3060RTX Laptop GPU vs 4060RTX Laptop GPU
TL;DR: Gaming
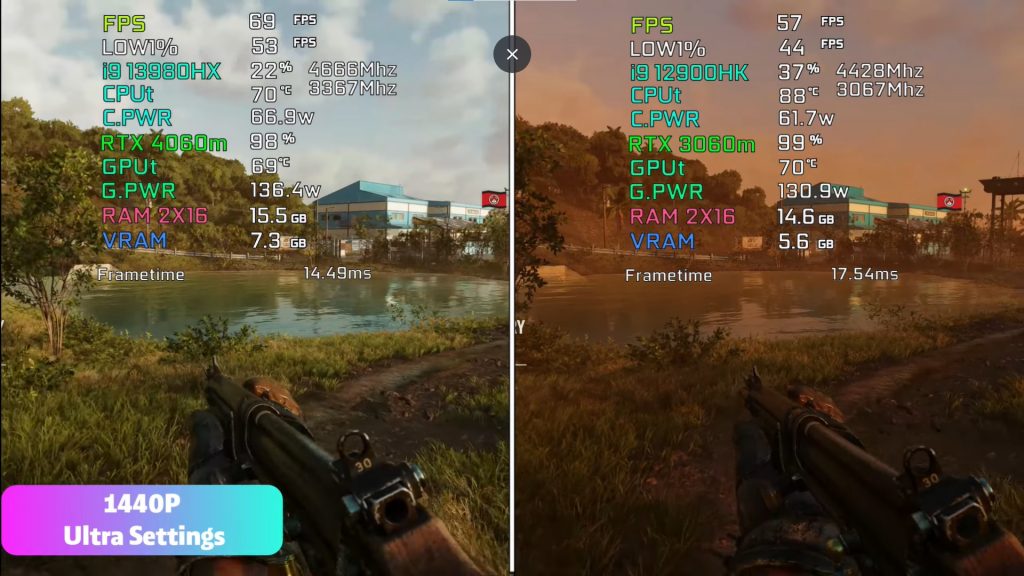
At high wattages the RTX 4060 nearly DOUBLES the performance of the 3060RTX with DLSS 3. Without DLSS 3, the 4060RTX is only 10-15% faster as you can see in the benchmarks of cyberpunk in the picture. Framerates only increase by about 15%.
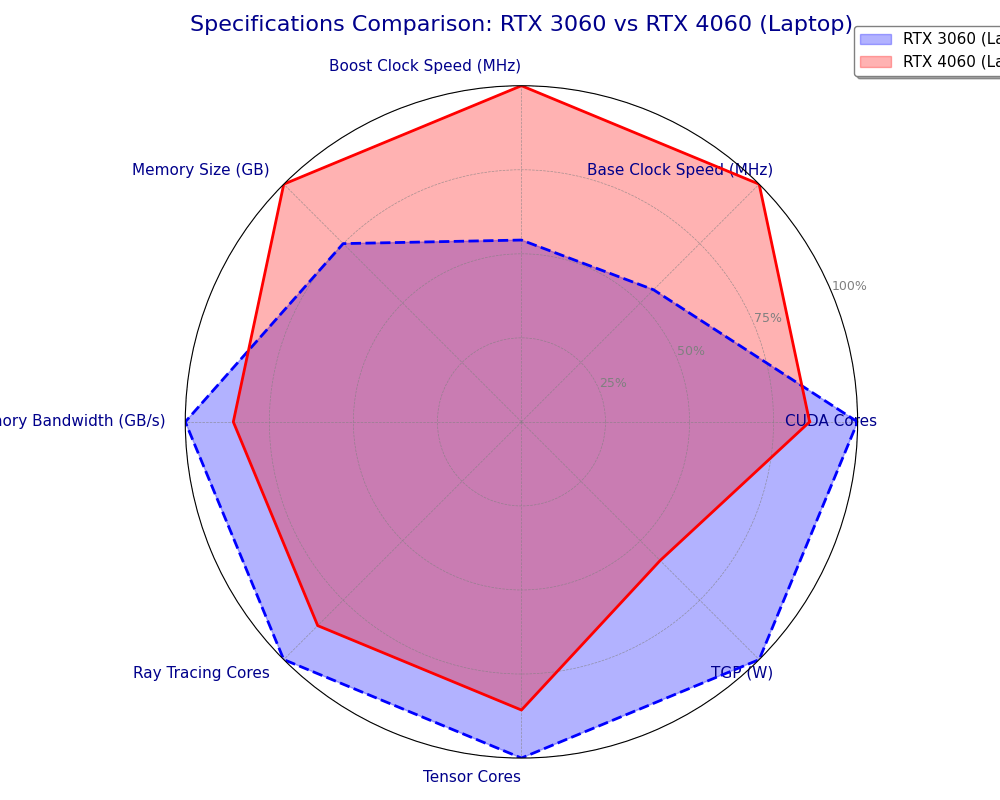
1. Specs Comparison: 3060RTX vs 4060RTX
| Specification | RTX 3060 (Laptop) | RTX 4060 (Laptop) |
|---|---|---|
| Architecture | Ampere | Ada Lovelace |
| CUDA Cores | 3,840 | 3,072 |
| Base Clock Speed (MHz) | 817 – 1387 | 1455 |
| Boost Clock Speed (MHz) | 1282 – 1702 | 2370 |
| Memory Size | 6 GB GDDR6 | 8 GB GDDR6 |
| Memory Interface | 192-bit | 128-bit |
| Memory Bandwidth (GB/s) | 336 | 272 |
| Ray Tracing Cores | 30 | 24 (3rd Gen) |
| Tensor Cores | 120 | 96 (4th Gen) |
| TGP (W) | 60 – 115 | 35 – 140 (Dynamic Boost) |
| DLSS Version | DLSS 2 | DLSS 3 |
TGP Variations
What It Means: Both GPUs offer a wide range of TGP values, but the RTX 4060 (35-115W) is notably more efficient, benefiting from the Ada Lovelace architecture. The RTX 3060 (60-115W) performs well at higher wattages, but struggles to match the RTX 4060’s efficiency at lower power levels.
The Deal: If your laptop is limited by cooling or power constraints, the RTX 4060 will perform better and stay cooler. However, at higher TGPs, the RTX 3060 can close the gap in some tasks, thanks to its wider memory bandwidth.
CUDA Cores
What It Means: The RTX 3060 has 3584 CUDA cores, while the RTX 4060 has 3072. While the 3060 has more cores, the 4060’s higher base (1470 MHz) and boost (2370 MHz) clock speeds give it an edge in single-threaded tasks and overall efficiency.
The Deal: CUDA-heavy workflows, like Blender rendering or machine learning, will generally favor the RTX 4060 for its faster clock speeds, despite the 3060 having a slight advantage in core count.
Tensor Cores
What It Means: The RTX 4060 has 4th-gen Tensor cores optimized for AI tasks like DLSS 3 and real-time AI-assisted workflows. The RTX 3060 has more Tensor cores (112 vs. 96) but uses 3rd-gen Tensor technology, which lacks advanced features like frame generation.
The Deal: AI-assisted tasks, such as using Photoshop’s AI tools or running DLSS 3 in games, heavily favor the RTX 4060. The RTX 3060 holds its own but doesn’t match the advancements in AI performance.
RT Cores
What It Means: The RTX 4060 has 24 3rd-gen RT cores, while the RTX 3060 has 28 2nd-gen RT cores. The 4060’s updated cores are faster and more efficient, particularly in real-time ray tracing scenarios.
The Deal: For ray-traced gaming or real-time rendering in Unreal Engine 5, the RTX 4060 offers smoother, more optimized performance. The RTX 3060 does well but falls short in modern ray-tracing benchmarks.
Memory Size
What It Means: The RTX 4060 comes with 8GB of VRAM, while the RTX 3060 is equipped with 6GB. This extra VRAM benefits the RTX 4060 in modern gaming and applications requiring large memory buffers.
The Deal: If you’re running memory-intensive tasks or playing modern AAA games at higher resolutions, the RTX 4060’s larger VRAM is the safer choice. However, in less VRAM-intensive tasks, the difference will be negligible.
Memory Interface and Bandwidth
What It Means: The RTX 3060 has a 192-bit bus and 336 GB/s bandwidth, compared to the RTX 4060’s 128-bit bus and 288 GB/s bandwidth. The narrower bus on the RTX 4060 can be a bottleneck in specific memory-heavy scenarios.
The Deal: For tasks like high-resolution video editing or texture-heavy games, the RTX 3060 may perform better due to its wider memory bus. The RTX 4060 compensates with architectural improvements, but it may struggle in older or highly memory-dependent applications.
Base and Boost Clocks
What It Means: The RTX 4060’s higher clocks (1470 MHz base, 2370 MHz boost) compared to the RTX 3060’s (817 MHz base, 1282 MHz boost) result in better real-time performance for gaming, rendering, and editing workflows.
The Deal: Applications that demand high single-threaded performance, like video editing previews or real-time rendering, benefit greatly from the RTX 4060’s higher clock speeds.
DLSS Support
What It Means: The RTX 4060 supports DLSS 3 with frame generation, while the RTX 3060 is limited to DLSS 2. DLSS 3 allows for better performance in modern games by generating additional frames.
The Deal: Games like Cyberpunk 2077 or Flight Simulator see a significant boost with DLSS 3 on the RTX 4060, making it a superior choice for gamers. The RTX 3060 remains a strong performer but cannot leverage DLSS 3 for newer titles.
2. Benchmarks: 3060RTX vs 4060RTX
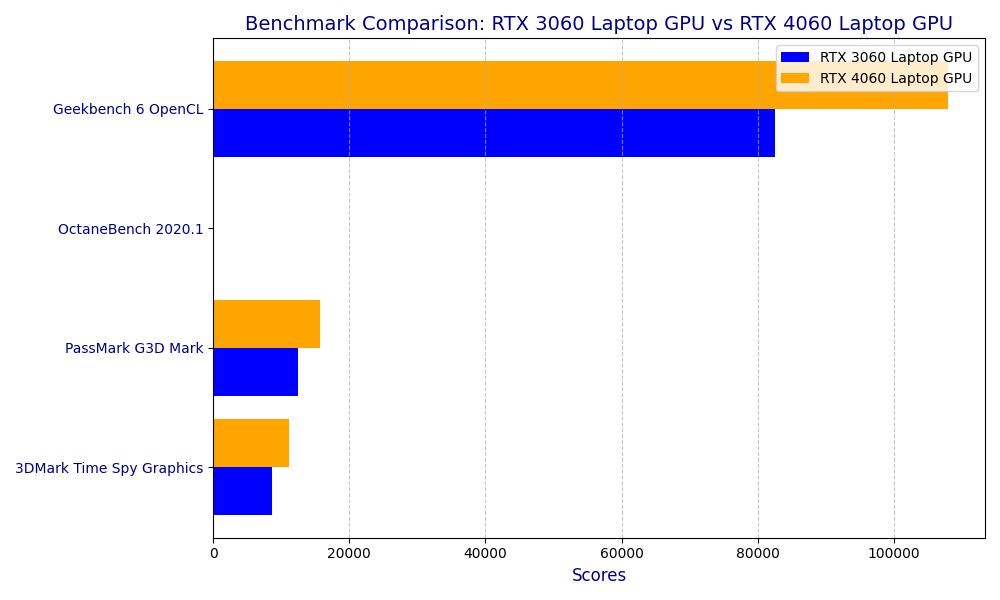
| Benchmark | RTX 3060 Laptop GPU | RTX 4060 Laptop GPU |
|---|---|---|
| PassMark G3D Mark | 13,352 | 13,500 |
| 3DMark Time Spy Graphics | 9,153 | 10,359 |
| Geekbench 6 OpenCL | 115,000 | 125,000 |
Important Nuances to Consider
TGP Variations
What It Means:
Both GPUs, the RTX 3060 and RTX 4060 Laptop GPUs, have TGP configurations ranging from 80W to 140W. The RTX 4060 benefits from the Ada Lovelace architecture, which is more power-efficient, allowing it to maintain performance even at lower TGPs. Meanwhile, the RTX 3060 performs well but relies on higher TGPs to close the performance gap.
The Deal:
In lower TGP configurations, the RTX 4060 Laptop GPU holds a consistent advantage due to its architectural efficiency. High TGP settings allow the RTX 3060 to maximize its performance, but the 4060 will still have the edge in modern workloads thanks to its improved optimizations.
Notes:
- The RTX 4060 Laptop GPU shows improved performance across all benchmarks compared to the RTX 3060 Laptop GPU, reflecting advancements in architecture and efficiency.
- Actual performance can vary based on laptop configurations, cooling solutions, and power limits.
Sources: NotebookCheck.net, PassMark Software, Geekbench Browser
3DMark Time Spy Graphics
RTX 3060: 9,153 points
RTX 4060: 10,359 points (~13% higher)
What It Means:
The RTX 4060 outperforms the RTX 3060 in this DirectX 12 benchmark, reflecting its newer architecture and improved performance per watt. The Ada Lovelace enhancements help the 4060 deliver higher frame rates in gaming and better efficiency in productivity tasks.
The Deal:
For gaming and general-purpose GPU performance, the RTX 4060 provides a clear upgrade. However, laptops with better cooling and higher TGP may reduce the gap between the two GPUs.
Geekbench 6 OpenCL
RTX 3060: 115,000 points
RTX 4060: 125,000 points (~8.7% higher)
What It Means:
The RTX 4060 shows stronger performance in OpenCL-based compute tasks, such as video encoding, AI-based applications, and simulations. The newer architecture allows for better resource utilization, especially in AI-assisted workflows.
The Deal:
If your workload involves AI tasks, like using TensorFlow or CUDA-accelerated applications, the RTX 4060 is the better choice. The RTX 3060 remains a solid option for users who prioritize cost efficiency and traditional workloads.
PassMark G3D Mark
RTX 3060: 13,352 points
RTX 4060: 13,500 points (~1% higher)
What It Means:
The PassMark G3D scores are close, suggesting similar levels of performance in general-purpose benchmarks. The RTX 4060 holds a slight edge due to its improved efficiency, but the RTX 3060 remains competitive.
The Deal:
In real-world applications, the RTX 4060’s architectural improvements may result in better performance for modern games and tasks. However, for users with laptops that prioritize cooling and power delivery, the RTX 3060 can still deliver excellent results.
3. Performance: 3060RTX vs 4060RTX
Gaming
High-TGP Configurations (115W RTX 4060 vs. 115W RTX 3060)
- Raw Performance: The RTX 4060 offers about a 10-15% improvement in gaming performance compared to the RTX 3060, but much of this gain comes from architectural efficiency and newer CPU pairings rather than a generational leap.
- With DLSS: DLSS 3 with frame generation is a game-changer for the RTX 4060. In supported games, it effectively doubles the frame rate compared to the RTX 3060, which is limited to DLSS 2. However, frame generation isn’t universally supported and adds latency, making it more suited for single-player or slower-paced games.
- At Max TGP: The RTX 4060 performs more efficiently and runs cooler than the RTX 3060 in extended gaming sessions. However, in memory-bound scenarios (e.g., 4K textures, high settings), the RTX 3060’s wider memory bus and bandwidth give it a slight edge.
Example Use Case: In Cyberpunk 2077, the RTX 4060 with DLSS 3 can nearly double the frame rate compared to the RTX 3060, but the RTX 3060 might feel smoother in older titles or scenarios that don’t support DLSS 3.
TL;DR: If you’re gaming on modern DLSS 3-optimized titles, the RTX 4060 offers a significant performance boost. For games without DLSS or older titles, the RTX 3060 remains competitive and provides better value in some cases.
Low-TGP Configurations (80W RTX 4060 vs. 80W RTX 3060)
- Efficiency: This is where the RTX 4060 shines. Its Ada Lovelace architecture allows it to deliver near-peak performance at lower wattages, making it ideal for thin-and-light laptops or laptops with constrained cooling systems. The RTX 3060, in contrast, struggles to maintain its performance in low-power scenarios, often hitting thermal limits.
- With DLSS: In lightweight gaming laptops, DLSS 3 helps the RTX 4060 punch above its weight, maintaining playable frame rates even at lower TGP configurations. The RTX 3060, without frame generation, can’t match this consistency.
Example Use Case: In a Zephyrus G14 or similar ultrabook, the RTX 4060 would deliver better frame rates with less heat and noise compared to the RTX 3060.
TL;DR: The RTX 4060 is the better choice for thin laptops or setups with limited cooling. The RTX 3060 performs admirably but is held back by its Ampere architecture in low-power situations.
Author Profile
- I am physicist and electrical engineer. My knowledge in computer software and hardware stems for my years spent doing research in optics and photonics devices and running simulations through various programming languages. My goal was to work for the quantum computing research team at IBM but Im now working with Astrophysical Simulations through Python. Most of the science related posts are written by me, the rest have different authors but I edited the final versions to fit the site's format.
Latest entries
 wowDecember 18, 20255 Best Laptops For World of Warcraft – Midnight & Classic (2026)
wowDecember 18, 20255 Best Laptops For World of Warcraft – Midnight & Classic (2026) LaptopsDecember 17, 2025The 4 Best Laptops For Virtualization of 2026 (10-50 VMs ATSM)
LaptopsDecember 17, 2025The 4 Best Laptops For Virtualization of 2026 (10-50 VMs ATSM) Hardware GuideDecember 17, 20252026 Beginner Guide to Reading Computer (Laptop) Specifications
Hardware GuideDecember 17, 20252026 Beginner Guide to Reading Computer (Laptop) Specifications LaptopsJune 30, 2025Best Laptops for Computer Science (July 2025 )
LaptopsJune 30, 2025Best Laptops for Computer Science (July 2025 )