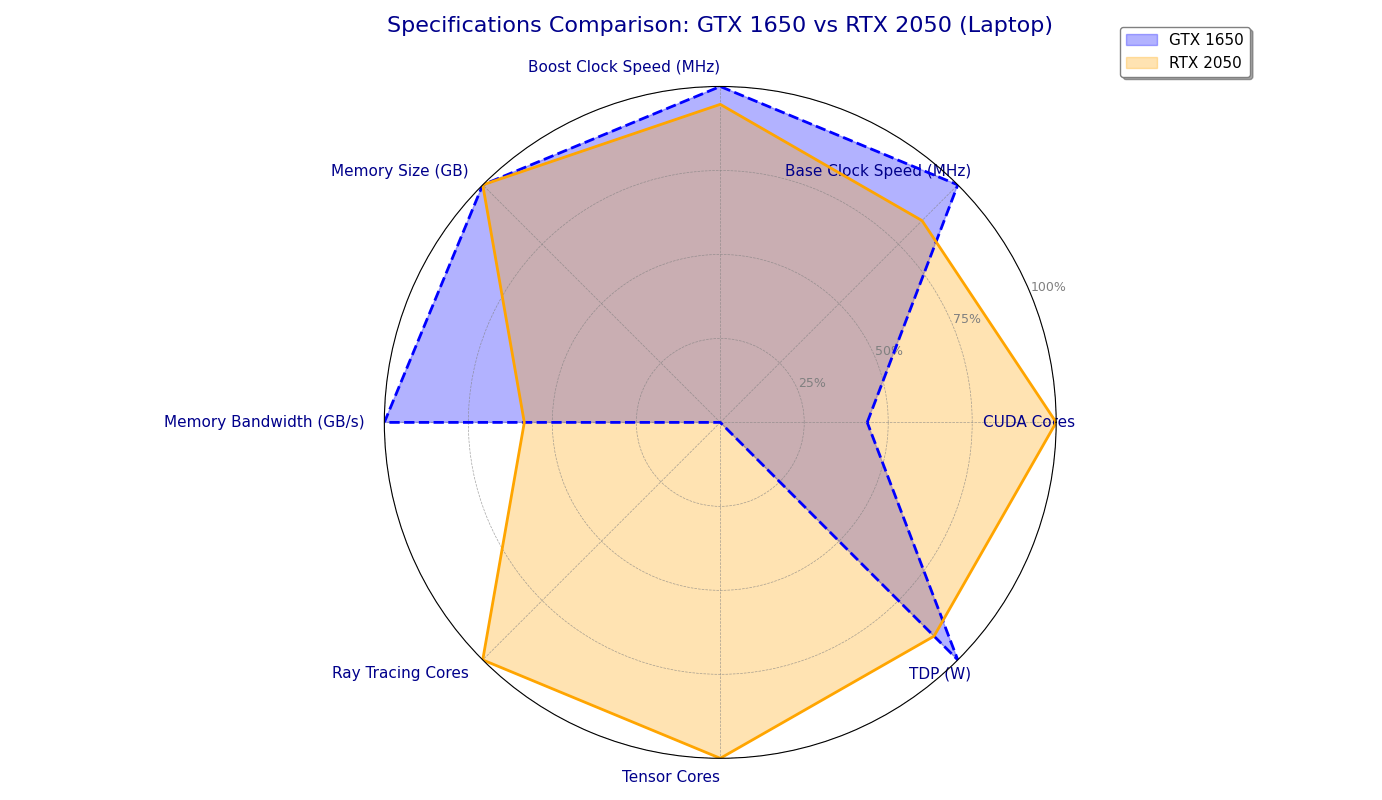
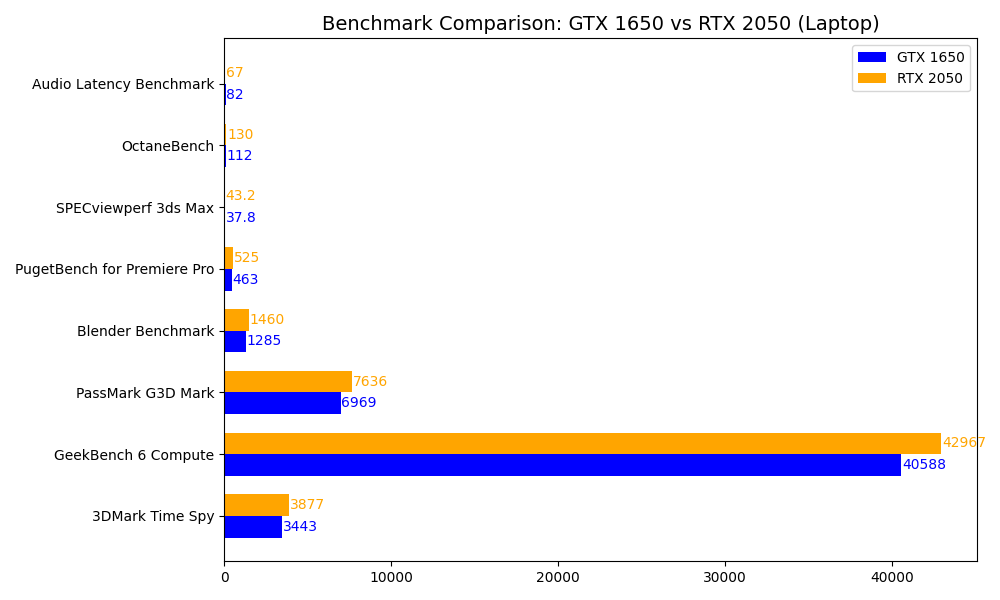
1650GTX Laptop GPU vs 2050RTX Laptop GPU
3. Performance : 1650GTX vs 2050RTX
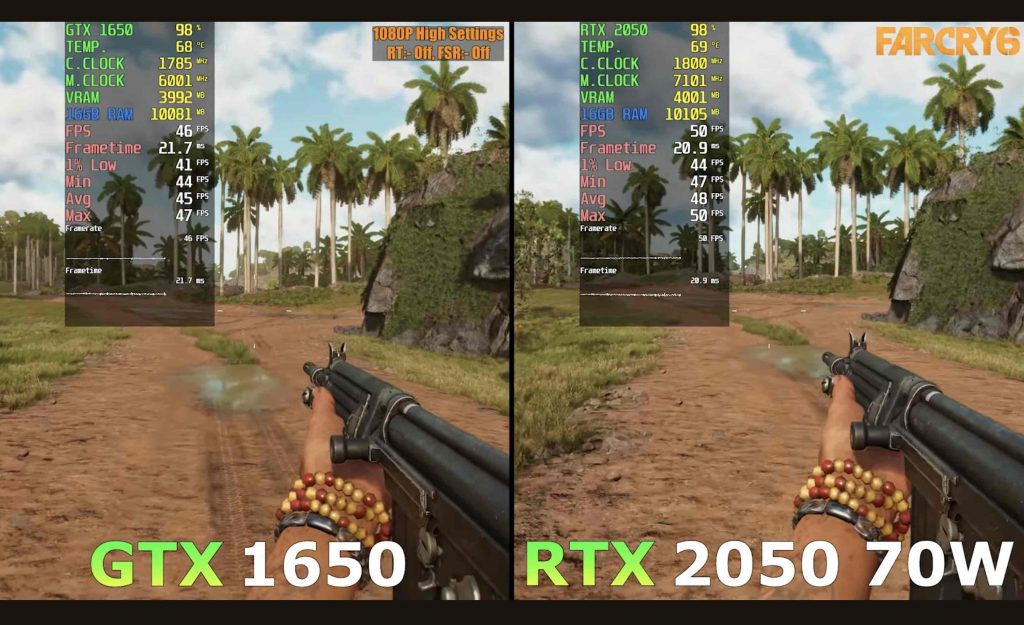
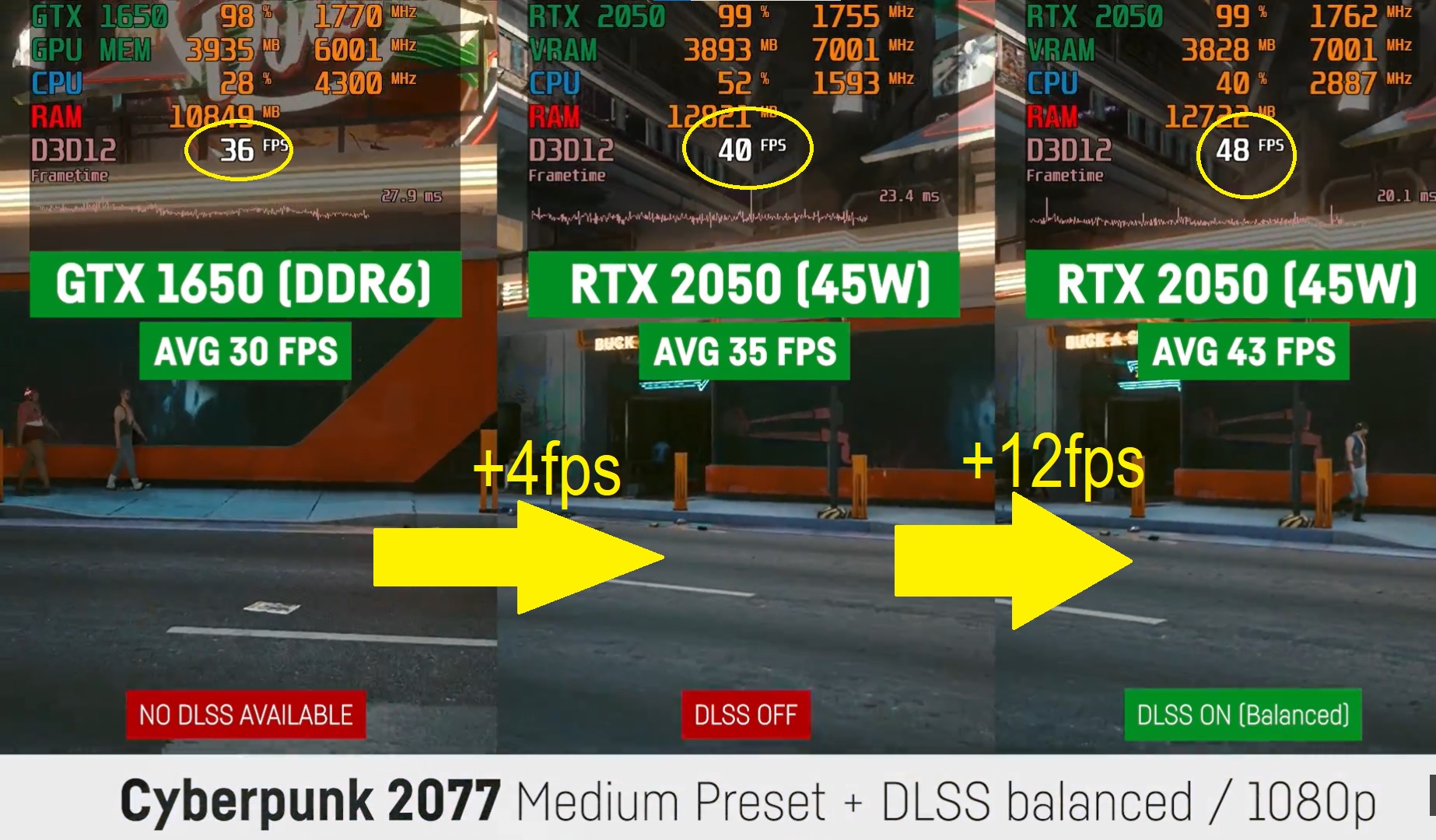
1. Gaming
RTX 2050: Minimal Performance Gains
- Why: With ray tracing cores and DLSS support, the RTX 2050 handles graphically demanding games BETTER at higher settings. However, performance gains are poor mostly about 2-5% more framerates.
- Example: The above example runs Far Cry 6 at high settings with FSR off and DLSS ON…even then the 2050RTX only performs slightly better.
GTX 1650: Not Good for RTX mode
- Why: doesn’t have RT cores thus cannot handle RTX mode. Nonetheless, for all other instances it show similar or same performance with the 2050RTX.
2. Video Editing
RTX 2050: Slightly Superior Performance
- Software: Adobe Premiere Pro, DaVinci Resolve, Final Cut Pro.
- Why: The RTX 2050’s tensor cores and CUDA core count enable faster video rendering, smoother timeline playback, and quicker effects application.
- Example: In Adobe Premiere Pro, the RTX 2050 processes GPU-accelerated effects like Lumetri Color grading and transitions faster, especially in 4K workflows.
- Use Case: Rendering a 10-minute 4K video with multiple GPU-accelerated effects will be ~10% faster on the RTX 2050 compared to the GTX 1650.
GTX 1650: Almost same performance as 2050RTX
- Why: While capable of handling most tasks at 1080p the same way as the 2050RTX, the GTX 1650 struggles with 4K timelines or complex effects due to fewer CUDA cores and no tensor cores.
- Example: Editing a 1080p YouTube vlog with light color grading will perform well on the GTX 1650 and the 2050RTX.
2. Photo Editing
RTX 2050: Faster with AI-Assisted Features
- Software: Adobe Photoshop, Luminar Neo, Topaz Gigapixel AI.
- Why: Tensor cores on the RTX 2050 accelerate AI-based tools like content-aware fill, super-resolution, and noise reduction.
- Example: Using Topaz Gigapixel AI to upscale a low-resolution image is significantly faster on the RTX 2050, cutting processing time by ~20%.
- Use Case: Professional photographers requiring advanced editing tools will benefit from the RTX 2050.
GTX 1650: Handles Standard Tasks
- Why: Still capable of running Photoshop and other tools smoothly for basic editing tasks.
- Example: Cropping, resizing, or applying basic filters in Photoshop will perform similarly on both GPUs.
4. 3D Modeling and Rendering
RTX 2050: Superior in GPU Rendering
- Software: Blender (Cycles), V-Ray, OctaneRender.
- Why: The RTX 2050’s CUDA core count and tensor cores enhance GPU-based rendering engines, accelerating ray tracing and AI denoising.
- Example: Rendering a complex 3D scene in Blender’s Cycles engine is ~13% faster on the RTX 2050.
- Use Case: Architects, animators, or VFX artists will notice faster previews and final renders on the RTX 2050.
5. AI-Assisted Applications
RTX 2050: Ideal for AI Workloads
- Software: TensorFlow, Topaz AI, Gigapixel AI, Adobe Sensei-powered tools.
- Why: Tensor cores accelerate deep learning tasks like neural network inference or AI image enhancements.
- Example: Using Adobe Photoshop’s AI-powered “Super Resolution” tool is nearly 2x faster on the RTX 2050.
- Use Case: Data scientists and creative professionals leveraging AI workflows will find the RTX 2050 invaluable.
GTX 1650: Limited in AI Applications
- Why: Lacks tensor cores, making AI tasks slower or relying entirely on CPU.
Conclusion
For gaming it’s pretty much an useless upgrade. Both perform equally well. While you can activate DLSS on the 2050RTX…you can use FSR on the 1650GTX and still get the same performance as the RTX 2050 or better. For video editing tools and photo editing tools that make good use of extra cores, in theory you can get a 10% performance gain. For AI based tools however, the 2050RTX is the best choice, the 1650GTX completely lacks the technology to accelerate performance with those tools (mostly relying on the CPU).
Author Profile
- I am physicist and electrical engineer. My knowledge in computer software and hardware stems for my years spent doing research in optics and photonics devices and running simulations through various programming languages. My goal was to work for the quantum computing research team at IBM but Im now working with Astrophysical Simulations through Python. Most of the science related posts are written by me, the rest have different authors but I edited the final versions to fit the site's format.
Latest entries
 wowDecember 18, 20255 Best Laptops For World of Warcraft – Midnight & Classic (2026)
wowDecember 18, 20255 Best Laptops For World of Warcraft – Midnight & Classic (2026) LaptopsDecember 17, 2025The 4 Best Laptops For Virtualization of 2026 (10-50 VMs ATSM)
LaptopsDecember 17, 2025The 4 Best Laptops For Virtualization of 2026 (10-50 VMs ATSM) Hardware GuideDecember 17, 20252026 Beginner Guide to Reading Computer (Laptop) Specifications
Hardware GuideDecember 17, 20252026 Beginner Guide to Reading Computer (Laptop) Specifications LaptopsJune 30, 2025Best Laptops for Computer Science (July 2025 )
LaptopsJune 30, 2025Best Laptops for Computer Science (July 2025 )