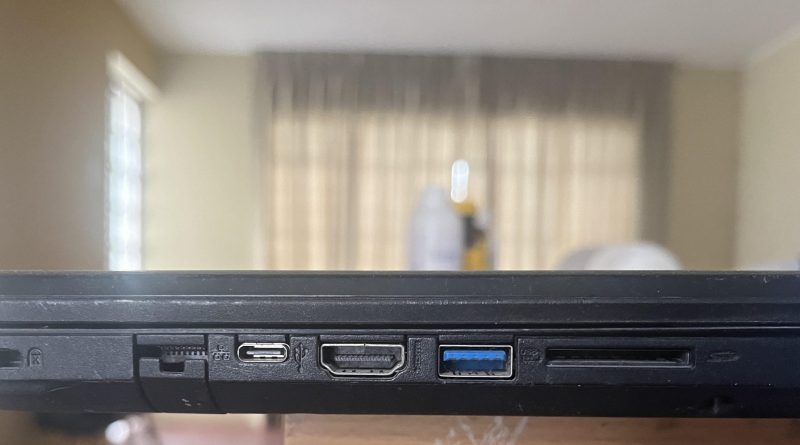
All Laptop Ports Guide: Usage & Speed
This guide provides an in-depth overview of ALL laptop ports, what they’re used for, and why they’re important so YOU KNOW what the PORTS your laptop comes with CAN DO:
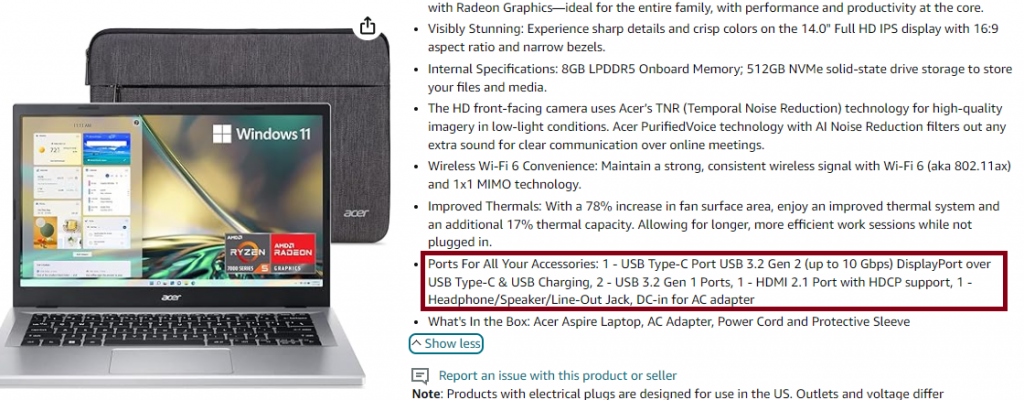
1. USB-A (USB Type-A)
The old rectangular USB port everyone uses to connect a mouse. They’re also widely used for connecting other peripherals and accessories. Everyone has seen it or used it once even my grandma has used it.

Uses:
- Connecting external drives, keyboards, mice, printers, and other devices.
- Transferring data between devices (e.g., USB drives, External Hard Disk Drives).
- Charging devices such as smartphones or tablets.
Now note that there’s a difference between “PORT” and “STANDARD”. The port indicates the “physical interface”, the shape of the connection.
The standard (USB 2.0, USB 3.0/3.1,etc) dictates which TYPE of connection it supports. Some standards or versions are faster than others.
Versions
- USB 2.0: Older, slower version. Transfers data at 480 Mbps
- USB 3.0/3.1 Gen 1: Faster data transfer speeds 5 Gbps.
- USB 3.1 Gen 2: Even faster speeds (10 Gbps).
If the standard is not specified, you can get a clue about which standards they support by looking at it:
Apperance
- USB 2.0 (Type-A): Typically, the interior plastic piece is black or white.
- USB 3.0/3.1 (Type-A): The interior plastic is usually blue to indicate faster data transfer speeds compared to USB 2.0. Some laptops may also label these ports with “SS” for SuperSpeed.

- USB 3.2 Gen 2 (Type-A): These may have the same blue plastic, or sometimes red, indicating even faster speeds.
- USB 3.2 Gen 2×2 or USB 3.1 Gen 2 (Type-A): These ports may use red or blue interiors but can vary between manufacturers.
2. USB-C (USB Type-C)

A smaller, reversible port not only does it support MUCH higher data transfer but also MUCH greater power delivery. This is the kind of port we all use to charge our phone with. It’s slowly replacing old fashioned USBs (at least the shaep is).
Uses:
- Charging laptops, smartphones, and other devices (supports up to 100W of power).
- High-speed data transfer: depending on the exact generation data transfer can change from 10-40Gbps.
- Connecting external displays (supports video output for HDMI, DisplayPort, etc.).
- Docking stations and hubs for multiple peripheral connections.
Just like USB-A , USB-Type C supports different standards which depend on your laptop:
Versions
- USB 3.1: Up to 10 Gbps, good for general use and faster data transfers.
- USB 3.2: Up to 20 Gbps, better for high-speed data transfers and more demanding tasks.
- Thunderbolt 3: Up to 40 Gbps, great for ultra-fast data, video output, external GPUs, and high-power charging.
- Thunderbolt 4: Also 40 Gbps, with enhanced features, better security, and improved performance for external devices and displays.
Advantages:
- Universal connectivity with one cable for data, power, and video.
- Reversible design means no need to worry about plug orientation.
3. Thunderbolt 3/4

Here’s the thing. This is technically a USB Type-C port but many manufacturers call this port “thunderbolt 3 or thunderbolt 4”. The physical interface is STILL UBS Type-C, it’s just that the standard it supports is thunderbolt 3/4 which has much higher data transfer speeds.
Uses:
- Ultra-fast data transfer (up to 40 Gbps).
- Connecting external monitors (supports 4K, 5K, and 8K resolution displays).
- Connecting external GPUs for gaming or high-end graphics processing.
- Daisy-chaining multiple devices using a single port.
- Charging laptops and other devices.
Advantages:
- Supports a wide range of high-performance devices.
- Thunderbolt 4 is the latest standard, offering greater reliability and security.
4. USB 3.1/3.2 (USB Type-C with DisplayPort)

A variant of USB-C that includes DisplayPort functionality, allowing it to handle video output in addition to data and power. Yeah, it has pretty much the same shape as USB-Type C and Thunderbolt 3/4 with the only difference being that it has the ability to handle video output.
Uses:
- Connecting external monitors.
- Transferring data and charging devices through the same port.
- Acting as an alternative to HDMI or DisplayPort cables for video output.
5. HDMI (High-Definition Multimedia Interface)

This is used to connect your laptop to external displays, TVs, or projectors for audio and video output. You also use it to connect a display to your Wii U, Nintendo Switch, etc.
Uses:
- Connecting to external monitors or TVs for high-definition video and audio.
- Projecting presentations onto larger screens.
- Streaming media to a TV from a laptop.
Versions:
- HDMI 1.4: Supports 4K at 30Hz.
- HDMI 2.0: Supports 4K at 60Hz.
- HDMI 2.1: Supports 8K at 60Hz and 4K at 120Hz.
6. DisplayPort (dP)

A digital display interface used to connect external monitors or projectors. Found less often on laptops compared to HDMI or USB-C. This is now only found on laptops. Personally haven’t seen one since 2016.
Uses:
- Connecting to external displays, especially monitors with high refresh rates or resolutions (up to 8K).
- Daisy-chaining multiple monitors with one cable.
Versions:
- DisplayPort 1.4: Supports 8K at 60Hz.
- DisplayPort 2.0: Supports 8K at 120Hz, 4K at 240Hz.
7. Ethernet (RJ-45)

This is what you use to connect the cable from your modem to your laptop for a WIRED internet connection whichi is many times faster than a WiFi connection. MacBooks don’t have them but
Uses:
- Connecting to the internet or local networks using an Ethernet cable.
- Faster, more stable internet connections than Wi-Fi, especially for gaming or downloading large files.
Advantages:
- Provides more reliable internet speeds, typically faster than wireless connections.
- Useful in environments with poor Wi-Fi connectivity.
8. 3.5mm Audio Jack

THis is the port you use to connect headphones microphones or headsets…it’s always a circular shape as shown in the pic.
Uses:
- Connecting headphones, earphones, or external speakers for audio output.
- Connecting microphones for audio input.
Advantages:
- Universal compatibility with most audio devices.
- Often combined into a single headphone/microphone jack.
9. SD Card / microSD Card

Cameras used SD Cards to store photos/videos. The port used on those devices are the same one seen on laptops. A rectangle shaped slot. It works for both SD Card and microSD Cards. Now microSD Cards are smaller as shown in the picture down below:

So if you want to connect a microSD Card to a laptop through the SD Card Slot, you will need an adapter.
Uses:
- Reading and transferring data from SD cards, such as photos and videos from cameras.
- Expanding laptop storage using SD cards.
Variants:
- Full-size SD card reader: Accepts standard SD cards.
- MicroSD card reader: Accepts smaller MicroSD cards often used in smartphones and action cameras.
10. Mini DisplayPort

A smaller version of the standard DisplayPort, used for connecting external displays. Usually found on older MacBooks or high-end laptops like the Dell XPS , Surface Book , etc.
Uses:
- Connecting to external displays for high-resolution video output (up to 4K).
- Often found on older or smaller laptops (before Thunderbolt 3/USB-C became the standard).
11. VGA (Video Graphics Array)

An older, analog video output port used to connect external monitors or projectors. You will not see this port unless your laptop is very old (pre 2016) and is thick.
Uses:
- Connecting to older projectors and monitors, especially in business environments.
- Still found on some business laptops for legacy support.
Limitations:
- Does not support high-definition video.
- Outdated compared to HDMI and DisplayPort.
12. Power Port (DC-in)

The is dedicated port for charging your laptop. It may have a different shape depending on the laptop. In fact, on MacBooks, it’s just a thunderbolt port now and has the same shape of USB Type-C ports.
Uses:
- Connecting the laptop to its charger for power.
- Varies in size and shape depending on the manufacturer and laptop model.
Note: Many modern laptops now use USB-C for charging instead of a dedicated power port.
13. Kensington Lock Slot

A small slot used with a laptop lock for physical security.
Uses:
- Securing the laptop to a desk or immovable object in public places or shared workspaces.
- Helps prevent theft.
14. eSATA (External Serial ATA)

Used to connect external hard drives and SSDs with faster data transfer speeds compared to USB 2.0.
Uses:
- High-speed data transfer between external drives and laptops.
- Connecting external storage devices for backups or file transfers.
Note: Rarely seen on newer laptops due to the rise of USB 3.0/3.1 and Thunderbolt, which offer faster transfer speeds.
15. SIM Card Slot

Found on laptops with LTE/5G capability, the SIM card slot allows the laptop to connect to cellular networks. I have only see it on the Surface Pro models. It isn’t something you find on a regular gaming laptop.
Uses:
- Enabling mobile data access on your laptop.
- Useful for travelers or professionals who need internet access in areas without Wi-Fi.
Author Profile
- Miguel Salas
- I am physicist and electrical engineer. My knowledge in computer software and hardware stems for my years spent doing research in optics and photonics devices and running simulations through various programming languages. My goal was to work for the quantum computing research team at IBM but Im now working with Astrophysical Simulations through Python. Most of the science related posts are written by me, the rest have different authors but I edited the final versions to fit the site's format.
Latest entries
 wowDecember 18, 20255 Best Laptops For World of Warcraft – Midnight & Classic (2026)
wowDecember 18, 20255 Best Laptops For World of Warcraft – Midnight & Classic (2026) LaptopsDecember 17, 2025The 4 Best Laptops For Virtualization of 2026 (10-50 VMs ATSM)
LaptopsDecember 17, 2025The 4 Best Laptops For Virtualization of 2026 (10-50 VMs ATSM) Hardware GuideDecember 17, 20252026 Beginner Guide to Reading Computer (Laptop) Specifications
Hardware GuideDecember 17, 20252026 Beginner Guide to Reading Computer (Laptop) Specifications LaptopsJune 30, 2025Best Laptops for Computer Science (July 2025 )
LaptopsJune 30, 2025Best Laptops for Computer Science (July 2025 )
