Best Intel Core i5 Processor Laptops 2025 (14th gen)
No questions….Core i5 laptops offer a solid balance between performance and budget.
A recent Core i5 laptop (12th gen and up) can handle AAA games like Call of Duty, Overwatch 2, and World of Warcraft well when paired with a entry-level GPU.
The integrated graphics can support light gaming and casual 3D work (AutoCAD, SolidWorks as well as photo and video editing (Photoshop, Premiere) .

Now the problem is…
With so many Core i5 laptops finding the best value takes time.
For instance…many Core i5 laptops come without a dedicated GPU. Yet, some models include one for around the same price. Ex: HP Victus (520) vs Lenovo V15 (500).
| Laptop | GPU | TGP | CPU | Display | Ideal Use | Buy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HP Victus $520 |
Radeon RX 6550M | 50W | Ryzen 5 7th Gen | 15″ 144Hz | High settings, Medium 3D work | View Price |
| HP Victus $580 |
RTX 3050 | 75W | Core i5 12th Gen | 15″ 144Hz | High settings, Medium 3D work | View Price |
| Lenovo V15 $500 |
Intel UHD Xe G4 (48EUs) | 45W | Core i5 13th Gen | 15″ 60Hz | Business, school, light gaming/3D | View Price |
Now …
Let’s not forget cooling and thermal design!
And don’t forget…
You also want to max out on other stats (RAM, SSD, Display).
Hardware Specs For Core i5 Laptops
Before we dive into the 8 Best Core i5 Laptops of 2025, here are quick tips to help you choose the right one. If anything’s unclear, check the final section.
CPU
Intel CPU names can be tricky. Focus on the letter at the end:
The number at the start (10, 11, 12…) shows the generation—higher is newer and better.
7th-gen and older are much slower. 10th-gen and up bring big gains in speed, graphics, and multitasking—great for light gaming and creative work.
RAM
4GB: Rare on Core i5s now—too little for Windows 11.
8GB: Standard. Good for gaming, editing, and multitasking.
16GB: Great for heavy apps and gaming. Rare, but easy and cheap to upgrade. Check my Dual-channel RAM post to see why you should consider the upgrade. iGPU performance will benefit from it too.
Storage
Stick with SSDs—they’re fast and reliable. Skip HDDs.
256GB: Enough for basic use and a couple of big games.
512GB: Better for games, editing, and storage-heavy work.
1TB: Best for gamers and content creators. More info.
You might also spot faster SSDs—(PCIe NVme 5.0) but they’re really only useful for massive file transfering work (photo editors, video editors, etc).
GPU
If you’re not gaming or doing 3D/editing, GPU doesn’t matter much. But if you are, avoid low-end ones:
Top 8 Best i5 Laptops
This section is divided into two categories based on user needs:
Power Users (1-4): Gamers & professionals doing video/photo editing or 3D modeling. All these laptops include a dedicated GPU. Ex:
- Laptop 1: Best specs-for-price ratio with the latest 13th-gen Core i5 CPU and a mid-range dGPU.
- Laptop 2: Most budget-friendly high-performance Core i5 with a dedicated GPU
Basic Users (4-8): General consumers doing tasks like web browsing, video streaming, simple gaming, and basic photo or video editing.
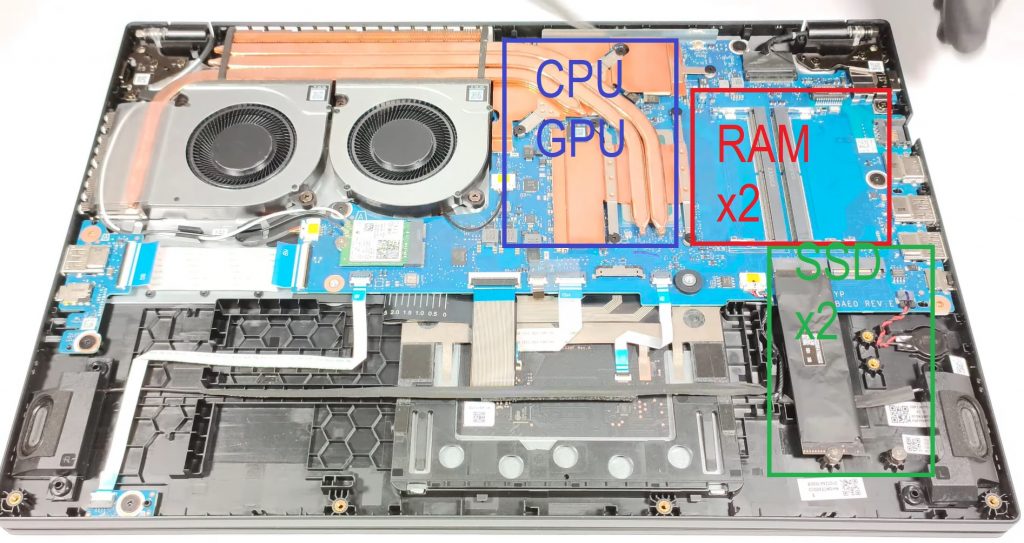
1. Acer Nitro 5
Best i5 Laptop with 4050RTX
Intel Core i5-13420H
8GB RAM
NVIDIA GeForce RTX 4050
512GB PCIe NVMe SSD
15.6″ FHD IPS 144Hz
4.66 lbs
Windows 11
| Speed | Turbo | Generation | Cores | Threads | Cache Size |
| 1.9GHz | 4.6GHz | 13 | 8 | 12 | 12MB |
2. MSI – GF63035
Best i5 Laptop for The Money

Intel Core i5 12450H
16GB DDR5 RAM
GeForce RTX 2050
512GB PCIe SSD
15” 144Hz FHD 1080p IPS
4.10lbs
| Speed | Turbo | Generation | Cores | Threads | Cache Size |
| 2.0GHz | 4.4GHz | 12 | 10 | 16 | 20MB |
In past reviews, I included a 1650GTX every time, but now there’s a new option: the 2050RTX, which is also an entry-level dedicated GPU often sold at very affordable prices.
Now… we could go with a 1650GTX, but a 2050RTX laptop is more likely to come with a more recent generation Core i5 CPU, an updated (and faster) SSD, and more RAM. Ironically, older 1650GTX models with older Core i5s are slightly more expensive as of late 2024.
Hardware
The 2050RTX has the same amount of vRAM and even the same number of CUDA cores as the 1650GTX.
This time, unlike the 1650GTX models of previous years, you get 512GB of storage, which is much more common on laptops with modern hardware. The SSD generation is still PCIe NVMe 4.0, but PCIe 5.0 will likely become more mainstream by mid-2025.
Performance
Compared to the 4050RTX we reviewed above (which costs around $150 more), the performance differences are significant for GPU-intensive tasks like gaming, 3D animation, and modeling. However, for anyone not doing professional-level work in these areas (yes, gaming is also a professional field now), a 2050RTX—or any 4GB vRAM GPU—should be more than enough.
Gaming, Photo, Video Editing: The generation difference between the Core i5 CPU in this model (12th gen) and the 13th gen in the Acer Nitro reviewed above has a minimal impact on gaming, photo editing, or video editing. As shown in my Intel CPU Generation Comparison Performance post here, the difference is quite small, and there should be no CPU bottleneck.
3D Modeling/Animation: For advanced work in CAD or animation with very large models, requiring extensive shaders, rigs, polygons, and parts, there will be a notable performance difference.
Final Rendering: Since final rendering in most programs (both video and 3D software) is multi-threaded, you’ll experience slower performance and longer render times with this model compared to the 13th gen Core i5 and 4050RTX, which both have better multi-thread performance and more CUDA cores running at higher clock speeds.
Design
One positive about this laptop is its design. It’s slightly different from most high-performance Core i5 laptops. All MSI laptops, by default, are much easier to upgrade, and they also have one of the best air-cooling systems. So, even under strenuous work, this machine should last a long time. I’d still recommend installing temperature monitoring software on any high-performance Core i5 laptop. As you can see below, it has two fans, several large pipes, and vapor chambers for optimal cooling
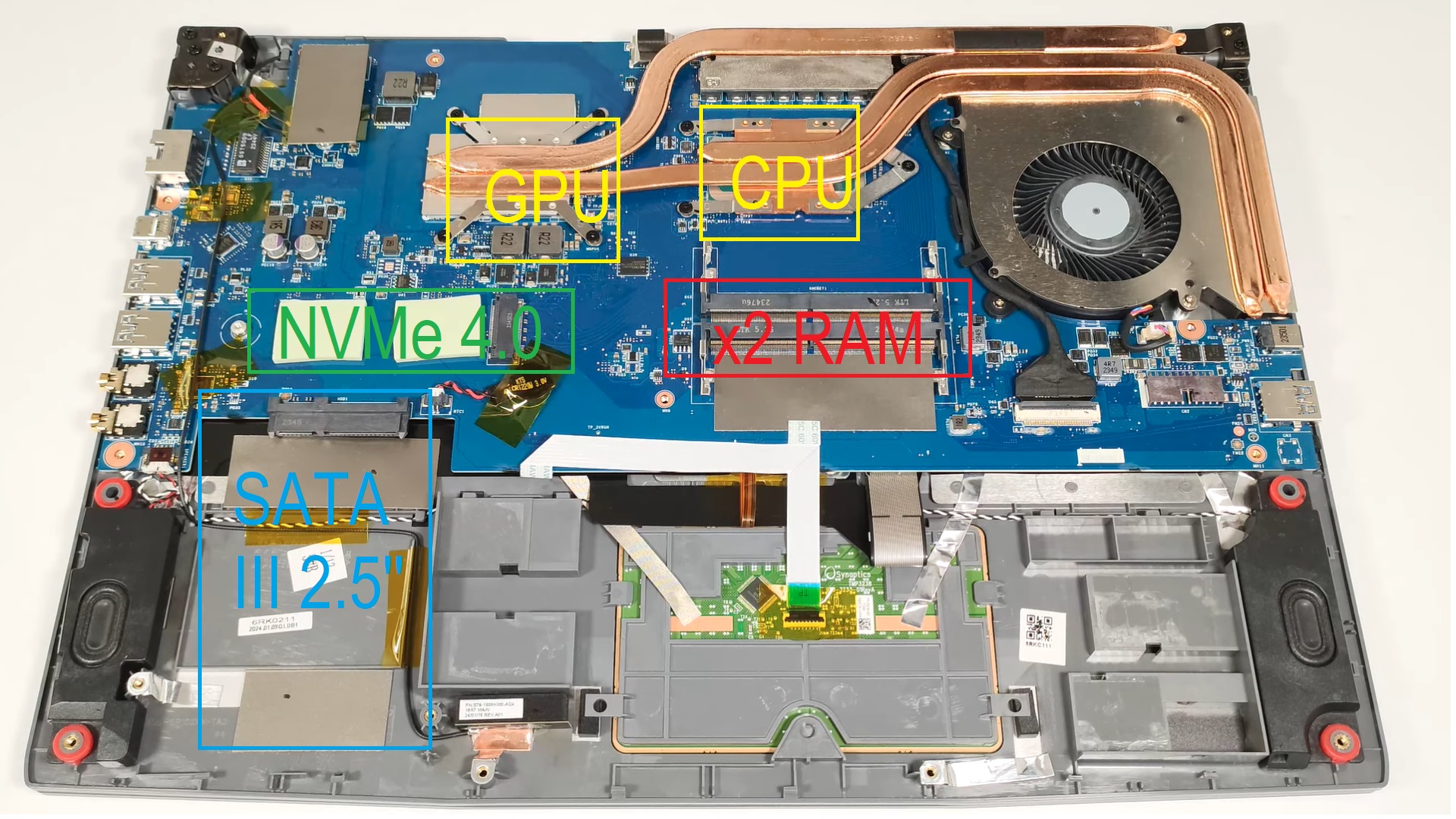
3. Acer Nitro 7
Best i5 Laptop CPU

14th Gen Intel i5-14450HX
16GB DDR4
NVIDIA Geforce RTX 4050
512GB PCIe NVMe SSD
17” full HD 144Hz IPS
5.3 lbs
| Speed | Turbo | Generation | Cores | Threads | Cache Size |
| 2.0 | 4.8 GHz | 14 | 10 | 16 | 20MB |
Now let’s look at the other end of the spectrum: a Core i5 laptop with the most powerful Core i5 CPU available in mid 2025.
Hardware
If you’re aiming for the latest Core i5, your best choice is the Core i5-14450HX.
This is a “high-performance” CPU, not to be confused with the “U” or “G” versions designed for budget machines and everyday tasks. The low-voltage “U” or “G” options should be released around mid-2025.
The performance boost from this Core i5 compared to previous generations is significant in both single-threaded and multi-threaded tasks. As shown in my post on Core i5 vs Ryzen 5 benchmarks, no Ryzen 5 or Core i5 CPU is faster than this one.
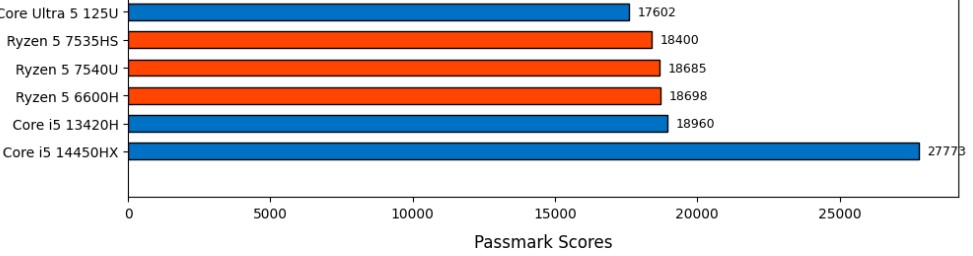
However, the downside here is price. You’re paying quite a bit more for this added CPU performance, and depending on what applications you use, it may not always be worth it.
Performance
Let’s break it down…
Gaming: For gaming, the difference is minimal. The extra cache and clock speed won’t impact frame rates as much as a better GPU would. This CPU would pair nicely with a 4060RTX, but older Core i5 CPUs can still handle up to the 4050RTX without bottlenecking.
3D Modeling: In 3D modeling, there’s a performance boost, though it’s more noticeable in rendering than in editing or modeling. For instance, a render that might take 50 minutes on a previous-gen Core i5 could take about 35 minutes on this 14th-gen Core i5.
Video Editing: Video editing sees some improvement, especially for in-editor rendering and final exports—as long as the GPUs are comparable in both wattage and performance. For photo editing, gains are minimal unless you’re batch-processing dozens of high-res images in Lightroom.
Design
These features generally apply to any laptop with a 14th-gen Core i5-14450HX. Compared to standard Core i5 models, you’ll get:
- Much easier upgrade access; in many models, you only need to remove a single screw to add extra RAM or SSD storage.
- Great thermal control.
- A more high-performance aesthetic.
- Cool backlit keyboards, which is a nice touch for gamers.
4. Acer Nitro 5 AN515
Best i5 Laptop – 3060RTX

Core i5-12500H
16GB RAM DDR4
NVIDIA GeForce 3060RTX 6GB vRAM
512GB PCIe NVMe
15” full HD IPS Display 144Hz
5.51lbs
2 hours
| Speed | Turbo | Generation | Cores | Threads | Cache Size |
| 2.5GHz | 4.5GHz | 10 | 6 | 12 | 12MB |
I’m sure many of you have seen Core i5 laptops with a 4GB vRAM GPU – pretty common, right? But I know some of you are specifically looking for a Core i5 with a 6GB vRAM GPU, like the 1660Ti, 2060RTX, or 3060RTX.
GPU: 3060RTX vs 6GBvRAM GPUs
Now, here’s the deal: While you’ll find a lot of Core i5 laptops with a 4050RTX, they don’t necessarily outperform the 3060RTX in every way. The 4050RTX does benefit from a newer architecture (Ada Lovelace), making it efficient and faster in some cases. However, the 3060RTX with its 6GB vRAM and higher memory bandwidth can still pull ahead in more memory-intensive tasks, especially if you’re pushing higher resolutions or working with bigger game assets.
But let’s talk about going beyond the 3060RTX. Sure, a 4060RTX would be faster, but there’s a catch: it can get bottlenecked by some Core i5s at higher resolutions (like 1440p) in specific situations. The more powerful 13th and 14th-gen Core i5s can handle it well, but older Core i5s might not unlock its full potential.
With that in mind, I found this 3060RTX model with a good balance of price and wattage. (And yes, wattage matters: lower-wattage 3060RTX models are generally cheaper, while higher wattages come at a premium.)
Performance
The 3060RTX is a genuine mid-range GPU from NVIDIA, and you’ll see a solid performance jump in all sorts of GPU-heavy applications. Here’s a quick breakdown for some key uses:
- Gaming: Epic settings are doable without a hitch. For MMORPGs like World of Warcraft, expect three-digit FPS at epic settings, while more graphically intense games, like Call of Duty or Warhammer, should run well on high settings. Lighter FPS games? You’ll hit epic/ultra settings easily.
- 3D Modeling: The 3060RTX has way more muscle than entry-level GPUs like the 1650GTX. For CAD and 3D animation, it’s more than enough for large models, lots of rigs, or complex assets. For most users, going beyond this (to something like an 8GB vRAM GPU) won’t add much unless you’re handling ultra-detailed projects.
- Video & Photo Editing: Total overkill for photo editing, but it really shines in video work. The 6GB vRAM is great for longer timelines and GPU-accelerated effects, meaning faster previews and smoother editing overall. It won’t impact rendering speed as much – that’s still mainly a CPU job – but for anything requiring real-time rendering, the 3060RTX will handle it like a pro.
BASIC USERS: So, all the laptops we’ve covered so far are geared toward people who need serious CPU and GPU power for demanding applications. Now, let’s shift to laptops for the average Joe – anyone who doesn’t need the high-performance graphics of the Core i5 “H” series CPUs.
These laptops can still handle photo editing, light video editing, and casual gaming (just expect to keep the settings low). They can even run 3D CAD software, but performance will be limited to smaller models.
These models are really meant for office work, school, everyday use, and basic gaming. Plus, they’re typically thinner, lighter, and more portable, which is perfect for those on the go.
5. Acer Aspire 5 14 Slim
Best Budget Core i5 Laptop

Core i5-1335U
8GB LPDDR5
Intel Xe Graphics
512GB SSD
14” Full HD IPS
3.75 lbs
3 hours
WiFi 6E
| Speed | Turbo | Generation | Cores | Threads | Cache Size |
| 1.3GHz | 4.6GHz | 13 | 10 | 12 | 12MB |
I know a lot of you are eager to get your hands on the latest low-voltage 14th-gen Core i5 ‘U’ series CPU. However, the 14th-gen budget Core i5 CPUs, like the Core i5-1440P and Core i5-1440U, haven’t fully hit the market yet. Even if you do see them listed on brand websites, they’re often priced high since they’re newly released, which might not be worth the extra cost.
These new releases may not give you the best value for your money right now, especially since even 11th-gen Core i5 laptops are still fast enough for office work, light gaming, and basic video editing.
Hardware
The most powerful yet affordable Core i5 ‘U’ series CPU currently available is the Core i5-1335U. Its clock speed is significantly higher than the 11th-gen equivalents, and Acer recently released a model featuring it in a slim, lightweight laptop priced under $400.
This model includes upgraded 8GB RAM and a 512GB SSD, so you won’t need to worry about upgrades. Acer didn’t skimp on other components either, as it also comes with an FHD display.
It’s been a popular pick, with 50 units sold within a week of release, so it may sell out soon. The value you’re getting for this hardware is almost unbeatable.
6. ASUS VivoBook 16
Best ASUS i5 Laptop

Intel Core i5-13500H
8GB RAM DDR4
Intel UHD Graphics
512GB PCIe NVMe
16” Full HD IPS
5.07lbs
5 hours
WiFi 6
| Speed | Turbo | Generation | Cores | Threads | Cache Size |
| 3.5 GHz | 4.7GHz | 10 | 12 | 16 | 18MB |
This is my favorite Core i5 laptop on this list for a simple reason: it has a 16″ display and a spacious keyboard. Since I mostly stay home typing and staring at a computer screen, these are the specs that matter most to me when choosing a laptop.
Hardware
This laptop is quite recent, a special version of the more expensive ASUS VivoBook 17, released around October 2024. If you look at the price-to-specs ratio, you’ll see why it’s likely to sell out quickly.
While the CPU may be overkill for average users, the “H” series performance CPU gives it some future-proofing, allowing you to handle heavier tasks and game at higher settings if needed.
Though it lacks a dedicated GPU, the integrated GPU on this CPU runs at higher clock speeds. RAM and SSD are solid, but if you’re looking to run heavy apps like photo or video editing and 3D modeling, upgrading to 16GB of RAM will help boost iGPU performance, as we’ve discussed.
What sets this model apart from other 16-17 inch Core i5 laptops under $500 is that it not only comes with a large FHD display but is also relatively thin and lightweight. And since it doesn’t have a dedicated GPU, the slim design won’t cause any major issues with cooling. It could easily serve as a desktop replacement due to its size, while still being easy to move around
7. Surface Pro 10
Best 2 in 1 Core i5 Laptop

Core Ultra 5 (135U)
8-64GB RAM DDR5
Intel Iris Xe Graphics
Up to 1TB
13” 2880 x 1920 120Hz
1.94lb and above
+15 hours
| Speed | Turbo | Generation | Cores | Threads | Cache Size |
| 1.6GHz | 4.4GHz | 13 | 12 | 14 | 12MB |
One main issue with most laptops we’ve looked at so far is their portability. They’re not overly heavy, but they aren’t ideal for taking everywhere. While there are plenty of lightweight laptops with Core i5 processors, like the ASUS ZenBook 13, the Surface Pro 10 stands out as the most portable option if you’re looking for a Core i5-equivalent device that’s ultra-light and ready for on-the-go work.
Hardware
The Surface Pro 10 offers configurations with Intel’s new Core Ultra 5 (135U) or Core Ultra 7 processors, with multiple options for RAM and storage. Unlike most laptops, the Surface Pro’s internals are not user-upgradable, so it’s smart to select the RAM and storage you’ll need right from the start.
Core Ultra 5 (135U) + 16GB RAM: Powered by Intel’s Core Ultra 5 (135U), this is a significant upgrade in power and efficiency, with 10 cores and 12 threads specifically designed for low-power tasks, making it ideal for multitasking and work applications. This model strikes a good balance, with enough power for tasks like photo editing, light video editing, and basic 3D modeling, but with the energy efficiency you’d expect from the latest mobile CPUs.
Storage: The Surface Pro 10 comes with 256GB as the base model. This is generally sufficient for standard use, including web browsing, document editing, and storing multimedia files. For heavier workloads or extensive media files, the 512GB or 1TB options are recommended, especially since the storage is not user-upgradable.
Design
The Surface Pro 10 is incredibly thin and portable, and despite its slim profile, it includes a variety of essential ports: USB-C with Thunderbolt 4 support, a headphone jack, and a Surface Connect port for docking. With a Surface Dock, you can add extra monitors and peripherals, essentially transforming it into a desktop setup at home or work.
2-in-1 Flexibility: This device is a 2-in-1, meaning it’s both a tablet and a laptop. Pair it with the Surface Slim Pen 2, and it’s perfect for digital note-taking, drawing, or sketching. You’ll get the same versatile, high-quality touch experience that makes it almost a direct competitor to the iPad Pro.
Battery Life: Microsoft claims the Surface Pro 10 can reach up to 15 hours of battery life for video playback. In real-world use, which includes tasks like browsing, video calls, and light multitasking, you can expect around 10-12 hours—enough to comfortably last a full workday on the go.
Keyboard + Trackpad: The Surface Pro 10’s detachable Type Cover keyboard is well-designed and responsive. The keyboard feels comfortable and is spacious enough for quick typing, and the trackpad, while not as large as some, remains smooth and accurate. Since the Surface Pro is now a 13-inch device, it offers a bit more room than previous models, which helps with extended typing sessions.
Cooling: The Surface Pro 10 has excellent thermal management. The Core Ultra 5 processor runs efficiently, which helps keep the device cool and quiet, making it perfect for focused work sessions or long study sessions.
By the way, if you’re a student, you might not be able to afford the latest Surface Pro 10. However, you can opt for older models—as long as they have a Core i5 and 8GB RAM, they should be plenty fast for schoolwork, long study sessions, and the intense multitasking that college often requires. The older models can even handle 3D modeling, video editing, and programming. Just remember not to go further back than the Surface Pro 6. The touch sensitivity and features will still be nearly the same.
8. MacBook Air
Best MacBook with Core i5 Laptop
10th Core i5 8250U
8GB RAM DDR4
Intel UHD Graphics 617
128-256GB Flash Storage SSD
13.3” Retina Display
3lb
12 hours
No DVD Drive
| Speed | Turbo | Generation | Cores | Threads | Cache Size |
| 1.6GHz | 3.4GHz | 9 | 4 | 8 | 6MB |
The latest MacBook Air models no longer use Intel Core i5 CPUs and probably won’t go back to Intel chips. They now feature Apple’s M3 chip, which is significantly faster and more efficient than even the most recent Intel Core i5 ‘U’ or ‘G’ series processors. The base M3 chip easily outpaces 13th-gen Core i7 processors in low-power laptops and does so while consuming less power.
For most users, though, the newer MacBooks may be more powerful than necessary for day-to-day tasks. If you’re into intensive work like programming, video editing, or multitasking with apps that can leverage multiple cores, the M3 chip will be incredibly capable. But if you’re mostly interested in what MacBooks have always done best—great keyboard, premium build, massive trackpad, Retina display, and excellent battery life—then the previous models with Intel chips can be a great, more affordable option.
Hardware
MacBook Air models from 2020 came with Intel 10th-gen Core i5 processors. Although a few years old now, these Core i5 CPUs can still handle most tasks with ease, including Zoom, Office, and multitasking across multiple browser tabs. When comparing this CPU’s performance to later generations, you’ll find the gap isn’t very significant up to the 12th generation and remains manageable even compared to the 13th gen.
Design
Because it’s a MacBook running macOS, even older models feel faster and more efficient than similarly aged Windows laptops. macOS is highly optimized for MacBook hardware, resulting in great performance and long battery life.
SSD: Older MacBook models also come with Apple’s proprietary SSDs, which are optimized for macOS and offer faster boot times and app launches compared to standard NVMe SSDs on most Windows laptops.
Retina Display: MacBooks since 2020 have featured the Retina display, which provides a resolution of 2560 x 1600, offering sharp text and images for everyday work or media viewing.
Beyond that, MacBook trackpads, keyboards, speaker systems, and build quality continue to lead the pack among ultrabooks, especially in models from 2020 and newer.
Battery: The battery on older Intel MacBook models (such as those from 2020) lasts about 10 hours. While that’s shorter than the 18-hour battery life on the M3 MacBooks, it’s still quite good compared to many Windows laptops in the same category.
There’s one major drawback: the price.
Adding more RAM or storage to these older Intel MacBooks can raise the price to levels close to that of a base M3 MacBook Air, which offers better performance and longer battery life. However, if you’re on a budget, going back a few years can save you a fair amount. MacBooks tend to hold up longer than most Windows laptops, both in terms of performance and physical durability. I’ve got an older Intel MacBook Air that’s still running strong after several years of daily use
How To Buy The Best i5 Laptop
For this article, I’ll focus specifically on Core i5 laptops and Core i5 CPUs.
If you’re interested in learning about other CPU lines, check out my articles on Core i3 and Core i7 laptops in the last section, where you’ll find a guide written in a similar format to this one.
For this article, I’ll assume you have some knowledge of basic computer jargon, as Core i5 laptops generally offer the best performance-to-budget ratio.
If not, please take a look at my sidebar posts to quickly get up to speed on basic computer terminology and concepts.
Processor
Turbo Boost
Everyone’s probably heard of Turbo Boost by now. When you see a CPU spec that says “Up to XX GHz,” that refers to Turbo Boost. Essentially, Turbo Boost lets a CPU temporarily reach higher speeds (like up to 4.5 GHz) when needed for intense tasks, but it doesn’t stay at that top speed all the time. Most of the time, it operates at a lower, “base” speed, especially for lighter tasks, to keep the system cool and efficient.
Turbo Boost is like a temporary power-up—useful but not meant to be constantly on. If a CPU keeps turbo-boosting for extended periods, it risks overheating. This is why a good cooling system is essential, especially in laptops, where space is tight. Higher clock speeds mean more heat, so efficient cooling is a must.
Intel CPU Labels: U, G vs. H, HX
Now, let’s break down those Intel processor labels.
H or HX Series
H series (and now HX in some cases) CPUs are the “High Performance” models, ideal for demanding applications like gaming, 3D modeling, and video editing. Originally, HQ stood for “High-Performance Quad-Core,” but as multi-core CPUs became standard, Intel simplified the label to H. These CPUs typically offer high clock speeds, more cores, and larger cache memory, which helps improve performance, especially for apps that involve a lot of data handling.
U or G Series
U (Ultra-Low Power) and G (often paired with graphics-focused improvements) CPUs are efficient and run at lower power. While not as high-powered as the H series, they still offer solid performance for everyday tasks. Most U and G CPUs support Hyper-Threading, doubling the thread count, which means a 4-core U or G CPU can handle 8 threads for smooth multitasking. These are great for typical office work, moderate multitasking, and light gaming, all while conserving battery life.
M or Y Series
M and Y CPUs are designed for ultra-thin, highly portable laptops. They’re efficient but more limited in performance compared to U and G CPUs. While they were once slower, newer M and Y CPUs (from the 8th generation onward) have improved quite a bit. They’re good for light tasks on the go, like web browsing and document editing, but aren’t suitable for gaming or heavy applications.
Choosing the Right Series for Your Needs
H Series
If you’re into gaming, video editing, or using software like AutoCAD or Blender, you’ll want an H or HX CPU. These high-performance CPUs offer faster clock speeds and more cores, so they handle heavy-duty tasks smoothly and are often paired with dedicated GPUs. For any work involving high clock speeds, an H or HX CPU is the way to go.
U or G Series
For most people who don’t need that level of power, U and G series CPUs are great choices. They provide enough speed for daily tasks, moderate multitasking, and basic photo or video editing. Because they consume less power, they also extend battery life and make laptops more affordable than high-performance models.
M/Y Series
M and Y CPUs are typically found in ultra-thin and light laptops. They’re fine for basic web browsing, watching videos, and document work, but don’t expect them to handle gaming or professional editing tasks.
Generations of Intel Core i5 CPUs (5th through 14th Gen)
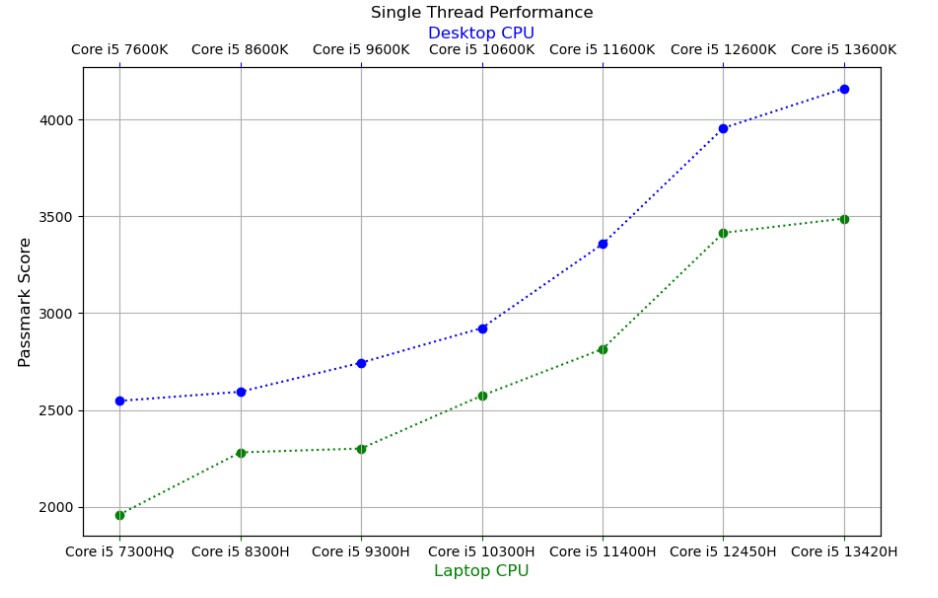
Intel Core i5 CPUs don’t disappear when a new generation is released, so you’ll often see several generations on the market. Here’s a quick overview of the major performance shifts over the years:
- 6th Gen (Skylake): Huge leap over 5th-gen, especially in battery life, speed, and graphics.
- 7th Gen (Kaby Lake): Minimal improvement over 6th-gen, so not worth choosing if a 6th-gen is cheaper.
- 8th & 9th Gen (Coffee Lake): Big jump in performance, with more cores and better graphics.
- 10th Gen (Ice Lake & Comet Lake): Improved clock speeds, some graphics updates, but mostly similar core counts to previous gens.
- 11th Gen (Tiger Lake): Boosted clock speeds and introduced Intel Iris Xe graphics for stronger integrated graphics.
- 12th Gen (Alder Lake): Introduced the hybrid core architecture (P-cores and E-cores), providing significant performance gains for multitasking.
- 13th Gen (Raptor Lake): Built on the hybrid core architecture, adding more E-cores and higher clock speeds, great for even better multitasking and efficiency.
- 14th Gen (Meteor Lake): Latest generation with further refinements in core efficiency and architecture, pushing battery life and multitasking performance even further.
And About Those Older Generations…
What about 4th gen and earlier? These CPUs are generally too old for modern tasks and may struggle to run current operating systems smoothly. If you come across a laptop with anything older than 5th-gen, it’s likely best avoided unless you’re okay with basic, single-task operations on an older OS.
RAM
8GB: Almost all Core i5 laptops today come with 8GB of RAM, which is enough for everyday tasks, light gaming, and general multitasking. For most users, 8GB is enough.
16GB: Many Core i5 laptops now offer a 16GB option, which is becoming more common and highly recommended if you’re planning on gaming, running virtual machines, doing heavier multitasking, or using apps like Adobe Premiere or CAD software. This additional RAM is beneficial for handling larger files and timelines in photo and video editing or 3D modeling, and it offers a noticeable performance boost in these contexts. If you upgrade to 16GB of RAM, it’s not just about having more memory to hold data; the upgrade will also boost performance for both the iGPU (in the absence of a dGPU) and the CPU, especially if the upgrade is done in dual-channel mode.
Storage
Solid State Drives (SSDs) vs. Hard Disk Drives (HDDs)
There are several types of storage devices on laptops, with SSDs being the fastest and the standard on virtually all modern Core i5 laptops from the 10th generation onward. Older HDDs are still seen on some laptops, but they’re much slower than SSDs and typically not worth the price unless the laptop is significantly discounted.
SSDs are especially useful for booting the system or launching applications, cutting load times down from minutes to seconds.
Within SSDs, there are different generations, with PCIe NVMe 4.0 and 5.0 being the latest. While these newer generations offer faster speeds, they’re only beneficial if you frequently load large assets or transfer files across devices. Otherwise, the performance difference among SSD generations is generally negligible for everyday use
Size
256GB: This is the standard capacity on most budget and mid-range Core i5 laptops. While this is sufficient for basic productivity, browsing, and light app usage, it may feel limiting if you have a large media library, plan to install multiple games, or work with large files.
512GB and Upgrade Options: For more demanding users, a 512GB SSD is ideal, and many Core i5 laptops allow you to upgrade the SSD later. Some laptops even support adding a second drive, so you could potentially have both an SSD for speed and an HDD for high-capacity storage. If you’re on a tighter budget, a 1TB HDD is a cheaper option, though keep in mind it will have slower read and write speeds, so it’s best used as secondary storage for files you don’t need to access as frequently.
Graphics Cards
Dedicated GPUs are available on Core i5 laptops (not on core i3 laptops) so you’ll get a mixed of integrated and dedicated GPUs when you shop for one:
Integrated Graphics Cards
This is the default graphics cards ALL laptops have even those with dedicated GPUs most of the time will have it and switch to integrated when you’re not using an application that requires it. It’s pretty pointless to talk about their performance because they will all perform more or less the same: pretty awful for high end 3D graphics applications.
However, they’re all good for the everyday stuff we all do: Zoom, streaming, youtube, basic video and photo editing, etc. You can also game with the most popular AAA franchises provided yo uset everything to low settings (only a few games will not even tolerate this kind of GPU).
Intel UHD: Just so you know these are the latest found on Core i5 laptops they can be Intel UHD 610, 615 or 620. These all have basically the same GPU: same architecture and just a slight increase in memory.
NVIDIA or AMD dedicated graphics
This is what you want if you’re running any application that requires HIGH HIGH graphics or GPU accelerated effects: 3D modeling, video editing and perhaps photo editing.
If you see a Core i5 laptop with a “HIGH performance ” CPU , it will by default come with a dedicated GPU. They will mostly be NVIDIA GPUs , AMD still doesn’t hold a strong position in this market so I’ll just give you some pointers for the dGPUs you will see when shopping for core i5 laptops.
Light Blue/Dark Green: These are good for light gaming and can run AAA titles at medium to high settings. They’re also great for getting started with video editing and 3D modeling software. For photo editing, like in Photoshop or Lightroom, this level should be sufficient—going higher might be unnecessary. The Dark Green ones are especially useful, as they come with more vRAM.
Light Green: This level is more than enough for most people. Even 3D CAD engineers should find it sufficient. These GPUs offer the highest performance you’ll typically get in Core i5 laptops.
Pink/Orange: These are the most expensive GPUs, and most users won’t need their full power. Only consider these if you’re looking to play games at very high resolutions or need to tackle extremely complex 3D work
| Name | Cores | vRAM | Speed |
| MX150 | 384 | 2GB-4GB | 1532 MHz |
| MX250 | 384 | 2GB-4GB | 1582 MHz |
| MX330 | 384 | 2GB | 1531 MHz |
| MX450 | 896 | 2GB | 1582 MHz |
| 1050 | 640 | 2GB-4GB | 1493 MHz |
| 1050 Ti | 768 | 4GB | 1620 MHz |
| 1650 | 1024 | 4GB | 1560 MHz |
| 1650 Ti | 1024 | 4GB | 1590 MHz |
| 3050 | 2048 | 4GB | 1500 MHz |
| 3050 Ti | 2560 | 4GB | 1485 MHz |
| 1660 Ti | 1536 | 6GB | 1590 MHz |
| 2060 | 1920 | 6GB | 1680 MHz |
| 3060 | 3584 | 6GB-8GB | 1780 MHz |
| 3070 | 5120 | 8GB | 1620 MHz |
| 3070 Ti | 5888 | 8GB | 1730 MHz |
| 4060 | 3072 | 8GB | 2370 MHz |
| 4070 | 4608 | 8GB | 2175 MHz |
| 3080 | 8704 | 10GB | 1710 MHz |
| 3080 Ti | 7424 | 12GB | 1590 MHz |
| 4080 | 7424 | 12GB | 2280 MHz |
| 4090 | 9728 | 16GB | 2040 MHz |
Battery Life
Author Profile
- I am physicist and electrical engineer. My knowledge in computer software and hardware stems for my years spent doing research in optics and photonics devices and running simulations through various programming languages. My goal was to work for the quantum computing research team at IBM but Im now working with Astrophysical Simulations through Python. Most of the science related posts are written by me, the rest have different authors but I edited the final versions to fit the site's format.
Latest entries
 wowDecember 18, 20255 Best Laptops For World of Warcraft – Midnight & Classic (2026)
wowDecember 18, 20255 Best Laptops For World of Warcraft – Midnight & Classic (2026) LaptopsDecember 17, 2025The 4 Best Laptops For Virtualization of 2026 (10-50 VMs ATSM)
LaptopsDecember 17, 2025The 4 Best Laptops For Virtualization of 2026 (10-50 VMs ATSM) Hardware GuideDecember 17, 20252026 Beginner Guide to Reading Computer (Laptop) Specifications
Hardware GuideDecember 17, 20252026 Beginner Guide to Reading Computer (Laptop) Specifications LaptopsJune 30, 2025Best Laptops for Computer Science (July 2025 )
LaptopsJune 30, 2025Best Laptops for Computer Science (July 2025 )