is the bare minimum needed to run CAD and 3D models with SolidWorks/ANSYS in engineering school.
- For 2D engineers, this is overkill since you won’t need a GPU. I’d recommend avoiding this laptop because it’s a bit heavy.
- The display is fantastic!
Performance: Core i5-11300H + MX450
As I’ve mentioned several times, most engineers will primarily deal with coding assignments and circuit design. It’s only the 3D engineers who’ll need to run 3D CAD models, which might require a dedicated GPU.
With its 2GB vRAM GPU, this laptop can handle SolidWorks projects with up to 200 parts before experiencing any lag. However, to get this level of performance, it’s crucial to buy a recent 2GB vRAM GPU, like the MX450 featured here.
Be cautious of older GPUs like the 940MX or MX250 you might find in refurbished laptops at a cheaper price. While these can also run 3D models in the same part range, they’ll start to struggle much sooner when you push the project complexity higher.
Display
The main reason I’m recommending this laptop is the display resolution and size. It has a 16” QHD display, offering the largest screen space among budget options.
This extra screen space is a game-changer for multitasking, allowing you to comfortably work with multiple windows side by side:
- A tutorial + your IDE (programming software)
- A YouTube video + Office (for note-taking)
Even more importantly, the larger screen size and QHD resolution make viewing code or scripts much easier. When working on long scripts for assignments or projects, having a full view of the structure helps identify and fix bugs/errors more efficiently.
For 2D engineers: If you don’t need the dedicated graphics, there are versions of this laptop without a GPU. Look for models made by HP or Lenovo with the same great display!
| Lenovo Idea Pro 5i | |
| PROS | CONS |
|
|
4. Surface Pro 10
Best Portable Laptop for Engineering 
Intel® Core Ultra 5 or Core Ultra 7 (13th Gen)
8GB-16GB RAM DDR5
Intel Iris Xe Graphics
128GB-1TB PCIe NVMe SSD
13” IPS 2880 x 1920 (PixelSense Display)
1.96lbs
Up to 15 hours battery life
Electrical , Computer , Chemical , Software
Civil, Mechanical , Aerospace & Aeronautical Engineers*
*ANSYS/SolidWorks/Civil 3D/Revit projects and assignments can run on the Surface Pro provided that they’re undergraduate level .
*CREO, CATIA projects will need the SurfaceBook 3 though these two is rarely used in engineering
This is, in my opinion, an even better choice than the Surface Laptop Studio if you’re looking for a 2-in-1 tablet, despite the lack of GPU power. That doesn’t mean it’s useless for software that requires decent performance.
In fact, the Surface Pro is even more popular than the Surface Laptop Studio or the Surface Book, which do have dedicated graphics. The reasons are pretty simple:
- Much lighter
- Same 2-in-1/Touchscreen design for note-taking, equation-writing, etc.
- Longer battery life (due to the lack of a power-hungry GPU)
- Cheaper
It gets insanely cheaper if you go for older models, which still have the CPU and RAM specifications we discussed in the recommended specs section.
Now the main question is: What kind of performance can you expect with the Surface Pro, which doesn’t have a dedicated graphics card?
Performance
None of the Surface Pro models, including the Surface Pro 10, have a dedicated GPU (no 4GB or 2GB vRAM). However…
They always come with the latest CPU available at the time of their release. For instance, the Surface Pro 10 is powered by Intel’s 13th-generation CPUs, and as we discussed earlier, this also means more powerful integrated graphics.
The integrated graphics in the Surface Pro 10 (Intel Iris Xe or AMD Radeon 780M, depending on configuration) can handle small 3D CAD projects like SolidWorks models under 100 parts.
- You may encounter some lag, especially with viewport rendering, but it won’t be so severe that it becomes unusable.
- For engineering school, where you’ll only deal with 3D CAD design projects a few times, this trade-off is worth it considering the other insane benefits of the Surface Pro series.
If you’re okay with occasionally using a computer lab or another computer for very complex 3D projects, the Surface Pro is still a fantastic choice for all the other tasks.
RAM: 8GB vs. 16GB
It’s critical to ensure your Surface Pro has at least 8GB of RAM, especially for running CAD software.
- Most recent models, like the Surface Pro 10, come with 8GB as the baseline, so this isn’t usually an issue.
- However, older models (like the Surface Pro 4 or earlier) may only come with 4GB of RAM, which is insufficient for modern engineering software.
If you can stretch your budget, 16GB of RAM is a great upgrade for 3D engineers.
- Why? More RAM means your integrated graphics will have more memory to work with, making performance much closer to what you’d get with a dedicated GPU.
- This massively improves viewport performance in SolidWorks or other 3D modeling software.
Display & Design
The Surface Pro 10 has the same PixelSense display found in previous models but with some enhancements.
- Resolution: 2880 x 1920 (higher than standard QHD, which is 2560 x 1440).
- Size: 13-inch display, slightly larger than older models (12 inches).
This high resolution compensates for the smaller display size, giving you plenty of screen real estate for multitasking.
- You’ll have no problem keeping multiple windows open side by side, whether it’s a tutorial and your IDE, or a browser tab and your notes.
- For programming, the high resolution helps immensely by allowing you to view more code at once, reducing the need to scroll.
Portability:
- The Surface Pro 10 is incredibly thin at 0.33 inches, making it far more portable than the Surface Laptop Studio 2 (0.86 inches).
- It weighs less than 2 pounds, which makes it an excellent option for slipping into your backpack alongside textbooks.
2-in-1 Note-Taking Features:
Like all Surface Pro models, the Surface Pro 10 is also a tablet with highly accurate note-taking capabilities. This makes it a fantastic replacement for notebooks and textbooks.
- While engineers may still need a physical notebook for working through equations and practicing physics problems, the Surface Pro is perfect for lectures, note-taking, and even sketching out ideas.
Older Models: Worth It?
Older Surface Pro models are still a great option if you’re on a budget.
- Surface Pro 7 and 8: These have slightly weaker CPUs but still offer excellent performance for engineering tasks and include similar high-resolution displays.
- Surface Pro 4 or earlier: Not recommended unless you only plan to do light tasks or 2D engineering. They may lack performance and have lower RAM (4GB), which can be limiting.
| Surface Pro 10 | |
| PROS | CONS |
|
|
5. Lenovo ThinkPad X1
Best Lenovo Laptop For Engineering
Intel Core i7 13th gen or Core i9
16GB-64GB DDR4 RAM
AMD Radeon Vega 7
512-2TB PCIe NVMe SSD
14-16” QHD or UHD resolution
2.24-4.14lbs
10+ hours
Electrical & Chemical & Software and Computer Engineers
Mechanical, Civil, AeroSpace, Aeronautical
Lenovo ThinkPads are the most popular “TRADITIONAL LAPTOP” among engineers. ThinkPads are ALWAYS the first choice for engineering work.
They’ll remain useful even AFTER engineering school (let’s hope you graduate!) due to the following reasons:
- Myriad of extra ports: The ThinkPads (T & X1 Carbon Series) regardless of release date always come with LOTS of ports. This cannot be said for modern ultrabooks, which prioritize portability by reducing the number of ports with each new version.
- Rock-solid design: ThinkPads are built like tanks. They can withstand serious working conditions and the everyday stresses of commuting and traveling. They’re durable enough to survive a few drops since they’re built with aluminum instead of plastic. On average, they can last about 8 years if you avoid serious accidents.
- Top-of-the-line keyboard: This is probably the number one reason why they’re so popular. While the previous laptops mentioned might not be ideal for those who program and type reports all day, ThinkPads are the BEST for that. The keyboard is EXTREMELY well-designed with long travel distance (how far keys press down) and high responsiveness. They feel like a typewriter that doesn’t require much force to register keystrokes—perfect for heavy typists.
- TrackPoint and Trackpad: The iconic red TrackPoint (the small red dot) acts like a ball mouse, and the spacious trackpad includes three clickable buttons. It’s super useful when working on the move or in cramped spaces.
- Linux compatibility: Not a huge deal for most engineers unless you specialize in data science or fields that require frequent use of programming packages. ThinkPads are highly compatible with Linux Distros, which means every piece of hardware works natively. Other laptops often have one or two features disabled due to a lack of Linux drivers.
Performance
Of course, this recommendation applies mainly to engineers (whether 3D or 2D) who don’t specialize in large-scale 3D CAD modeling. These are typically 2D engineers—like electrical, computer, chemical, etc.—who spend their time programming, designing 2D/small 3D models, and testing devices via computer.
Unfortunately, Lenovo ThinkPads don’t typically come with dedicated graphics cards. So they aren’t ideal for professional 3D CAD engineers working on large-scale models. However, if you’re a 3D engineering student and want to use a ThinkPad during school, it’s still a great choice!
Pro tip: Make sure you pick a model with a recent CPU. This will allow you to run the smaller 3D CAD models you’ll encounter in engineering school. Also, don’t forget to get one with 16GB of RAM or upgrade it if you’re a 3D engineering student.
| Lenovo ThinkPad X1 | |
| PROS | CONS |
|
|
6. Acer Aspire 5
Cheap Laptop For Engineering
Core i5-1335U
8GB LPDDR5
Intel Xe Graphics
512GB SSD NVMe PCIe 4.0
15.6” FHD
3.7 lbs
8 hours
Electrical & Chemical & Software and Computer Engineers
Mechanical, Civil, AeroSpace, Aeronautical
Performance: Core i5 13th gen (or older generations)
Core i3/Ryzen 3:
If you’re shopping for very cheap laptops because you’re on a tight budget (and plan to leave the 3D projects to the lab computers), you don’t have to buy this model. You can go for slower but much cheaper laptops with a Core i3 or Ryzen 3.
Now, when I say they’re slower, that’s relative. Those laptops, as long as they have recent CPUs (5th or 7th gen Ryzen 3 or 10th–13th gen Core i3), are still multicore and have decent clock speeds to make multitasking a BREEZE. They’re a fantastic choice for 2D engineers since there’s no need for powerful integrated graphics (they have weaker graphics). Another perk is their longer battery life and lighter weight.
Core i5/Ryzen 5:
I chose this model as the cheapest laptop for engineering on the list because the Core i5/Ryzen 5 ensures it’s useful for all types of engineering and projects during engineering school. That’s right, even 3D engineers can use this laptop to run 3D models in SolidWorks, CATIA, and ANSYS. As long as the number of parts and complexity of the projects remain small (as expected in introductory 3D modeling courses), this laptop should handle them with only minor lag in the viewport.
8GB vs. 16GB RAM:
Remember, for the integrated graphics to work best, you need extra RAM. These budget laptops typically come with 8GB RAM (and sometimes even just 4GB!). You should upgrade to at least 8GB for programming and non-3D CAD design, and ideally to 16GB for 3D CAD modeling in ANSYS, CATIA, and SolidWorks.
Upgrading the RAM is straightforward. The only hassle is dealing with the MANY screws on a laptop. If you’re not comfortable doing it yourself, take it to your school’s IT department—they’ll likely do it in 10 minutes (assuming they’re not too hesitant to help).
| Acer Aspire 5 | |
| PROS | CONS |
|
|
7. MacBook M4 Pro Chip
Best MacBook For Medical School 
M4 12 Core CPU
24 GB Unified Memory
16‑core GPU
512GB-2TB SSD
14.2-16 inch Liquid Retina XDR display 3024-by-1964
4.7lb
13 hours
Electrical & Chemical & Software and Computer Engineers
Mechanical, Civil, AeroSpace, Aeronautical
You’re probably thinking I’m crazy to even suggest a MacBook, but you’d be surprised to see how many students, including engineering students, use MacBooks. So are they a NO-NO or a YES-YES?
It depends.
They’re a YES-YES if you are willing to compromise a few things. It’s a NO-NO for any engineering (student or pro) focusing solely on 3D CAD work.
What’s the Catch?
The main problem with MacBooks is the operating system. While MATLAB, AutoCAD, and LabVIEW can all run on a Mac—as well as pretty much ANY software for coding/programming (MacBooks are a top choice for non-engineering programmers)—they cannot run many of the most popular 3D CAD design software like SolidWorks, CATIA, or ANSYS.
Ports? That’s not an issue because MacBooks do have ports. Yes, they don’t have USB or RJ-45/Ethernet ports, but they have Thunderbolt ports, which can easily be used with adapters.
The real issue lies with DAQ boards and circuit design software, which typically only have Windows versions. This makes it very difficult to work with circuit design tasks on a MacBook, as most of the software for these tasks is written for Windows (see the featured image of this post). Sure, you might find a couple of options compatible with macOS, but there’s no guarantee your class or department will use them.
Hold Up, There’s a Solution!
You can install Windows on a MacBook too! Here are two ways to do it:
- Install Parallels: Parallels is software that lets you run Windows on top of macOS. You can use it whenever you need to run Windows-only software.
- Buy a pre-2020 MacBook: MacBooks made before 2020 have Intel chips and BootCamp, which lets you install Windows natively. You can switch between macOS and Windows with a simple restart.
Why Go Through All This for a MacBook?
While some engineering students buy MacBooks to look cool, there are actually good reasons to consider one:
- Extremely portable and thin
- Longest battery life on any laptop
- The best keyboards ever designed (super useful for programming)
- Large and responsive trackpads (you may not even need a mouse)
- Superb high-resolution displays (see more content at once)
- Extremely solid build quality
- No need to pay for antivirus or worry about viruses
And most importantly:
They’re built for coding and programming, making them the top choice for computer engineering students!
They’re also great for all engineers since most software used in engineering programs involves programming and light 2D/3D modeling, where MacBooks excel.
How Are MacBooks Built for Programming?
The Terminal is one of the most widely used programming tools after IDEs. Most programming languages and packages are natively available on macOS and easily accessible through the Terminal. This significantly improves workflow efficiency compared to Windows, whose terminal feature is still catching up.
Performance
What about performance for engineering software like AutoCAD?
3D Engineers: As long as you buy a MacBook Pro model released within the past eight years (with at least 8GB RAM), you’ll be able to run AutoCAD, MATLAB, and IDEs with no lag whatsoever.
Some MacBook Pro models come with Radeon GPUs (dedicated graphics). While they’re AMD-branded, they work well with 3D modeling software (compatible with macOS) because they have vRAM. The newer M-series chips (M1, M2, M3, and M4) also perform well with 3D modeling software, provided projects remain at school-level complexity.
2D Engineers: If you’re a 2D engineer, you don’t need to limit yourself to MacBook Pros. Even the MacBook Air (new or old) will be sufficient.
Performance
Now what about performance for engineering software like AutoCAD?
3D Engineer: As long as you buy a “MacBook Pro” model released within the 8 years or so (withi 8GB RAM), you should be able to run AutoCAD, MatLab, IDEs with no lag whatsoever.
There are a few MacBook Pro models that have dedicated graphics usually Radeon GPUs. Now..even though they are from a different brand (AMD) they still work well with 3D modeling software (compatible with OSX) because they hav vRAM. As for th newer M chip models (M1, M2 & M3 M4) they also work well with 3D modeling software (as long as projects remian school level).
2D engineer: Now if you are a 2D engineer, you don’t have to limit yourself to MacBook Pros. You can even buy the MacBook Air (whether or old or new).
| SoC | CPU Cores | GPU Cores | RAM |
|---|---|---|---|
| M1 | 4 Effiency cores & 4 Performance Cores | 7 | 16-32GB |
| M2 | 4 Effiency cores & 4 Performance Cores | 10 | 16-32GB |
| M1 Pro | 2 Efficiency cores & 6 Performance cores | 14 | 16-32 GB |
| M1 Pro | 2 Efficiency cores & 8 Performance cores | 14 | 16-32 GB |
| M1 Pro | 2 Efficiency cores & 8 Performance cores | 16 | 16-32 GB |
| M1 Max | 2 Efficiency cores & 8 Performance cores | 24 | 32-64 GB |
| M1 Max | 2 Efficiency cores & 8 Performance cores | 32 | 32-64 GB |
| M2 Pro | 2 Efficiency cores & 8 Performance cores | 19 | 16-32GB |
| M2 Max | 2 Efficiency cores & 10 Performance cores | 38 | 32-96GB |
| M3 | 4 Efficiency cores & 4 Performance cores | 10 | 6-16GB |
| M3 Max | 4 Efficiency cores & 12 Performance Cores | 40 | 48-128GB |
OSX: Unix System – Computer & Electrical Engineers!!!
I’ve mentioned that MacBooks are especially good for programmers in computer and electrical engineering, and that’s particularly true if you’re interested in machine learning, AI, or any data science-related topics. If you’ve never used a MacBook, the learning curve will be quick. However, mastering the terminal and relying on it for almost everything will take some time, but it’s one of the most valuable skills to have if you want to become a top programmer in the industry.
Cost
Many people want a MacBook and are willing to compromise on software compatibility, but the price can be a significant issue because they are notoriously expensive.
But there’s a hack to get one cheaper: buying older models. Performance-wise, at least for engineering school, there should be no noticeable difference between newer and older MacBooks. Just keep the following in mind:
2D Engineer: You can grab ANY MODEL, literally ANY. Even the 4GB MacBook Air will be sufficient. However, it’s better to get MacBooks with USB ports (2015-2019 models), as they’ll make connecting peripherals much easier without needing adapters.
3D Engineer: You can also grab ANY MODEL, as long as you’re willing to use computer labs for 3D CAD work. If you’re opting for older models, I recommend choosing one with USB ports (again, 2015-2019 models) for easier connectivity.
| MacBook Pro M4 | |
| PROS | CONS |
|
|
8. ASUS ZenBook 14 14X
Best Windows UltraBook for Engineering Students
Intel Core i5-13500H
 8GB RAM DDR5
8GB RAM DDR5
Intel Iris Xe Graphics
512GB
14.5” 2.8k resolution OLED
3.44lbs
Electrical , Computer , Chemical , Software
Civil, Mechanical , Aerospace & Aeronautical Engineers*
I keep posting about the ASUS ZenBook every year, and this year is no exception. They’re a great, great alternative to the MacBooks and much cheaper. You still get ALL the superb qualities:
- Super high-resolution display
- Super fast CPU
- Very good portability
- Super thin
- Long battery life
At a much cheaper price!
Performance: 2D & 3D CAD engineering
This is a laptop that’s ideal for 2D engineers. It has the right CPU and RAM with all the cool features mentioned above and doesn’t waste power on a dedicated graphics card (which would make the laptop as expensive as a MacBook).
However…
3D engineers will have to deal with some lag when using the viewport for those occasional 3D CAD design projects in SolidWorks, ANSYS, or Catia.
Nonetheless, if I were a 3D engineer, I wouldn’t think twice about it. If I know 3D CAD modeling isn’t going to be my primary focus (but rather research), OR if I plan to rely on AutoCAD (which isn’t as GPU-demanding) for my senior project, then I’d go for this laptop—or even a cheaper, portable laptop, even if it has less CPU power.
Note: Unlike other budget portable machines, this laptop has a very, very long battery life and includes a numpad integrated into the trackpad. Since 13” or even 15” portable laptops usually don’t have space for a dedicated numpad, this is a very, very useful feature—especially for number crunching on reports, sheets, and tables. These can be read (e.g., by Python) to create graphs.
| ASUS ZenBook 14 14X | |
| PROS | CONS |
|
|
Laptops for Working Engineers 9-10
The following laptops have too much power for engineering students. They are reserved for engineers who are either about to join a 3D CAD modeling department at a company or plan to do so very soon.
If you’re a student, you may find the following laptops useful, but under no circumstances should you consider laptop #10. Don’t even look at it—it’s far too powerful. It’s only listed here for the small group of 3D CAD engineers reading this, and even for them, it might be overkill.
You’re welcome to read about it for informational purposes, though.
9. Acer Nitro 17
Best Laptop For 3D CAD engineering

AMD Ryzen 7 7840HS
16GB RAM DDR5
NVIDIA GeForce RTX 4060 Laptop GPU
1TB GB PCIe NVMe SSD (Free Slot for upgrade)
17.3″ QHD 165Hz IPS
6.61 lbs
2 hours
Electrical , Computer , Chemical , Software
Civil, Mechanical , Aerospace & Aeronautical Engineers
This is a powerful gaming laptop equipped with a very recent 8GB vRAM dedicated GPU. Of course, we’re not choosing this laptop because it can play all games at Epic settings with high frame rates, but because the vRAM and CUDA cores within the GPU are incredibly useful for GPU renderers and the viewport in 3D CAD modeling software.
Performance: 4060RTX
Since GPU renderers are not commonly used, the most significant advantage of this laptop is its 8GB vRAM. Having 6–8GB of vRAM is an excellent starting point for achieving high performance in the viewport of very large models. Below is a list of 6GB vRAM GPUs released in the past five years or so:
| Name | Cores | vRAM | Speed |
| 1060 | 1280 | 6GB | 1670 |
| 1660 Ti | 1536 | 6GB | 1590 |
| 2060 | 1,920 | 6GB | 1680 |
| 3060 | 3584 | 6GB | 1780 |
| 4050 | 2560 | 6GB | 2370 |
| 4060 | 3072 | 8GB | 2370 |
Now…
There are many more powerful GPUs, like the 4080 and 4090, with vRAMs of up to 16GB. While those are excellent options, it’s incredibly rare for someone in engineering to work with models that require that much vRAM. Even the 8GB vRAM of the 4060RTX might be more than most people need. However, since 4060RTX laptops are not significantly more expensive than those with 6GB vRAM GPUs like the 3060RTX or 4050RTX, it’s better to choose the 4060RTX to stay future-proof, so to speak.
Design
Why did I choose this laptop over other 4060RTX models, and why should you?
Primarily for the size and resolution. This laptop features a 17-inch display with QHD resolution. As we’ve discussed before, this provides an extremely large amount of screen space, allowing you to view more of your code or 3D model. It also makes it easier to fit more quick-action tools from AutoCAD or SolidWorks on the screen, enhancing productivity.
Large laptops have another advantage: better heat dissipation. With more physical space, they can handle heat and high temperatures more effectively as there’s more room for hot air to dissipate. Additionally, the RAM and storage are maxed out, making upgrades to 32GB RAM unnecessary unless you’re working with exceptionally complex and large rendering projects (more RAM reduces rendering time).
If you’re a student, this is a great laptop for power-intensive tasks. However, be aware that it’s very, very heavy—not ideal for frequent transport. This laptop is best suited for staying in one place. If you need portability, consider getting a smaller, lightweight laptop (like an 11-inch model) for schoolwork and programming, while reserving this laptop for power-hungry software at home.
| Acer Nitro 17 | |
| PROS | CONS |
|
|
10. Lenovo ThinkPad P16 Gen 2 – RTX 5000 Ada
Best Workstation For Engineering

Core i9-13950HX
128GB RAM
NVIDIA RTX 5000 Ada 16GB vRAM
4TB SSD NVMe
16″ UHD (3840 x 2400) TouchScreen
8 lbs
1 hours
This laptop features the famous “workstation graphics card” you’ve likely heard so much about. However, before purchasing a workstation GPU, you need to be very, very well-informed, as they are expensive and might be overkill—even if you work in the 3D CAD design department.
Hardware
First…
You need to be cautious of workstation GPUs that are too weak to justify their high price tags. It is very common to find overpriced workstation GPUs, and some of them even perform worse than budget gaming laptops with good old 4GB vRAM GPUs.
For example, it’s not unusual to find a workstation GPU like the P1000 on a laptop costing more than a laptop with a 1650GTX, despite the latter offering more GPU power for 3D modeling tasks.
Below is a very useful table to compare the hardware (GPUs) in workstation laptops to understand their price-to-performance ratio. You can do this by noting the ‘consumer’ GPU equivalent. For instance, RTX 3000 laptops sell for around $2000–$2500, yet you can find laptops with 6GB vRAM GPUs like the 2070RTX or 4050RTX selling for $1000.
| Workstation GPU | Consumer Equivalent | Cores/Shaders | Clock Speed | vRAM |
| RTX 3000 | 2070RTX+ | 1280 | 1380 | 6GB |
| RTX 4000 | 2070/2080 | 2560 | 1560 | 8GB |
| RTX 5000 | 2080RTX+++ | 3072 | 1350 | 16GB |
| RTX A2000 | ~3050Ti | 2560 | 1200 | 4GB |
| RTX A3000 | ~3060RTX | 4096 | 1560 | 6GB |
| RTX A4000 | ~3070RTX | 5120 | 1560 | 8GB |
| RTX A5000 | ~3080RTX | 6144 | 1695 | 16GB |
| RTX A5500 | ~3080Ti | 7424 | ??? | 16GB |
| RTX Ada 3500 | ~4070RTX | 8GB | ||
| RTX Ada 4000 | ~4080RTX | 12GB | ||
| RTX Ada 5000 | ~4090 RTX | 9728 | 16820 | 16GB |
Does this mean all workstation GPUs are useless because their ‘gaming’ GPU equivalents are cheaper? Not necessarily. To understand the real difference, let’s check out their performance:
Performance
While it’s true that workstation GPUs are tailored for 3D modeling work, most engineers—especially 3D CAD engineers—may not find them particularly useful. It’s a very broad topic that might require a dedicated post, but in summary, they are only beneficial when working with very, very complex and large 3D models.
To give you an example, take a look at the picture below:
The model above can be handled easily by the Acer Nitro 5 with its 6GB vRAM, though you might experience some lag and occasional artifacts while using the viewport. The difference is that a workstation GPU like the RTX 5000 Ada will provide much greater stability while drawing and navigating the viewport. There will be significantly less lag compared to gaming GPUs, and no artifacts at all.
That said, you don’t need to purchase a laptop with the RTX 5000 Ada GPU, which is excessively expensive. A workstation GPU with 6GB vRAM, as shown in the table, will deliver comparable performance for the model above.
The RTX 5000 Ada only becomes essential when working with models that are five times more complex and larger than the one shown above. But let’s be honest—that’s a rare scenario for most engineers.
In summary, here are the instances where you should consider buying a laptop like this one:
- When working at a company with a consumer GPU (even one with 16GB vRAM) but still experiencing lag while using the viewport.
- To minimize lag as much as possible when dealing with very large models (1000–5000 parts).
- To eliminate errors and artifacts for a smoother, more accurate design workflow.
- To unlock plugins and features that are only supported with workstation GPUs. (For a list, check your software’s official website.)
| Lenovo ThinkPad P16 Gen 2 | |
| PROS | CONS |
|
|
How To Buy The Best Laptop For Engineering
In this section we’re going to go over a typical engineering curriculum, take example projects, revisit the software used for said project and talk about the hardware required for it.
Before we get to that though..
The Engineering Department
Check your engineering department’s website and head over to the IT section for the following:
Computer Labs
Chances are, no in fact, I am 100% sure there is at least TWO labs which have dozens of computers with powerful hardware and all the engineering software you’ll need already installed in your school.
I would 100% recommend you use the labs for those ‘hardware demanding’ projects which as you’ll see in this section is limited to perhaps ONE per year. Then buy and use ANY laptop of your liking for homework, programming, designing. Since those tasks do not require anything more than a cheap laptop you can focus on laptop’s form factor and weight.
Note that im not saying you use the labs only and not use a laptop while in school. You will obviously need a laptop to write papers, program, design, research, do homework. Just don’t focus on power so much.
Remote Access
Did you know, you may not even have to go to the lab when those ‘hardware core engineering projects’ show up? A lot of departments now have the remote access feature which as the name implies will let you access these computers remotely.
All you need is a laptop that has an internet connection. Yes, you can even run and design 3D models through remote access.
As for the internet connection, a good basic internet connection should give you NO LAG when hovering over the tools or dragging polygon lines to draw. If your project requires a LOT of precision when drawing, then if your internet connection isn’t good enough you may just have to head over to the lab.
The Engineering Curriculum
With that said let us see how the typical curriculum looks and dig in deeper into each of the classes that require an engineering software.
We won’t be able to do this for every engineering field so we’ll just pick one.
I’ve decided to pick the MECHANICAL curriculum because it is the MOST versatile in terms of software.
In other words, mechanical engineers have to run circuits, program , design with different types of 3D CAD software and so on.
If you are interested in knowing what your curriculum looks like, check the following links.
Aerospace & Aeronautical
Chemical
Civil
Electrical
Computer
Software
Mechanical
| MECHANICAL ENGINEERING | |
| Freshman Year | |
| Fall Semester
Chemistry I Calculus I Social Science Core Class English Core Class Linear Algebra |
Spring Semester
Physics I Calculus II Introduction to Programming Engineering Graphics English Core Class II |
| Sophomore Year | |
| Fall Semester
Physics II Calculus III Creative Decisions and Design Engineering Materials Statics |
Spring Semester
Circuits and Electronics Differential Equations Computing Techniques Dynamics of Rigid Bodies Social Science Elective |
| Junior Year | |
| Fall Semester
Instrument & Electronics Lab Mechanics of Deformable Bodies Thermodynamics Fluid Mechanics Economics Humanities Elective |
Spring Semester
System Dynamics Heat Transfer Experimental Methods Lab Engineering Economics Statistics and Applications Social Science Elective |
| Senior Year | |
| Fall Semester
Machine Design Design, Materials and Manufacture ME Systems Lab Elective Elective |
Spring Semester
Senior Design Project ME Elective Humanities Free Elective Free Elective Free Elective |
The following are the most commonly used software for EACH of these classes. How do I know? I’ve taken these classes but if you still don’t believe me you can download the curriculum of each of these classes by heading over to your professor’s website for the course.
I know this is the mechanical engineering curricula but as you’ll find out sooner or later. Electrical , Aeronautical , computer engineers will use a combination or variation of the following too.
It’s only civil engineers and chemical engineers that ones not usingLabView & Mobile Studio/DAQ Board software because those are for circuit design and testing but will definitely use all the rest (especially CAD Software).
| Course | Software |
| Introduction to Computing | MatLab |
| Engineering Graphics | CAD Software (Ex: AutoCAD) |
| Calculus III | MatLab |
| Creative Decisions and Design | Optional 3D design software |
| Circuits and Electronics | LabView |
| Computing Techniques | MatLab |
| Instrument & Electronics Lab | Mobile Studio / DAQ Board software |
| Experimental Methods Lab: | C++, Matlab, Excel |
Additional engineering software for each field
If you go a step further like I recommended, these are basically a summary of very niche software for each engineering field.
| Major | Software |
| Electrical & Computer | CAD Electrical, SPICE, LabView |
| Chemical | MatLab, Excel, MathCad, ChemCad |
| Aeronautical & Aerospace | CATIA, SolidWorks, ANSYS, MatLab |
| Civil | Civil 3D, Revit |
| Mechanical | SolidWorks, Inventor, ANSYS, MatLab |
Hardware Requirements For Engineering Student Software
Finally, here are the hardware requirements. If you are a beginner in computer terminology check my posts on beginner guide to laptop/computer specs.
| Software | CPU | RAM | GPU | Comments |
| MatLab & Mathcad | Any Intel or AMD | 8GB RAM | Integrated. Dedicated is optional |
A dedicated GPU will speed up extremely intensive simulations. However only graduate students or researchers run those projects. |
| Mobile Studio / LabView | Any CPU even celeron & pentium | 1GB RAM | —- | You will need to buy a USB to serial port adapter so you can plug in a data acquisition system. |
| Programming languages (C++) | Any CPU | 8GB RAM | — | High-end CPUs are only useful for very intensive data science calculations and such. |
| Excel | Any CPU | 8GB RAM | — | You only need to add more RAM if you have to process a lot of data, again only grad students and researchers MIGHT come across this issue. |
| ASPEN, ChemCAD, Electrical CAD
|
Any CPU | 8GB RAM | — | No need for dedicated (discrete) GPU. Even 3D models run fine with integrated graphics. |
| 3D CAD (Revit, Civil 3D, SolidWorks, Inventor, CATIA) | Quad Core CPU | 8GB RAM | 4GB vRAM GPU |
4GB vRAM GPUs would be the maximum for engineering students. |
| CAE ( ANSYS ) | i5 or i7 processor 8GB RAM 1GB vRAM |
Workstation GPU | Although the site says workstation GPU that’s only required for working engineers. Students can use a simple discrete GPU and may not even run into ANSYS while in school. |
Now let’s talk about each computer spec and how it relates to 3D modeling & engineering software. Please keep in mind that the following needs a bit of computer knowledge. Be sure to read my guide on computer specs for beginner.
1. CPU (Processor)
You’ve seen above most engineering software have no special requirements for a CPU.
That’s because most of the software are basically about 2D graphcs which are just simple low-data images that even your phone can display images. Programming is just basically typing text (code) for calculations which your phone can do as well.
3D Modeling CPUs
The issue starts when you deal with 3D models and graphics. Those are going to be significantly more hardware demanding because rendering objects with all physical laws means there’s a LOT of data to be calculated.
That doesn’t mean you have to get a CPU from NASA because your phone can ALSO render 3D objects, that just means you need to a slightly faster than average CPU.
Windows 11 & 12
Also take into consideration that Windows 10 or Windows 11 and Windows 12, takes a lot of resources too. In fact, that is an equally important consideration when picking up a CPU. NOT ALL CPUs can run Windows fast enough to have a decent workflow!
All of the following listed CPUs work equally fast for the full version of Windows. The difference between these is their performance for engineering software:
Intel CPUs
CPU
Base (P)
Turbo (P)
Cores (P/E)
i3 8130U
2.2
3.4
2
i3 8145U
2.1
3.9
2
i3 1050G1
1.2
3.4
2
i3 10100U
2.1
4.1
2
i3-1115G4
3
4.1
2
i3 1215U
3.3
4.4
2/4
i3 1315U
3.3
4.5
2/4
i5 8265U
1.6
4.9
4
i5 8250U
1.6
3.4
4
i5 1115G4
2.4
4.2
4
i5 8300H
2.3
4
4
i7 8550U1.844
i5 1235U3.34.410
i7 1165G72.84.74
i5 1240P3.34.412
i5- 9300H
2.4
4.1
4
i5- 10300H
2.5
4.5
4
i5-11300H
2.6
4.4
4
i5 11260H
2.6
4.4
6
i7 8750H
2.2
4.1
6
i5 12450H
3.3
4.4
8
i5 12500H
3.3
4.5
8
i5 13420H
1.5
4.6
8
i5 13500H
1.9
4.7
6+8
i5 14500H
1.9
4.5
6+8
i7 9750H
2.6
4.5
6
i7 10750H
2.6
5
8
i7-11375H
3.3
5
4
i7 1260P
3.4
4.7
12
i7-11370H
3.3
4.8
4
i7-11800H
3.3
5.0
6
i9 8950K
2.9
4.8
6
i9 9900K
3.6
5.1
8
i9-11900H
2.5
4.9
8
i9 10890K
2.4
5.3
8
i9-11980HK
3.3
5
8
i7 14700HX
3.9
5.5
6+8
i9-14900HX
4.1
5.8
(8P + 16E)
*P=performance Core E=efficient Core
AMD CPUs
| CPU | Max Speed | Cores(Threads) |
| Ryzen 9 8945HS | 5.2 | 8 – 16 |
| Ryzen 9 7940HS | 5.2 | 8 – 16 |
| Ryzen 9 6980HX | 5 | 8 – 16 |
|
Ryzen 9 6900HS
|
4.9
|
8 – 16 |
| Ryzen 7 8845HS | 5.1 | 8 – 16 |
| Ryzen 7 7840HS | 5.1 | 8 – 16 |
| Ryzen 7 7745HX | 5.1 | 8 – 16 |
| Ryzen 7 6800HS | 4.7 | 8 – 16 |
| Ryzen 7 6800H | 4.7 | 8 – 16 |
| Ryzen 9 5900HX | 4.6 | 8 – 16 |
| Ryzen 9 4800HS | 4.4 | 8 – 16 |
| Ryzen 7 5800H | 4.4 | 8.- 16 |
| Ryzen 7 4800H | 4.2 | 8 – 16 |
| Ryzen 5 7535HS | 4.55 | 6-12 |
| Ryzen 5 6600H | 4.5 | 6-12 |
| Ryzen 5 5600H | 4.2 | 6 – 12 |
| Ryzen 5 4600H | 4.0 | 6 – 12 |
| Ryzen 5 3550H | 3.7 | 4 – 8 |
| Ryzen 5 7530U | 4.5 | 6-12 |
| Ryzen 5 3500U | 3.7 | 4 – 8 |
| Ryzen 5 7320U |
4.1 | 4 – 8 |
| Ryzen 3 5300U | 3.8 | 4 – 8 |
| Ryzen 3 4300U | 3.7 | 4 – 8 |
| Ryzen 3 3300U | 3.5 | 4 – 8 |
Pink & Orange: Overkill for engineering students unless you want to play games at very high settings. Useful for graduate school projects and working engineers though.
Green: Fine choices for all degrees. If you want to run 3D modeling software, then make sure you pick a Ryzen 5 or Core i5 from this group (Avoid 7th generation Ryzen CPUs due to lower graphics performance).
Blue: These are usually found on laptops that have more ‘GPU power’ (discrete graphics) hence I’d only recommend these to engineering students who want to focus on 3D modeling projects (electives and such). We’ll talk more about this in the next GPU section.
2. GPU (Graphics Card)
The most important hardware of this entire post and the reason why most of you are even reading this section.
Q: Who needs discrete GPUs? Should I spend money on them?
Short Answer: Mechanical, Civil and Aeronautical engineering students MIGHT need a dedicated GPU. The rest only need to focus on CPU.
Long Answer: As you probably know there are two types of graphics cards: integrated and dedicated GPUs, the integrated comes by default on every laptop and the dedicated is an additional piece of hardware that usually adds hundreds of dollars to the overall cost.
Both can run 3D modeling software. However, the 3D models that “3D Engineers” like Mechanical and Civil work with are a bit more complex AND bigger thus there MAY be a need for dedicated graphics if they want a quicker workflow with such projects (integrated graphics can run them too but viewport will be slow).
Keep in mind, though, that there’s only a few times during your five years in engineering school you’ll come across these projects and you have the option to use the LAB!
Thus whatever your engineering field is investing money on a dGPU for engineering school is ALWAYS optional.
Q: What about workstation GPUs? Are they better?
Below you can see a regular “consumer” or “gaming” graphics card running one of the most hardware demanding 3D CAD Software: Solidworks.
In fact,
Integrated graphics from recent and powerful CPUs can run Solidworks just fine too as shown below:
The model below above is quite big and yet there seems to be no issues. You will see models below that level of complexity, much less complex probably, in engineering school. This is why Im telling you over and over workstation GPUs or even spending too much money on computer power is just a waste of time and only OPTIONAL.
Recommended Graphics Cards
Now if you do want to run 3D modeling simulations on your laptop with ZERO LAG during your stay in college (which is understandable if you are a mechanical or civil engineer), then discrete graphics do become somewhat useful. You should avoid those in red because their performance is too low despite being dedicated GPUs:
| NVIDIA | Cores | vRAM | Speed |
| MX 350 | 640 | 2-4GB | 1354 |
| MX 450 | 896 | 2-4GB | 1580 |
| 1050 | 640 | 2GB-4GB | 1493 |
| 1050 Ti | 768 | 4GB | 1620 |
| 1650 | 1024 | 4GB | 1560 |
| 3050Ti | 2560 | 4GB | 1485 |
| 2050 | 2048 | 4GB | 1477 |
There are far more GPUs useful from other brands like AMD and older versions of the ones presented here but they’re all rare to find. The ones on the table are the most popular ones.
Who needs a Workstation laptop then?
Probably nobody reading this.
If you are going to graduate school or eventually work in the field , the chances that you’ll need a workstation laptop or GPU are very very low.
Most engineers dealing with 3D work (civil, mechanical) will still be fine with a 4GB vRAM dedicated GPU.
You will only need a workstation GPU or laptop IF your job is focused on 3D modeling products , objects , carc, etc, for simulation and testing purposes. In fact, even then you will probably do just fine with a 6GB vRAM dGPU such as the ones shown below:
| Name | Cores | vRAM | Speed |
| 1060 | 1280 | 6GB | 1670 |
| 1660 Ti | 1536 | 6GB | 1590 |
| 2060 | 1920 | 6GB | 1680 |
| 3060 | 3584 | 6GB | 1780 |
| 4050 | 2560 | 6GB | 2370 |
Only a small subset of actual engineers will need the workstation GPUs such as the NVIDIA Quadro and AMD FirePros mostly because they need to unlock special features only available on workstation graphics or because they need to work with MUCH MUCH bigger objects (think about a simulation that has 1000-10 000 parts all interacting with each other) and not just any workstation GPU but rather a workstation laptop with lots of vRAM.
3. RAM (Random Access Memory)
FAR more important than graphics card (since most modern processors are way too fast & graphics cards are not a concern for engineering projects since is school).
RAM is where SOFTWARE, the operating system and everything else running in your computer will be temporarily stored. Since speed is rarely an issue, it is RAM the most common bottleneck especially for 3D CAD software.
If you don’t have enough everything will be slow. A slow computer means a slow workflow and you don’t want that during finals week or just before finals where it’s more likely to lack RAM due to the amount of chrome tabs + software you’ll have open all at the same time .
4GB: This is not enough for the simple reason that Windows 10 and Windows 11 take at least 3.5GB that means you will only have 500MB left for the the engineering software running in the background in a typical day (an IDE for programming + LabView) and let’s not forget you’ll probably be using youtube and browsing around the web too.
8GB: This is the bare bone minimum for a fast workflow, there’s almost zero chance you’ll need more. Even 3D modeling, the most hardware demanding software, will run just fine with 8GB RAM again because engineering students only work with small sized models .
16GB: I like 16GB RAM because the amount of programs I run simultaneously can get pretty insane. Good news is that you don’t need to get 16GB on a laptop, you can just get 8GB (which most modern laptops have) then upgrade it to 16GB later. I have a tutorial here on how to upgrade RAM here, it’s quick, cheap and easy.
4. Storage (SSD vs HDD)
Im sure you’ve heard of the term SSD and HDD. The former stands for Hard Disk Drive and the latter for Solid State Drive. I’m pretty sure you also know that Solid State Drives are the fastest storage devices now. What you probably didn’t know is that….
1. SSDs are available virtually on EVERY single modern laptop made within the past 3 years
2. SSDs are x5 aster than HDDs
3. There are different SSD types but they’re all equally fast for engineering student purposes.
It is pretty redundant to talk about ALL the advantages that come with a fast storage drive because you will get one anyways.
Now if you followed my advice at the start of this post and want to use your current old laptop for engineering you can do that too! If it’s too slow for you now if you can upgrade its RAM & Storage (have 16GB RAM and an SSD) it will probably be fast enough for everything even small models in 3D CAD software.
How much storage do you need?
I’d say ~256GB which is what most laptops have. If you want to install games on your laptop then you will run out of space pretty quickly but that doesn’t mean you’ll have to pick another laptop. Again you can just upgrade yours, check my tutorial on how to upgrade storage to see how easy it is.
6. Weight & Display
Weight is EXTREMELY important and you MUST find a laptop that’s lightweight if you have a high budget (they’re usually expensive).
Buying something that’s heavy only means not bringing to school and collect dusk back at your house or dorm.
Although not always the case , weight is pretty much related to how big your display is.
| Size | Weight |
| 13” | 2.5lb-3lb |
| 15” | 3.5lb-4.5lb |
| 17” | 5lb-7lb |
| 16” | 5lb |
Exceptions to the above rule are ultrabooks like the LG Gram, MacBook Pro & Surface Series. But if you want low weight on a budget machine, start looking for 13” laptops first then 15” laptops.
Display Size vs Workflow For Engineering
13”: If you are a mechanical, electrical, chemical or any type of engineering student. I would strongly advice you to invest your money on a 13” laptop. It’s going to make ALL the difference for your productivity. Laptops with the CPU & RAM size I’ve recommended that are still 13” can be very expensive though.
15”’: These laptops are way cheaper and still have the CPU & RAM size recommended. Most laptops with dedicated GPUs are this big, you are not going to find a 13” laptop with a dedicated GPU because there’s no space to fit in a dedicated GPU.
17”: Strongly advice to buy a laptop this big if you’re an actual engineer since chances are you’re not going to move around a lot and the extra screen space will massively improve your workflow as you’ll have more toolbars available and you’ll be able to see larger chunks of code at a time to follow code logic and spot bugs.
FHD vs QHD vs UHD: Resolution
Resolution will also give you extra screen space. Since high resoluton means more pixels, size of objects can be scaled down in size thus giving freeing up more screen space.
FHD: is the bare minimum for CAD work and this is virtually present on any laptop above 450 dollars or any laptop with the specifications we have talked about. It’ll be very rare for you not to get a FHD. Be sure to double check because it isn’t that uncommon to find HD or HD+ laptops which are cannot handle multiple windows as well.
QHD or UHD:They are 2k and 4k resolutions respectively. (QHD = 2x FHD ). Both will massively expand the screen space available but unfortunately they are QUITE expensive and they are RARELY found on laptops under 800. There is one model I have listed that has a QHD display around 600-700 dollars called the Lenovo Ideapad Pro 5i above.
7. Connectivity & Ports
You don’t really have to worry about what ports your laptop has because today there are adapters for just about every connection you need. You’ll need the following ports during your engineering school:
Serial port: No laptop made within the past 10 years will have this port but they are useful to connect DAQ systems (Data Acquisition Systems) which are used for circuit design & labwork. If you come across a DAQ system that only uses a serial port, you’ll just have to get this adapter.
HDMI port: These are useful to connect to external display. If you are giving a presentation you’ll need an HDMI port, most projects , if not all, only work with HDMI or ‘mini’ display ports. Again you don’t have to worry about it, just buy an adapter too.
Bluetooth: this is very very useful for engineering purposes. You can connect to many engineering devices via bluetooth and you can also share files between co-workers or colleagues with the bluetooh function. All laptops have bluetooth now.
5. Operating System
Windows vs Mac
If you are an engineering student, it doesn’t matter because although engineering software has been written for Windows the most basic ones that are used in engineering school (like AutoCAD) have a Mac Version and all programming languages work even better on a Mac.
It’s only going to be a problem for circuit design and lab software for which you may have to use Parallel’s or BootCamp. Bootcamp can be used only on older models (Pre-2020).
Comments?
If you have any questions, comments, suggestions, etc, please leave a comment below. I will reply as soon as I can. I apologize for being absent for so long but I promise I will reply ASAP now.
Author Profile
- I am physicist and electrical engineer. My knowledge in computer software and hardware stems for my years spent doing research in optics and photonics devices and running simulations through various programming languages. My goal was to work for the quantum computing research team at IBM but Im now working with Astrophysical Simulations through Python. Most of the science related posts are written by me, the rest have different authors but I edited the final versions to fit the site's format.
Latest entries
 Hardware GuideFebruary 26, 2025How to Make your Laptop Last Forever
Hardware GuideFebruary 26, 2025How to Make your Laptop Last Forever Hardware GuideFebruary 25, 2025A Beginner Guide to Reading Computer (Laptop) Specifications
Hardware GuideFebruary 25, 2025A Beginner Guide to Reading Computer (Laptop) Specifications Hardware GuideFebruary 23, 2025Laptop Buying Guide: Every Specification Explained
Hardware GuideFebruary 23, 2025Laptop Buying Guide: Every Specification Explained LaptopsFebruary 23, 2025What is a MUX Switch For Gaming Laptops? How Important is it?
LaptopsFebruary 23, 2025What is a MUX Switch For Gaming Laptops? How Important is it?


good detailed information for laptop shopping. Thanks for your information
Here i have a blog i started after purchasing a laptop after reading your guide Technology-tutor
Would you recommend the Acer E15 as a suitable alternative to the E5?
That was a typo, I fixed it thanks. Yes, the Acer 15 is fine. Make sure it has a dedicated graphics card from 940MX onwards. I have that GPU myself on one of my laptops.
what if I want to prepare for my professional career afterwards, should I go all out for laptop? Or desktop would be more preferable?
Not every engineer out there uses heavy programs like AutoCad SolidWorks Catia, etc. And if your
job requires you to do so, the company will provide you with computers far more powerful or even go as far as giving you money to buy your own set up. I know this from experience.
But if you do want to become an expert with any of these programs and start practicing with CAD/CAE programs right now a desktop would be more preferable. A laptop is useful for the small projects you’ll have to do during engineering school.
What If I was going into mechanical engineering and was going to buy the new Razer blade stealth 8th gen i7 with 16gig ram and integrated hd 620 graphics, but I also bought the eGPU with a GTX 1070 that I can have in my dorm room that I can plug into the laptop and have a dedicated gpu? Would this work for heavier solid works projects or is it over kill?
That’s not a bad idea at all ! if your choosing the razer blade for portability you are better off with the Surface Book 2 (unless you plan on gaming with the razer).
GTX 1070 is overkill pretty much for anything….I dare to say even gaming.
I doubt you’ll see “heavy solidwork projects” as an undergrad and even if you do, you’ll be better off heading to the lab. You don’t want to work on a huge project with thousands of parts on a 12” screen.
This is a good advice, but i’m quite doubtful on my program. I am studying electrical engineering. In my autocad we were taught to make a 3d model. Btw, electronics is separate in my program. I was planning on getting laptops with gtx series because of the possibility of using autocad in my majors and the 3d model. But after reading your advice, i’m now thinking of getting ultrabooks with the mx150 and i5 8****u or i7 8****u other than the i5 8300h with gtx1050. The mx150 ones are quite light than the i5 8300h which has gaming in their name. Thinking of getting the dell g7 before but now thinking of inspiron 15 or asus s15.
AutoCAD is the weakest 3D modeling software out there, you could even get away with an integrated card. The MX150 is more than sufficient for undergrad courses and you can even use it after you graduate.
As for me, I’m steering away from engineering and starting my phD in Physics this spring and I’m all for the surface Pro 4. You can use AutoCAD in it no problems plus you get to take notes (this is super useful for me) and share your notes/solutions on discord/whatsapp/web etc in a flash.
If you have the cash get the surface pro, this is enough for an EE student (you get portability + power). If you can’t afford the Pro, definitely get the MX150 laptop if you are dealing with autocad in 3D.
Thanks for the reply. I took your advice. I aimed for something light. Surface devices are scarce in my market. I bought the hp envy 13, i5 8250u with mx150, 8gb ram. Just going to have a dongle with me when i’m in need of hdmi or vga port. I’d say the cad is not much important at the moment or will not. Currently dealing with matlab.
Hi, I want to say a big thank you for this article. It is both elaborate and thoughtful in content, which is helpful for me as a first-generation college student planning on doing CE. Navigating everything on my own is quite challenging already, but your advice and extensive knowledge have made it a bit easier for me.
No problem!