Best Laptops For Interior Design in 2025
So, you’re looking for the best laptop for interior design because:
- You’re in your second year of interior design school
OR - You just joined a company and need an upgrade from that ancient rig you’ve been using
Let’s get straight to it: you’ve probably done a ton of research and realized the graphics card is the main factor. And yeah, you’re right—it’s crucial.
BUT…
There’s so much conflicting info out there about which GPU is best for interior design software.
Here’s the deal:

This $900 laptop is running Lumion Pro with a 6GB vRAM GPU, and guess what? There’s still plenty of power left (just check out that vRAM bar).
The mistake a lot of people make is shelling out for insanely overpowered GPUs that cost a fortune—thanks to every other site hyping up “workstation GPUs” or “gaming graphics cards” for $1,500+.
The truth?
- If you primarily use software like Revit, SketchUp, or Lumion, you don’t need to spend more than $650.
- If you outsource the 3D modeling (using tools like 3DS Max or Blender) and stick to interior design software for drawing, you can go even cheaper—no dedicated GPU needed!
However…
If you’re planning to create jaw-dropping 3D visuals and run 3D rendering software like V-Ray, you’ll need to spend around $650–$700 for a laptop with at least a 4GB vRAM dedicated GPU.
But let me be clear:
You do NOT need a workstation GPU. You don’t need to spend $1,500, $1,000, or even close to that.
Here’s where I’m coming from:

My brother and I are borderline experts on this topic because back in college, our parents couldn’t afford expensive laptops. We had to dig deep and figure out how to get the most bang for our (very small) buck.
Here’s what we learned:
- If most of your work involves drawing and sketching, you’re good with a laptop in the $450–$600 range.
- If you need to render high-quality visuals, aim for something $600+.
The key is finding the right balance of performance and price based on your specific needs. Don’t get sucked into the marketing hype—trust me, your wallet will thank you!
Laptop Hardware for Interior Design
Before we talk about the best laptops for interior design, let me quickly elaborate on the hardware. You are welcomed to skip this section.
Software
You’ve probably heard about each of the following software:
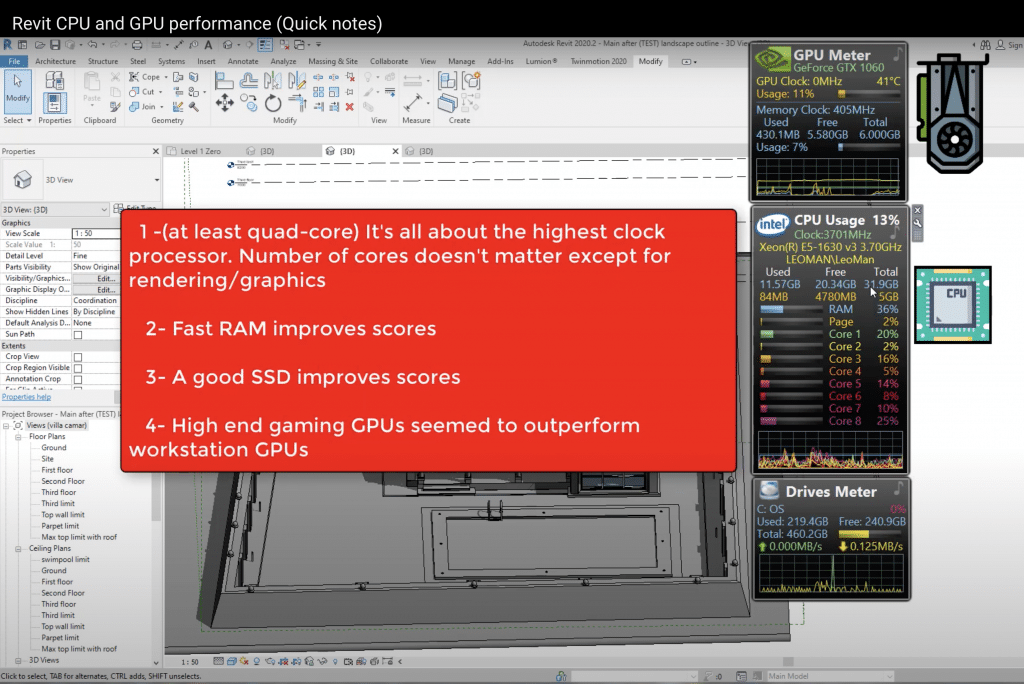
The last five in red will be used for walkthroughs and high quality rendering thus if you’re using those you need to pay close attention to the graphics card.
Note: AutoCAD & Revit are the least hardware demanding of the group. If you’re using those software in blue with just AutoCAD you can get away with very cheap laptops as outlined in my AutoCAD post.
GPU: 4GB vRAM minimum
a) For those using any or all the software highlighted in red & pink, you will be fine with a 4GB vRAM dGPU such as:
b) 2GB vRAM GPUs are good if you’re on a budget. Workflow will only be slower if you use the heavy software highlited in pink.
Howevere if you use..
c) 3DS Max & Rhino (especially for high quality rendering) you want a 6GB vRAM dGPU:
***Most will not need for 8GB vRAM GPUs or workstation GPUs. More details in the last section****
CPU: Min Core i5 or Ryzen 5
Cores make rendering faster and clock speed make drawing & drafting faster.
Most CPUs have high core counts so the focus should be on clock speed if you find two laptops with the same GPU but different CPUs.
If you end up with two laptops that have the same GPU but different CPUs. You can use my post here to compare their Multicore & single core performance.
RAM: 8GB RAM Min
8GB: Absolute minimum for Interior Design to run fast since Windows can take 4GB !!!
16GB: It will improve GPU performance in cases where you work with very large models. Regardless get 16GB RAM because it’s cheap to upgrade. No need to get 16GB RAM out of the box.
Storage: SSD (Solid State Drive)
SSDs will load up projects/files/models and the software lightining fast. They’ll also boot up your machine in 5 seconds flat compared to the slow HDDs.
Luckily, they’re virtually in every recent laptop.
If buying old laptops or using a desktop, do the upgrade and get an SSD. You don’t want clients waiting 5 minutes for things to load while they stand behind you breathing over your shoulder.
Don’t worry too much about SSD type…all of them are fast for Interior Design. However, if you’re transfering/moving tons of files and if you’ve got a lot of cash…PCIe 5.0 are the fastest.
Display: 15-17” FHD
Min: 15” FHD
This is the baseline for laptops with dGPUs, so you’re pretty much covered here.
QHD (2500×1600 resolution)
Why go beyond FHD? Simple:
- More pixels = more screen space. You can fit more tools, interfaces, and panels on your screen.
- Fewer dropdown menus to deal with, since everything is visible at once.
- A bigger canvas for drawing and designing, giving you more room to work comfortably.
See. QHD vs FHD post for some examples.
Top 5 Best Laptops For Interior Design
Most interior designers work with Lumion , Revit & some of the creative cloud software for which you only need a 4GB vRAM dGPU.
4GB vRAM GPUs also get you decent performance with 3DS Max & Rhino. It is very rare you’ll need 6 GB vRAM unless you work with very high quality rendering and walkthroughs regularly.
1. MSI GF63

This laptop should handle 95% of what interior designers (and students) need, whether it’s for sketching, drafting, or even GPU and CPU rendering software. It’s affordable, powerful enough, and easy to upgrade—what more do you want?
GPU: RTX 2050
Let’s start with the RTX 2050. It’s a “basic” GPU with 4GB vRAM, but don’t let that fool you—it’s the successor to the 1650 GTX, and it’s a solid performer.
Sure, there are “better” GPUs on paper, like the RTX 3050 (also 4GB vRAM), which might cost you an extra $100. But here’s the thing: for drafting, viewport navigation, and software like Revit or AutoCAD, you don’t need more than 4GB vRAM. These programs barely tap into the GPU for most tasks, and what really matters here is your CPU.
If you’re into GPU rendering and want to shave 25–30% off render times, then yeah, upgrading to a 3050 Ti might make sense. If you can find a laptop with one for the same price, by all means, grab it. But for most interior design workflows, the RTX 2050 gets the job done without breaking a sweat.
CPU: 12th Gen Intel Core i5-12450H
This laptop runs on a 12th-gen Intel Core i5-12450H, one of Intel’s high-performance chips. As of 2025, 14th-gen Intel CPUs are rolling out, but here’s the deal: the performance jump between the 12th, 13th, and 14th gens for design tasks is negligible. You’re not missing out.
Where you will see a difference is compared to older chips like the 10th or 9th gen. The 12th-gen CPUs offer a significant boost in clock speed and core performance, which makes a real difference when you’re applying functions, working on complex sketches, or rendering. That’s why I’d take this CPU over an older model with a fancier GPU like the 1650 GTX—it’s all about balance, and clock speed is king.
Performance: 3D Design Software + Rendering
This setup can handle SketchUp, Enscape, Revit, and similar programs like a champ.
For example, a design rendered in Enscape 2.7 using a 4GB vRAM GPU (similar to the RTX 2050) was completed in about 20 minutes. For interior designers, that’s more than fast enough. Viewports in programs like Revit or SketchUp will run smoothly, and rendering times will be reasonable.
If you’re worried about lag, it only becomes an issue with extreme projects—think walkthroughs of 15-20 story buildings in software like 3DS Max. Even then, it’s more of a minor delay during rendering rather than anything workflow-breaking. Back in the day, I used a 2GB vRAM GPU (which is way weaker than the RTX 2050), and it still handled most tasks just fine.
Design: Lightweight and Easy to Upgrade
For a laptop with a 4GB vRAM GPU, this one’s pretty lightweight and thin—it’s not going to weigh you down. It’s also easy to upgrade, which is a big deal if you plan to keep this laptop for a while.
- RAM: You can bump it up to 32GB if needed. For rendering large, high-quality designs, having 16GB+ RAM can make a noticeable difference in speed and performance. But out of the box, 8GB RAM will get you through most tasks just fine.
- Storage: There are two slots for storage upgrades, though you can only use one. Still, having the option to add more space later is a nice touch.
| MSI GF63 | |
| PROS | CONS |
|
|
2. Lenovo Ideapad i5 Pro
Best Cheap Laptop For Interior Design
Intel Core i5 11300H
8GB RAM DDR4
NVIDIA MX450 2GB vRAM
512GB PCIe NVMe SSD
16″ QHD 2.5K IPS Display
4.2 lbs
3 hours (Interior Design) / 8 hours (Basic Tasks)
The truth is, most interior designers don’t need to run high-quality walkthroughs of entire skyscrapers. For the majority of designers, walkthroughs are limited to one-bedroom apartments or single floors—nothing that requires heavy rendering or crazy GPU power. For that kind of work, a modern 2GB vRAM GPU is more than enough.
GPU: MX450 (2GB vRAM)
The MX450 is perfect for small walkthroughs and viewport work. The best part? Laptops with 2GB vRAM GPUs are usually much cheaper—typically $100–200 less than machines with 4GB vRAM GPUs like the RTX 2050.
Here’s the kicker: you might not even need a dedicated GPU.
When You Don’t Need a Dedicated GPU
If you’re mostly handling small projects—think houses, single floors, or kitchen remodels—using tools like SketchUp, Revit, or AutoCAD, you can totally get away with a laptop that doesn’t have dedicated graphics. A modern Core i5 or Ryzen 5 CPU will include integrated graphics (like Intel Iris Xe or Radeon Vega) that are more than enough for these tasks. These laptops are much cheaper and still deliver snappy performance.
Just one warning: If you’re skipping a dedicated GPU, make sure to buy a laptop with the latest Core i5 or Ryzen 5. Older CPUs will lag when drawing or sketching, which can ruin your workflow. For simple remodeling work like the examples below, you’ll be fine even without the latest and greatest:
- Construction documents for kitchen remodeling.
- Cabinet elevations.
- Basic 3D SketchUp work.
- Photoshop and Illustrator with all features unlocked.
Simple Remodeling Projects: 2GB vRAM GPUs
For slightly heavier tasks, like walkthroughs of small apartments or single-floor designs, a 2GB vRAM GPU like the MX450 is ideal. It adds that extra viewport performance for smooth navigation without the overkill (or price) of a 4GB GPU.
Why This Laptop Isn’t the Cheapest Option
Let’s be real—laptops with an MX450 should cost around $500, but this model is closer to $600. So why did I choose this more expensive option? Look closer at the specs:
- QHD Resolution (16-inch Display):
This isn’t just a big screen—it’s a high-resolution QHD display (2560×1440). That’s twice the resolution of FHD, giving you way more workspace. You can fit more tools, menus, and references on your screen without feeling cramped. - Workspace Boost:
The larger canvas makes a huge difference when working on complex designs. You can have your interface and quick actions right in front of you without constantly diving into menus. It’s a productivity game-changer.
For just $100 more, this is an incredible deal. You’re getting a larger, sharper display AND a dedicated GPU for smoother viewport performance. If you’re serious about design but don’t want to break the bank, this is the perfect middle ground.
| Lenovo Ideapad 5i Pro | |
| PROS | CONS |
|
|
3. Lenovo LOQ 15IRH8
The Best Laptop For Interior Design in 2023

Ryzen 7 7435HS
16GB RAM
NVIDIA GeForce RTX 4050
512GB SSD PCIe NVMe
15” FHD IPS 144Hz
3.7 lbs
4 hours Web Surfing / 2 Interior Design 
This laptop is for a super specific group of interior designers: the ones working on huge remodeling projects where you need to render entire floors and rooms at the same time for walkthroughs.
Most of these projects are usually split between a team, but if you’re flying solo and need to handle the whole thing yourself, this machine can do it without breaking a sweat.
For regular modeling or drafting, even for big spaces like stadiums or auditoriums, you can stick with weaker laptops (we’ve already covered those). This is strictly for walkthroughs and rendering.
RTX 4050: Walkthroughs and VT-Ray Rendering
Here’s the deal: if you’re doing high-quality, large walkthroughs in 3DS Max or similar software, this is where the RTX 4050 with 6GB vRAM comes in clutch.
Not only does it crush walkthroughs, but it also cuts down rendering times in VT-Ray or other GPU-based renderers. The 4050 has thousands of cores running at high speeds, so rendering is significantly faster compared to laptops with 2GB or 4GB vRAM GPUs, which either have fewer cores or slower performance.
Do you really need more than 6GB vRAM?
Short answer: Nope.
If you’re upgrading from a 4GB vRAM GPU and thinking about jumping to an 8GB vRAM GPU like the RTX 4060 or 3080, save your money. For interior design, 6GB is the sweet spot.
8GB+ GPUs are useful, sure, but only in edge cases—like massive, collaborative architecture projects for something like a stadium concert venue. And even then, that’s more of an architect’s gig, not interior design.
[Tip] Don’t overthink it—6GB vRAM is more than enough for any interior design project, no matter the software. [/Tip]
Why this laptop is perfect for the job:
- CPU: Ryzen 7 7435HS – Solid, reliable, and can handle large project files without breaking a sweat.
- GPU: RTX 4050 with 6GB vRAM – Exactly what you need for rendering and walkthroughs, no more, no less.
- Display: 15.6″ FHD, 144Hz – Crisp visuals and smooth refresh rates for both design work and presentations.
- RAM: 16GB – More than enough to multitask like crazy.
- Storage: 512GB SSD – Fast and plenty of room for most projects.
Bottom Line
The Lenovo LOQ 15.6″ Gaming Notebook is perfect for handling massive walkthroughs and heavy rendering without overpaying for unnecessary specs. 6GB vRAM is the ceiling for interior design, and this laptop hits it perfectly without going overboard.
TL;DR: If you’re working on huge projects that need walkthroughs, this laptop gets the job done. Anything more is just flexing for no reason.
| Lenovo LOQ | |
| PROS | CONS |
|
|
4. Surface Laptop Studio 2
Best Laptop or Tablet For Interior Design

13th gen Core i7-13700H
16GB LPDRR5 RAM
NVIDIA RTX 4050 80W
512 GB NVMe PCIe 4.0 SSD
14.4” 2400 x 1600 2 in 1 Tablet-Laptop w/ Stylus
4.37lbs
5-8 hours
Surface devices are basically a cheat code for interior designers who love sketching with a stylus.
These things are insanely responsive. The stylus feels so natural it’s like you’re sketching in a real notebook. And yeah, you can use the stylus for more than just sketching—think lines, shapes, painting, and other tools—but there’s definitely a learning curve. If you’re into working with a stylus, though, you’ll pick it up super fast.
2-in-1 Convertible Laptop: Microsoft Surface Vibes
The Surface Laptop Studio is the model I’m featuring here, but let’s be real: any Surface device (Surface Pro, Surface Book, etc.) made in the last four years is going to give you the same killer sketching and drawing experience. So, you don’t have to buy this specific model.
Why the Laptop Studio? Simple: dedicated GPU options. The Surface Pro doesn’t have one, so it’s more limited for 3D rendering work.
GPU Options
- RTX 4050: Perfect for interior designers who need a dGPU for rendering.
- RTX 4060: Honestly, overkill for most design tasks.
- Ada Workstation GPUs: Way over the top unless you’re doing heavy-duty professional rendering or architecture.
Surface Pro with integrated graphics: If you don’t need a dGPU, this is a cheaper option with better battery life (no GPU draining the power). It’s awesome for sketching in Revit or SketchUp, and you can leave rendering to another computer or outsource it.
Touchscreen + Stylus = Game Changer
Whether it’s the Laptop Studio or the Surface Pro, the touchscreen and stylus combo is next-level. Flip the screen backward, and boom, you’ve got a tablet that doubles as your digital canvas.
Imagine this:
- You’re commuting or chilling somewhere, sketching out rough ideas with the stylus.
- Then, you get home, flip it back into laptop mode, connect a mouse and keyboard, and finish up the project.
- Productivity = through the roof.
Plus, if you’re meeting clients or at a construction site, you can make edits on the spot, standing up, while someone’s watching and giving feedback. Talk about efficiency.
For Students
If you’re still in school, this is THE device for you. It’s not just great for design and CAD classes—it can replace your laptop, books, notebooks, and even pencils. Learn how to use the stylus with OneNote, and you’ve got everything you need for note-taking, sketching, and organizing in one device.
Hardware Upgrades? Nope.
Here’s the catch: None of the Surface models are upgradeable. You’re stuck with whatever RAM and storage you pick at checkout. So, think carefully before you buy.
Price
Yeah, the newer models are pricey—like, really pricey. But the good news is you don’t need the latest and greatest. Even older models (as long as they’re less than four years old) will handle sketching and interior design software just fine.
TL;DR
Surface devices (like the Surface Laptop Studio or Surface Pro) are perfect for interior designers and students who love sketching with a stylus. They’re portable, flexible, and insanely responsive for drawing and note-taking. Just know what specs you need before buying because you can’t upgrade them later.
| Surface Laptop Studio 2 | |
| PROS | CONS |
|
|
5. MacBook M4 Pro Chip
Best MacBook For Interior Design
M4 16 Core CPU
18GB Unified Memory
10 Core GPU
512GB SSD
16.2” Liquid Retina 2234×3456
4.7lb
13 hours
MacBooks are often overlooked for interior design because they can’t natively run Windows. But let’s set the record straight: they’re still an excellent choice for designers, and plenty of professionals in the field use MacBooks effectively.
That said, using a MacBook for interior design will mean a few workarounds for certain software. Here’s what you need to know:
Software Compatibility: macOS & Design Tools
If you’re sticking with software like SketchUp, Blender, and the Adobe Creative Suite, a MacBook is all you need. These programs run flawlessly on macOS, and the M4 Pro chip ensures everything is smooth, even with large projects.
However, if you rely on Revit or 3DS Max, you’ll need to run Windows. Fortunately, there are ways to do this depending on your MacBook model:
- M-Chip Models (M1, M2, M3, M4)
- Use a virtual machine like Parallels to run Windows.
- Virtual machines can handle software like Revit and AutoCAD without issues, as long as your projects aren’t overly complex.
- Performance might dip slightly, but for most design tasks, it’s manageable.
- Intel-Based MacBooks (Pre-M1, e.g., 2019 MacBook Pro)
- Install Windows natively using BootCamp.
- This method makes full use of your hardware, offering better performance for demanding 3D modeling or rendering tasks.
- You can run both macOS and Windows on the same MacBook and choose which OS to boot when powering up.
Rendering on MacBooks
Rendering with a MacBook is entirely possible, but it depends on the renderer you use:
- GPU-Based Renderers (e.g., V-Ray): These won’t work with macOS because most renderers are optimized for NVIDIA GPUs, which aren’t supported by MacBooks.
- CPU-Based Renderers (e.g., Blender): Perfectly compatible with MacBooks, and the M4 Pro chip delivers impressive rendering speeds for CPU-bound tasks.
If rendering is a significant part of your workflow, make sure your renderer supports macOS or plan to use a virtual machine for Windows-based tools.
Why Consider a MacBook Pro?
MacBooks have several advantages for interior designers:
- Portability: The M4 Pro MacBook Pro is lightweight and easy to carry, making it perfect for on-site visits or working on the go.
- Battery Life: Up to 20 hours of battery life on the M4 Pro means you won’t be chained to an outlet during long client meetings.
- Display: The Retina XDR display offers near-perfect color accuracy and clarity, crucial for presenting designs or working on detailed projects.
- Trackpad & Keyboard: The MacBook’s trackpad and keyboard remain the best in the industry—responsive, precise, and built for long hours of work.
Final Thoughts
The MacBook Pro M4 Pro is a fantastic choice for interior designers, especially if your workflow relies on SketchUp, Blender, or Adobe Creative Suite. It’s portable, powerful, and has one of the best displays you’ll find on any laptop.
If your work depends on Revit or 3DS Max, consider using a virtual machine (M-chip models) or BootCamp (Intel models) to run Windows. Either way, a MacBook is more than capable of handling your design needs.
TL;DR: The M4 Pro is the ultimate MacBook for interior designers, but older models with Intel CPUs are still great if you need native Windows support.
| M4 MacBook Pro | |
| PROS | CONS |
|
|
How to Find The Best Laptop For Interior Design
Below is a list of the most commonly used software for interior design. The links will take you to the official site’s hardware requirements page.
Software
- AutoCAD 3D or AutoCAD Architecture: By the way AutoDesk Provides a free 1-year license
- Revit Architecture (AutoDesk provides a free 1-year license to students as well)
- Adobe Photoshop (Any version)
- Adobe Acrobat(or other PDF Creator)
- Google Sketch Up Pro
- Podium
- Rhino
- 3DS Max
It isn’t likely you’ll use ALL of these.
You’ll be limited to mostly three:
Sketch-up: simple 3D sketches.
AutoCAD or Revit: remodeling.
3DS Max or Lumion: walkthroughs.
Hardware Specs for Interior Design
Because Lumion, 3DS Max & Revit are the most hardware demanding software of the group (though most will just use Revit) we’ll only talk about specs for those three software.
CPU
CPU is in charge of drafting/drawing and rendering. The following is based on my experience with the software and benchmark studies by Pudget Systems on Revit under different CPUs.
Modeling or Designing
Regardless of the software you use, designing/drawing/modeling will ALWAYS ALWAYS be a single-threaded task.
What I mean by this is the software will only use ONE CORE and the higher the speed of that core, the faster the performance will be. It doesn’t care about the speed of subsequent cores.
Now…
If you research this fact you may come across articles claiming that drafting/modeling in Revit is now multi-threaded (it uses more than one core).
That’s true but that’s still MOSTLY limited to ONE core. Most of the functions you use on a regular basis are STILL single-threaded.
Even when you perform those ‘multi-threaded’ functions…your software isn’t likely to use use much power from subsequent cores. It may use about 20% 10% and 5 % of the total power of subsequent cores (ex: calculating walls and loading all elements in view).
Here’s a list of all the functions that are multithreaded for Revit.
Most CPUs now have at least 4 cores with the most recent and powerful ones have 6-8 so yes you’ll get multi-core performance boosts from any CPU anyway.
Which CPU to pick for fast drawing then?
Since modern CPUs are multi-core anyways, focusing on the CPU’s clock speed becomes the smartest choice.
Clock speed is measured in GHZ and turbo is the highest clock speed a CPU can go up to. Here’s the tricky part though, despite the numbers you’ll see below. (Base clock speed and Turbo)
Intel
CPU
Base
Turbo
Cores
i5-10300H
2.5
4.5
4
i5-11300H
2.6
4.4
4
i5 11260H
2.6
4.4
6
i5 12500H
3.3
4.5
—
i5 13420H
1.5
4.6
8
i5 13500H
1.5
4.9
8
i7 11375H
3
5
4
i7 11370H
3.3
4.8
4
i7 11800H
2.3
4.6
8
i7 13620H
1.8
4.9
10/16
i7 13650HX
3.6
4.9
10/16
Those clock speeds are not ALWAYS used by a laptop. Whether or not a laptop is able to hit those numbers depends on the laptop design and whether the CPU is able to withstand those high temperatures over long periods of time. This is one of the reasons why AMD CPUs may be able to have better clock speed performance despite having lower clock speed numbers.
AMD
CPU
Base
Turbo
Cores
Ryzen 9 7940HS
4.0
5.2
8
Ryzen 9 6980HX
5
Ryzen 9 5900HX
3.3
4.6
8
Ryzen 7 7745HX
3.6
5.1
8
Ryzen 7 7840HS
3.8
5.1
8
Ryzen 7 6800HS
Ryzen 7 6800H
Ryzen 7 5800H
3.3
4.4
8
Ryzen 5 7535HS
3.3
4.5
6/12
Ryzen 5 6600H
3.3
4.5
6
Ryzen 5 5600H
3.3
4.2
6
**12th & 13th generation Intel CPUs seem to have more ‘cores’ but in reality a lot of these extra cores do not support hyperthreading. More detaiils in my upcoming post. Point is you should pick them because of their seemingly high clock speed not cores!
***Also when comparing an AMD vs an Intel CPU, you can’t just guide yourself by the numbers. For example a Ryzen 7 5800H (4.4GHz) isn’t as fast as a Core i5 11300H (4.4GHz). In this scenario, you use benchmarks. However, CPUs with the same color have approx the same perfomance.
Rendering: Multi-Core
No matter what rendering software, rendering will always always always be multi-threaded. That means, the more cores you have the faster the rendering will be.
Since you spend most of the time drafting/modeling, it’s wiser to focus on clock speed over the number of cores.
The real decision comes down to choosing a 4 core or a 6-8 core CPU, however higher core counts give you diminishing returns. For example, higher than 8 cores (10-12) may only reduce the time it takes to render something say from 30 to 25 min.
2. GPU (Graphics Card)
These are the instances where a GPU (graphics card) is used the most:
- Viewport (panning, zooming, orbiting, rotating, etc) when drafting.
- During Viewport. Revit seems to only use the GPU slightly. However, this may not be the same for all other 3D design sfotware (3Ds Max, Maya, Lumion,etc) where it DOES become crucial especially when LOD (level of detail) approaches 400.
- Thus if you’re mostly relying on Revit for your 3D designs (along with sketch up) GPU is not important. Your CPU is. This means you can save quiet a lot of bucks avoiding unnecessary GPU power.
- Walkthroughs
- Highly GPU dependent regardless of software.
- Rendering
- It’ll speed up rendering, the same way having extra CPU cores do.
- However, this GPU-rendering is limited to a few software/renderers:
- Revit does not use GPU for rendering.
- V-ray RT is a GPU dependent.
- V-ray advanced only uses the CPU.
- Lumion uses the GPU & CPU for rendering.
If you render with Rhino, 3DS Max or any GPU-dependent renderers then you must know the difference between integrated and dedicated and also be able to tell which one is the best dedicated graphics.
A) Integrated GPUs
Integrated graphics are usually labeled as Intel Xe, Intel Iris, Radeon Vega X, Intel HD, Intel UHD,etc. Basically anything that says Intel or Vega is very likely to be integrated.
They come by default with a CPU. A specific CPU will be assigned the same integrated graphics regardless of laptop.
However, integrated GPUs are much much weaker than dedicated GPUs in general.
Obviously integrated GPUs are not IDEAL for Revit & AutoCAD and cannot spend more than 550 bucks, you can make do especially with low LOD models.
B) Dedicated Graphics Cards
Once projects on Revit & AutoCAD step into the 100MBs OR you start using 3D modeling software for walkthroughs and high quality renders then you have get a dedicated GPU.
Dedicated GPUs usually have the keywords “NVIDIA” “Radeon RX” “GeForce” “RTX”.
Because they have way more extra “cores” and their own “vRAM” which can go up to 16GB (on laptops) as opposed to .5MB (integrated) they can process heavy amounts of graphic data faster.
The Cores are mostly useful for GPU-rendering.
NVIDIA
Cores
vRAM
Speed
MX250
384
2GB-4GB
1582
MX350
640
2-4GB
1354
1050
640
2GB-4GB
1493
MX450
896
2-4GB
1580
1050Ti
768
4GB
1620
1650
1024
4GB
1560
2050RTX
2048
4GB
1470
1060
1280
6GB
1670
3050Ti
2560
4GB
1485
1660 Ti
1536
6GB
1590
2060 RTX
1920
6GB
1680
2070
2394
8GB
1620
3060
3584
8GB
1780
4050
2560
6GB
2370
2080
2944
8GB
1710
3070
5120
8GB
1620
4060
3072
8GB
2730
3070Ti
5888
8GB
1485
3080
6144
8GB
1710
4070
4608
8GB
2175
3080Ti
7424
16GB
1590
AMD
| Name | Shaders | vRAM | Speed | NVIDIA Equivalent |
| Pro RX 555X | 768 | 2GB | 855 | MX150/MX250 |
| RadeonRX 540 | 512 | 4GB | 1219 | ~950M |
| Radeon RX 550 | 640 | 4GB | 1287 – 1476 | +950M |
| Radeon RX 560X | 1024 | 4GB | 1172 – 1275 | 1050GTX |
| RX 580 | 1536 | 6GB | 1077 | ~1060GTX |
| RX 5500M | 1408 | 8GB | 1327 – 1645 | ~1660Ti |
| RX 6700M | 2304 | 10GB | 1792 | ~3060RTX |
| RX 6800M | 2560 | 12GB | 2116 – 2300 | ~3070RTX++ |

Let’s not forget that most interior designers BARELY make use of the power of dedicated graphics..then even if these workstation graphics are powerful…there’s no need to buy them anyways.
- High Point University Interior Design Computer Specs
- South Dakota State University Interior Design Department
- Bellevue College Interior Design Computer Recommendations
A few more tips:
- Old dedicated graphics (Ex: GTX 770M) is likely to be imcompatible with 3D modeling software for interior design. Anything older than the 9th generation (960GTX) GPUs are risky.
- Don’t worry about the story of ‘gaming GPUs are not compatible with Interior Design software’. It’s bollocks. As long as they’re recent and not old, they will be compatible.
- Not to mention that these recent gaming GPUs have architectures that are very similar to ‘recommended’ workstation graphics. It’s going to be nearly impossible for them not to work.
- You MIGHT get a few bugs with gaming GPUs as opposed to workstation GPUs but you’ll just have to click OK and move on, it won’t affect your workflow or stop you from working.
- Less bugs and glitches
- Official support from AutoDesk if something goes wrong.
- the need to use special plug-ins that only run on workstation laptops.
Before you do any purchase, please take a good look at the following table:
Pay very close attention to the ‘Equivalent’ column.
This will tell you where the workstation graphics in question stands in terms of perofmance and value by comparing it to gaming GPUs that have similar performance.
This is important to avoid being RIPPED OFF as vendors love to increase prices of workstation graphics cards for no reason.
| Workstation GPU | Equivalent | Cores/Shaders | Clock Speed | vRAM |
| P500 | MX150- | 256 | 1519 | 2GB |
| P520 | MX150 | 384 | 1493 | 2GB |
| K2100M | GT 750M | 576 | 667 | 2GB |
| K3100 | 765M- | 768 | 706 | 4GB |
| P620 | MX250/1050 | 512 | 1442 | 4GB |
| M620M | 950M- | 512 | 1018 | 4GB |
| M1000M | 950M | 512 | 1072 | 4GB |
| Pro WX 3200 | RX 550 | 1082 | 640 | 4GB |
| M2000M | 950M/960M | 640 | 1197 | 4GB |
| M1200 | 960GTX | 640 | 1150 | 4GB |
| P1000 | 1050GTX | 512 | 1519 | 4GB |
| P2000 | 1050Ti | 768 | 1468 | 4GB |
| T2000 | 1650/1660Ti | 1024 | 1785 | 4GB |
| T1000 | 1650- | 768 | 1455 | 4GB |
| RTX 3000 | 2070RTX+ | 1280 | 1380 | 6GB |
| RTX 4000 | 2070/2080 | 2560 | 1560 | 8GB |
| RTX 5000 | 2080RTX+++ | 3072 | 1350 | 16GB |
| RTX A2000 | ~3050Ti | 2560 | 1200 | 4GB |
| RTX A3000 | ~3060RTX | 4096 | 1560 | 6GB |
| RTX A4000 | ~3070RTX | 5120 | 1560 | 8GB |
| RTX A5000 | ~3080RTX | 6144 | 1695 | 16GB |
| RTX A5500 | ~3080Ti RTX | 7427 | ??? | 16GB |
3. RAM
Since most interior designers rarely make use of dedicated graphics, RAM is actually the second most important thing after CPU.
Revit & AutoCAD: Draftting/Modeling
Most laptops do not come with 16GB RAM by default so you’ll have to do the upgrade yourself. (You can buy a laptop with 16GB RAM out of the box but they’re usually much more expensive whereas an upgrade can cost you 15 bucks).
When you render, the amount of details (data) is increased significantly, the software takes your final work and starts adding high quality pixels all over. All this process happens between the RAM and the CPU, the RAM becomes the container for the CPU processing.
All this data is still stored on RAM and most of the time , the amount of data is SO large that the software has to partitioned the data in chunks for it to fit in RAM (container is too small).
Thus , a large chunk of data can get queued.
If you have lots of RAM (big container), no need to partitioned data and no need to queue the data for processing. The constraint will be down to your CPU or GPU or both (depending on the renderer).
32GB RAM is as much of a big container as people will need. With this much, the typical large and high quality render might take 20 min.
Increasing the container (RAM) to 64GB might cut down the time to 18 min. There are diminishing returns beyond 32GB and even 32GB might be too much (16GB RAM might take 25 min).
4. Storage
Sketches and drawings (on Sketch Up, Revit , so on) don’t really take up much space. You can have a thousand of these and even the a merely 128GB storage will only be 20% full.
Instead of worrying about how much storage you can get out of a laptop, you should instead focus on the TYPE of storage.
However , choosing the fastest storage speeds has advantages outside of those drawing.
SSD vs HDD: Storage Speed
SSDs are nearly universal in laptops today and that’s a good thing, they have massive advantages over the old fashioned HDDs. With SSDs…
- Opening files and saving files take an instant.
- From the moment you launch your Interior Design software to the moment it’s ready for you to work, it’s literally seconds.
- Ex: Revit has a bucketload of libraries for diagrams, surfaces, textures, lightining ALL needed to load for you to use the software.
- This will take a very long time (minutes) with HDDs to load.
- Ex: Revit has a bucketload of libraries for diagrams, surfaces, textures, lightining ALL needed to load for you to use the software.
- Opening large files in 3DS Max, Rhino, AutoCAD and 3D design software is much faster as well. They might take 30 sec in the most extreme cases as opposed to several minutes with HDDs.
- Windows will also be ready in minutes. Your computer will be up and ready a few seconds after you turn it on.
Because virtually every laptop made within the past 4 years has a Solid State Drive now.
They may be PCie NVMe, SATA III, etc, but they will all have the same benefits and almost equal speed for the tasks just mentioned.
If you want to be a perfectionist and want the best storage speed. As of 2024, the fastest SSD are PCIe 4.0. You may see the release of PCIe 5.0 this year however.
Hard Disk Drive Upgrade
It is likely a lot of people reading this might only need to replace the HDD for an SSD they have on their laptop. Doing that will increases performance all over (outside of viewport & drawing & rendering).
You’ll be surprised to see what a huge difference an SSD makes to a laptop that doesn’t have it.
5. Display
I’m sure you’ve come across lots of specs about displays: constrant ratios, brightness levels, colorspace, gamut,etc.
They’re all meaningless because every laptop ahs all the brightness, contrast ratio and gamut for you to design with no errors as the client inteded. So Ignore most specs except for two: size & resolution. Why? Because…
It’s always easier to work with a bigger & more detail view of your work.
The amount of extra screen space also allows you to fit more toolbars and quick action buttons which eliminates the need to use drop down menu, this increases your workflow and reduces the time it takes to finish a project. There will be less time looking for a function and more time sketching.
Resolution
The obvious way to incrase your screen area is by choosing the bigger display.
Laptops are limited to 17”. However, it may not be wise to choose a 17” display because that makes it bulkty, heavy and more difficult to carry around. If weight is not an issue, then it’s all good.
Another way to increase your workspace area is by choosing a high resolution display.
High resolution basically means more pixels and more pixels means more objects can be rendered withouth the need to use much screen space. How? By reducing icons & objects to smaller sizes yet still keeping them high quality.
HD & HD+ (768p and 900p): These resolutions are very very low and must be avoided at all costs. HD is obselete and you will only find them on cheap old laptops only. HD+ is common on laptops under 450 bucks, they are not that bad but there’s no point in buying laptops with these low resolution displays when you have laptops with high resolution costing you just as much.
FHD (1080p): This is the minimum for any serious interior design work and its virtually available on every laptop with a dedicated GPU (+550 dollars). In 2024, they’re common around 350-450 dollars too! Ocassionally you’ll find it under 350 dollars.
QHD (2.5k): This is becoming more and more common on 600+ dollar laptops. This is a very very good feature, if you have the cash you may want to focus on this rather than extra power you won’t need.
UHD (4k): the highest resolution found on laptops. Unfortunately, you’ll only find them on laptops over 2000 dollars. Not worth it, QHD displays are enough.
Comments
If you have any questions, suggestions please leave a comment below. I will reply ASAP and also update this post accordingly.
Author Profile
- I am physicist and electrical engineer. My knowledge in computer software and hardware stems for my years spent doing research in optics and photonics devices and running simulations through various programming languages. My goal was to work for the quantum computing research team at IBM but Im now working with Astrophysical Simulations through Python. Most of the science related posts are written by me, the rest have different authors but I edited the final versions to fit the site's format.
Latest entries
 wowDecember 18, 20255 Best Laptops For World of Warcraft – Midnight & Classic (2026)
wowDecember 18, 20255 Best Laptops For World of Warcraft – Midnight & Classic (2026) LaptopsDecember 17, 2025The 4 Best Laptops For Virtualization of 2026 (10-50 VMs ATSM)
LaptopsDecember 17, 2025The 4 Best Laptops For Virtualization of 2026 (10-50 VMs ATSM) Hardware GuideDecember 17, 20252026 Beginner Guide to Reading Computer (Laptop) Specifications
Hardware GuideDecember 17, 20252026 Beginner Guide to Reading Computer (Laptop) Specifications LaptopsJune 30, 2025Best Laptops for Computer Science (July 2025 )
LaptopsJune 30, 2025Best Laptops for Computer Science (July 2025 )