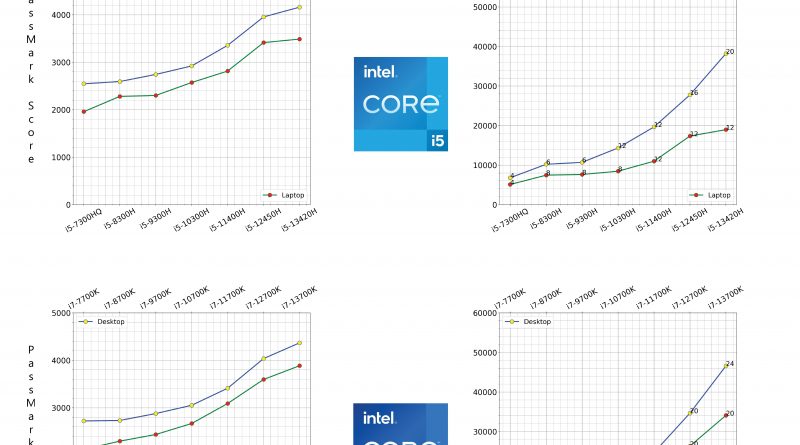
Intel CPU Generations Performance Comparison – 2025
We’ll use “passmark scores” as benchmarks in order to give you a general idea of the performance differences between Intel Core CPU generations.
Passmark benchmarks use several thousands of benchmarks taken from different rigs all over the world.
The full summarized CHART is shown below but a detailed and zoomed in analysis of each section follows after.
Update 2025: The 14th generation CPUs are out. The graph will soon be updated to include 14th gen Intel Core CPUs (i7 and i9). But note that there isn’t 14th gen Core i5 and Core i3 CPUs as of May 2025 yet.
🎯 Just want a shortlist of laptops with the best CPU performance/money ratio?
👉 Click here to check out the best core i3 laptops & the best core i5 laptops as of 2025.
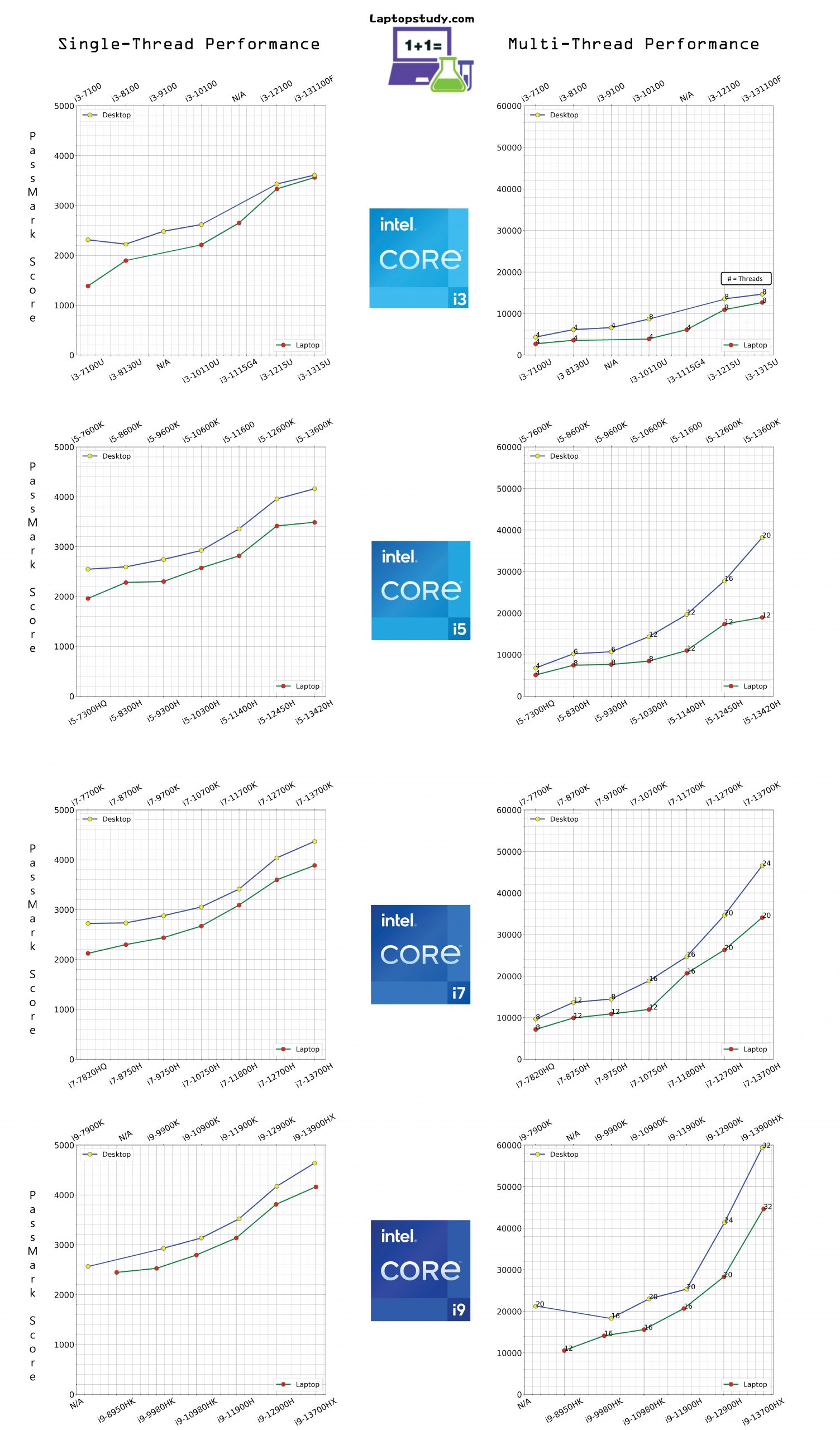
Intel Core i3 Generations Comparison
| CPU | Cores | Threads | Lowest Speed | Highest | Cache |
| Core i3 7100U | 2 | 4 | — | 2.4 | 3MB |
| Core i3 8130U | 2 | 4 | 2.2 | 3.4 | 4MB |
| Core i3 10110U | 2 | 4 | 2.1 | 4.1 | 4MB |
| Core i3 115G4 | 2 | 4 | 3 | 4.1 | 6MB |
| Core i3 1215U | 6 | 8 | 3.3 | 4.4 | 10MB |
| Core i3 1315U | 6 | 8 | 3.3 | 4.5 | 10MB |
| CPU | Cores | Threads | Lowest Speed | Highest | Cache | RAM |
| Core i3 7100 | 2 | 4 | — | 3.9 | 3MB | DDR4-2400 |
| Core i3 8100 | 4 | 4 | — | 3.6 | 6MB | DDR4-2400 |
| Core i3 9100 | 4 | 4 | 3.6 | 4.2 | 6MB | DDR4-2400 |
| Core i3 10100 | 4 | 8 | 3.6 | 4.3 | 6MB | DDR4-2666 |
| Core i3 12100 | 4 | 8 | 3.3 | 4.3 | 12MB |
DDR5 4800MT/s
|
| Core i3 13100 | 4 | 8 | 3.4 | 4.5 | 12MB |
DDR5 4800MT/s
|
Single-Thread Benchmarks
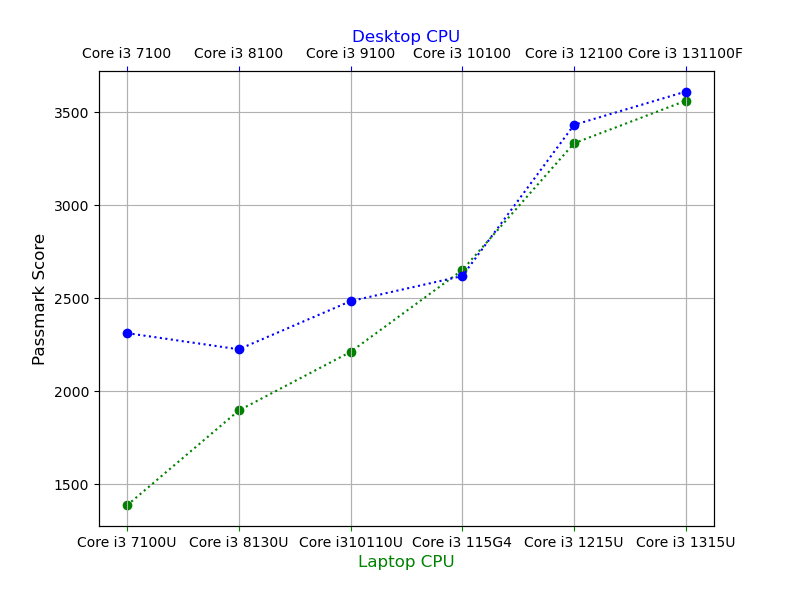
- The second biggest peroformance jump is from the 10th to 12th generation CPUs for laptops (25% increase) and 10th to 12th gen for desktops (31% increase).
- This does not SEEM to be due the higher clock speed of 12th gen CPUs (clock speed gains aren’t significant) but rather the addition of +4MB of Cache Memory (6MB vs 10MB) and the ability of 12th generation CPUs to support DDR5 RAM.
- The highest performance gain for laptops is from 7th gen to the 8th gen.
- The 8th gen laptop Core i3 CPU is 36% faster.
- There’s a small increase in cache size but a large increase in clock speed (~+1GHz).
- There’s only a 7% performance gain from the 12th to 13th gen for laptops and 5% for dekstops.
- There’s only slight increase in clock speeds between these two generations.
- Cache size is the same as well as RAM speeds.
Multi-Thread Benchmarks
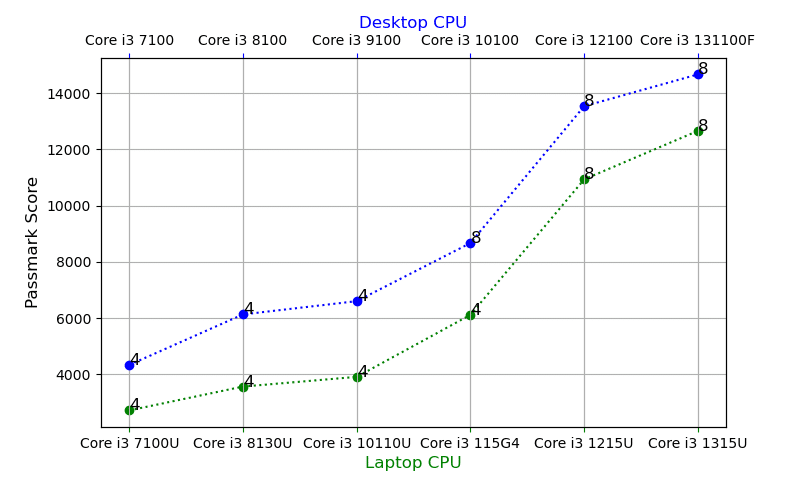
- The greatest performance increase is seen with 12th gen Core i3 CPUs.
- There’s a 56% increase for desktops (10th to 12th) and 80% for laptops (11th to 12th).
- The performance jump seems to be due to clock speed performance of the extra cores since the number of threads is the same.
Intel Core i5 Generations Comparison
| CPU | Cores | Threads | Lowest Speed | Highest | Cache | RAM |
| Core i5-7300HQ | 4 | 4 | 2.5 | 3.5 | 6MB | DDR4-2400 |
| Core i5-8300H | 4 | 8 | 2.3 | 4 | 8MB | DDR4-2666 |
| Core i5-9300H | 4 | 8 | 2.4 | 4.1 | 8MB | DDR4-2666 |
| Core i5-10300H | 4 | 8 | 2.5 | 4.5 | 8MB | DDR4-2933 |
| Core i5-11400H | 6 | 12 | 2.7 | 4.5 | 12MB | DDR4-3200 MT/s |
| Core i5 12450H | 8 | 12 | 3.3 | 4.4 | 12MB | DDR5 4800 MT/s |
| Core i5 1315U | 8 | 12 | 3.4 | 4.6 | 12MB | DDR5 5200 MT/s |
| CPU | Cores | Threads | Lowest Speed | Highest | Cache | RAM |
| Core i5 7600K | 4 | 4 | 3.8 | 4.2 | 6MB | DDR4 2400 |
| Core i5 8600K | 6 | 6 | 3.6 | 4.3 | 9MB | DDR4-2666 |
| Core i5 9600K | 6 | 6 | 3.6 | 4.3 | 9MB | DDR4-2666 |
| Core i5 10600K | 6 | 12 | 4.1 | 4.8 | 12 MB | DDR4-2666 |
| Core i5 11600K | 6 | 12 | 3.9 | 4.9 | 12 MB | DDR4-3200 |
| Core i5-12600K | 10 | 16 | 3.7 | 4.9 | 20MB | DDR5 4800 MT/s |
| Core i5-13600K | 14 | 20 | 3.5 | 5.1 | 20MB | DDR5 5600 MT/s |
Single-Thread Benchmarks
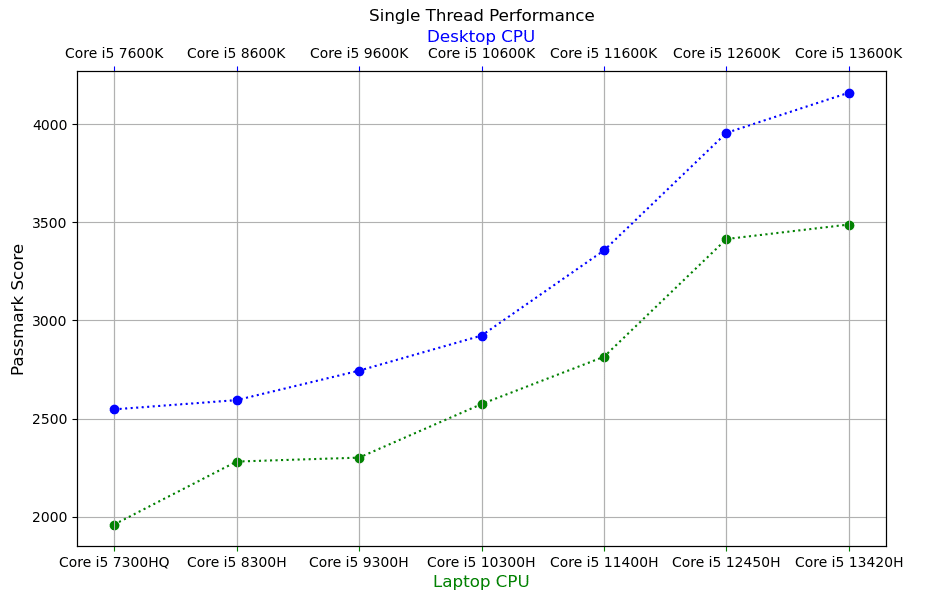
- There’s MINIMAL performance gains from the 12th to 13th generation laptop CPUs
- The Core i5 11400H & i5 12450H CPUs almost the same boost clock speed (4.4GHz vs 4.5GHz) yet the 12th gen CPU is 21% faster.
- This is due to the ability of the 12th Core i5 to maintain a higher average clock speed that’s closed to the maximum advertised number. Also, the ability to support DDR5 RAM.
- This is the biggest performance jump between adjacent generations.
- The lowest performance jumps for Core i5 laptop CPUs are from the 8th to 9th generation AND from the 12th to the 13th gen.
- The second biggest performance jump is from the 10th to the 11th generation: 10% for laptops and 14% for desktops.
- There’s a significant increase in CACHE MEMORY and a slight increase in RAM speed.
Multi-Thread Benchmarks
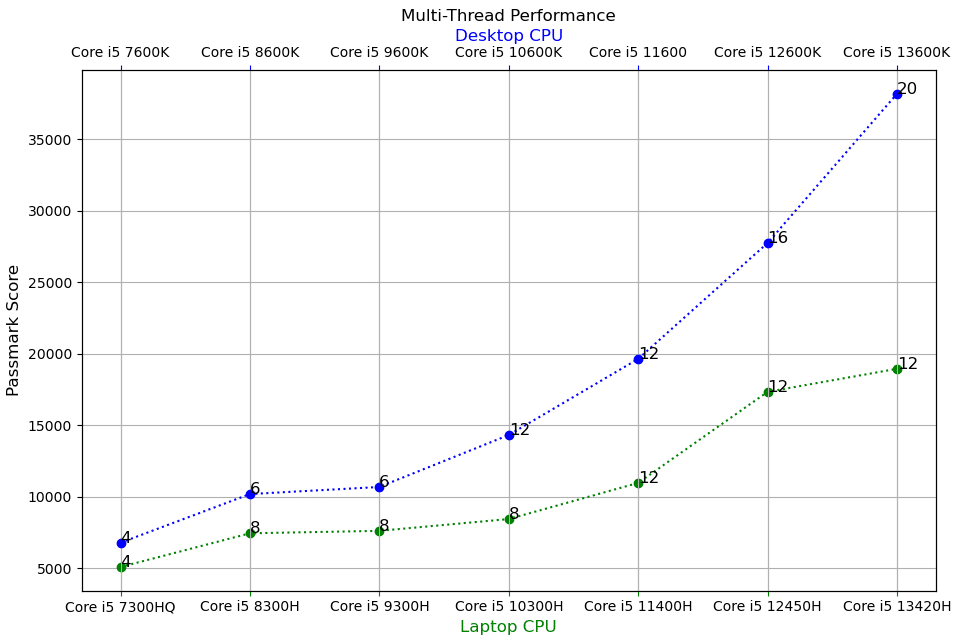
- The biggest performance jump is from the 11th to the 12th generation.
- For laptops, multicore performance increases by 58%.
- For desktops, performance incrases by 41%.
- Unlike the single-thread benchmarks, there’s a significant bump (37%) in multicore performance from the 12th to the 13th for DESKTOPS.
Intel Core i7 Generations Comparison
| CPU | Cores | Threads | Lowest Speed | Highest | Cache | RAM |
| Core i7-7820HK(HQ) | 4 | 8 | 2.9 | 3.9 | 8MB | DDR4-2400 |
| Core i7- 8750H | 6 | 12 | 2.2 | 4.1 | 9 MB | DDR4-2666 |
| Core i7- 9750H | 6 | 12 | 2.6 | 4.5 | 12MB | DDR4-2666 |
| Core i7-10750H | 6 | 12 | 2.6 | 5 | 12MB | DDR4-2933 |
| Core i7-11800H | 8 | 16 | 2.3 | 4.6 | 24MB | DDR4 -3200 MT/s |
| Core i7-12700H | 14 | 20 | 3.5 | 4.7 | 24 MB | DDR5 4800 MT/s |
| Core i7-13700H | 14 | 20 | 3.7 | 5 | 24MB | DDR5 5200 MT/s |
| CPU | Cores | Threads | Lowest Speed | Highest | Cache | RAM |
| Core i7-7700K | 4 | 8 | 4.2 | 4.5 | 8MB | DDR4-2400 |
| Core i7-8700k | 6 | 12 | 3.7 | 4.7 | 12 MB | DDR4-2666 |
| Core i7-9700k | 8 | 8 | 3.6 | 4.9 | 12 MB | DDR4-2666 |
| Core i7-10700K | 8 | 16 | 3.6 | 5 | 16 MB | DDR4-2933 |
| Core i7-11700K | 8 | 16 | 3.6 | 5 | 16 MB | DDR4-3200 |
| Core i7-12700K | 12 | 20 | 3.6 | 5 | 25MB | DDR5 4800 MT/s |
| Core i7-13700K | 16 | 24 | 3.4 | 5.4 | 30MB | DDR5 5600 MT/s |
Single-Thread Benchmarks
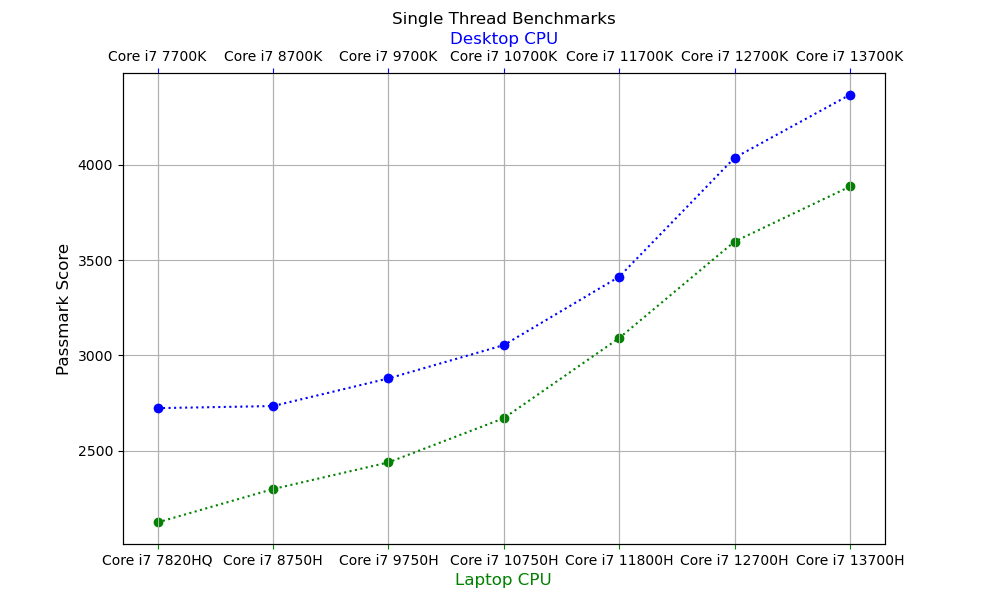
- There are SIGNIFICANT performance jumps from the 11th to the 12th and 13th generations.
- The biggest performance gains are from the 11th to the 12th generation: 12% gains for laptops, 15% for desktops.
- The second biggest performance jumps are from the 10th to the 11th gen: 11% increase for desktops, 15% for laptop CPUs.
- The performance gains from the 12th to the 13th gen are: 8% for laptops, 8% for desktops.
- There are no significant performance gains from the 7th to the 10th generation desktop CPUs.
Multi-Thread Benchmarks
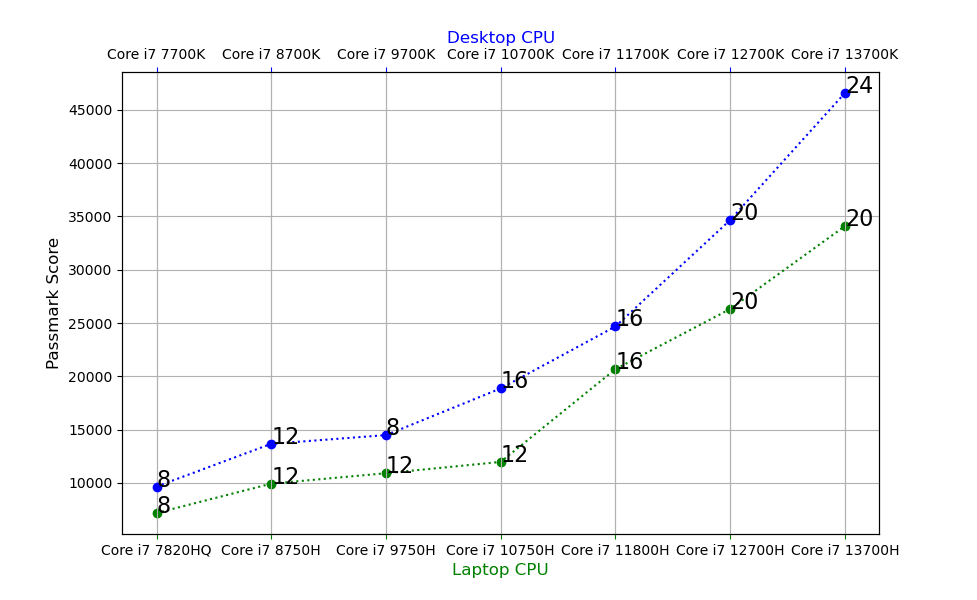
- For desktops, the biggest performance increase is from the 12th to the 13th generation: 34% gains for desktop CPUs & 30% increase for laptop CPUs.
- For laptops the biggest inrease is from the 10th to the 1th gen: 72% multicore performance gains.
- This is due to the number of threads going from 12 to 16.
Intel Core i9 Generations Comparison
| CPU | Cores | Threads | Lowest Speed | Highest | Cache | RAM |
| Core i9-8950HK | 6 | 12 | 2.9 | 4.8 | 12MB | DDR4-2666, |
| Core i9-9980HK | 8 | 16 | 2.4 | 5 | 16MB | DDR4-2666 |
| Core i9-10980HK | 8 | 16 | 2.4 | 5.3 | 16MB | DDR4-2933 |
| Core i9-11900H | 8 | 16 | 2.5 | 4.9 | 24MB | DDR4-3200 MT/s |
| Core i9-12900H | 14 | 20 | 3.8 | 5 | 24 MB | DDR5 4800 MT/s |
| Core i9-13900HX | 24 | 32 | 3.9 | 5.4 | 36MB | DDR5 5600 MT/s |
| CPU | Cores | Threads | Lowest Speed | Highest | Cache | RAM |
| Core i9-7900X | 10 | 20 | 3.3 | 4.5 | 13MB | DDR4-2666 |
| Core i9-9900K | 8 | 16 | 3.6 | 5 | 16MB | DDR4-2666 |
| Core i9-10900K | 10 | 20 | 3.7 | 5.3 | 20MB | DDR4-2933 |
| Core i9-11900K | 10 | 20 | 3.5 | 5.3 | 16MB | DDR4-3200 |
| Core i9-12900K | 16 | 24 | 3.2 | 5.2 | 30MB | DDR5 4800 MT/s |
| Core i9-13900K | 24 | 32 | 3 | 5.8 | 36MB | DDR5 5600 MT/s |
Single-Thread Benchmarks
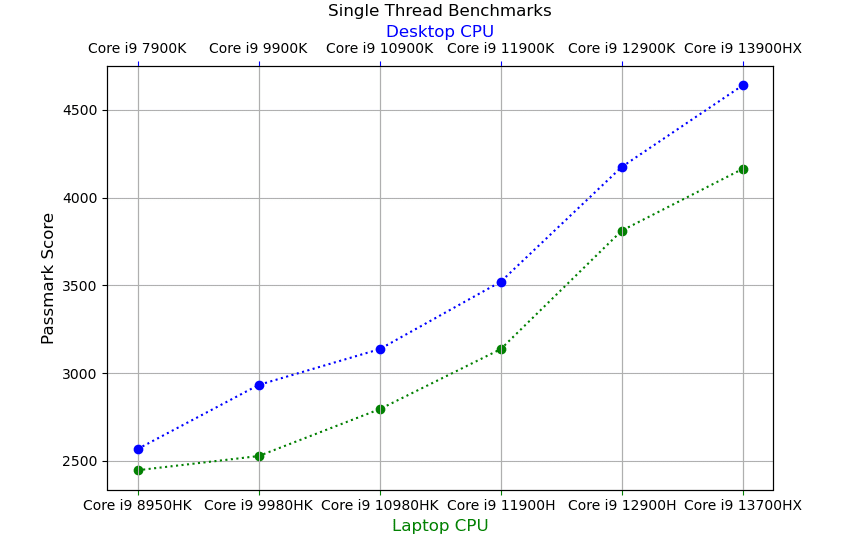
- The biggest performance jumps are from the 11th to the 12th generation.
- For desktops: and for laptops:
- The performance jump from the 12th to the 13th generation is the second most significant.
- For desktops:
- For laptops:
- The amount of clock speed increase in Core i9 CPUs in this interval is HUGE: 0.4GHz (laptops) and 0.6GHz (desktops).
- Cache Size increases by 12MB (laptops) and 6MB (desktops).
- There’s also support for faster DDR5 RAM.
Multi-Thread Benchmarks
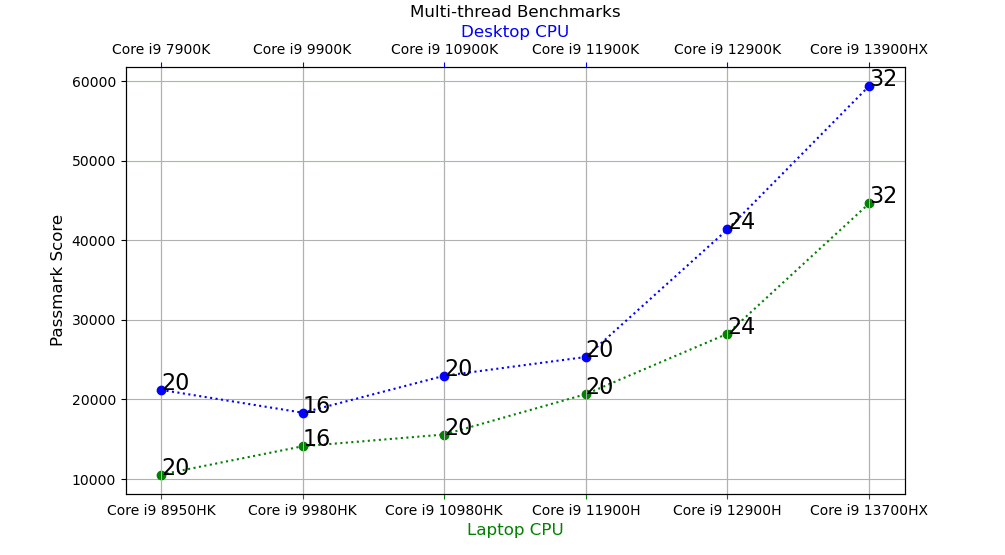
- The biggest multicore performance gains are from the 12th to 13th generation.
- For laptops, 8 more threads are added which inreases performance by 57%.
- Likewise for desktops, 8 more threads (total of 32) increasing performance by 43%.
- Multi-core performance from the 8th to the 11th generation for both desktops and laptops are not SIGNIFICANT.
- There’s only an 8% performance increase across FOUR generations!
Author Profile
- I am physicist and electrical engineer. My knowledge in computer software and hardware stems for my years spent doing research in optics and photonics devices and running simulations through various programming languages. My goal was to work for the quantum computing research team at IBM but Im now working with Astrophysical Simulations through Python. Most of the science related posts are written by me, the rest have different authors but I edited the final versions to fit the site's format.
Latest entries
 wowDecember 18, 20255 Best Laptops For World of Warcraft – Midnight & Classic (2026)
wowDecember 18, 20255 Best Laptops For World of Warcraft – Midnight & Classic (2026) LaptopsDecember 17, 2025The 4 Best Laptops For Virtualization of 2026 (10-50 VMs ATSM)
LaptopsDecember 17, 2025The 4 Best Laptops For Virtualization of 2026 (10-50 VMs ATSM) Hardware GuideDecember 17, 20252026 Beginner Guide to Reading Computer (Laptop) Specifications
Hardware GuideDecember 17, 20252026 Beginner Guide to Reading Computer (Laptop) Specifications LaptopsJune 30, 2025Best Laptops for Computer Science (July 2025 )
LaptopsJune 30, 2025Best Laptops for Computer Science (July 2025 )